Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (487.4 KB).
Figure 1 .
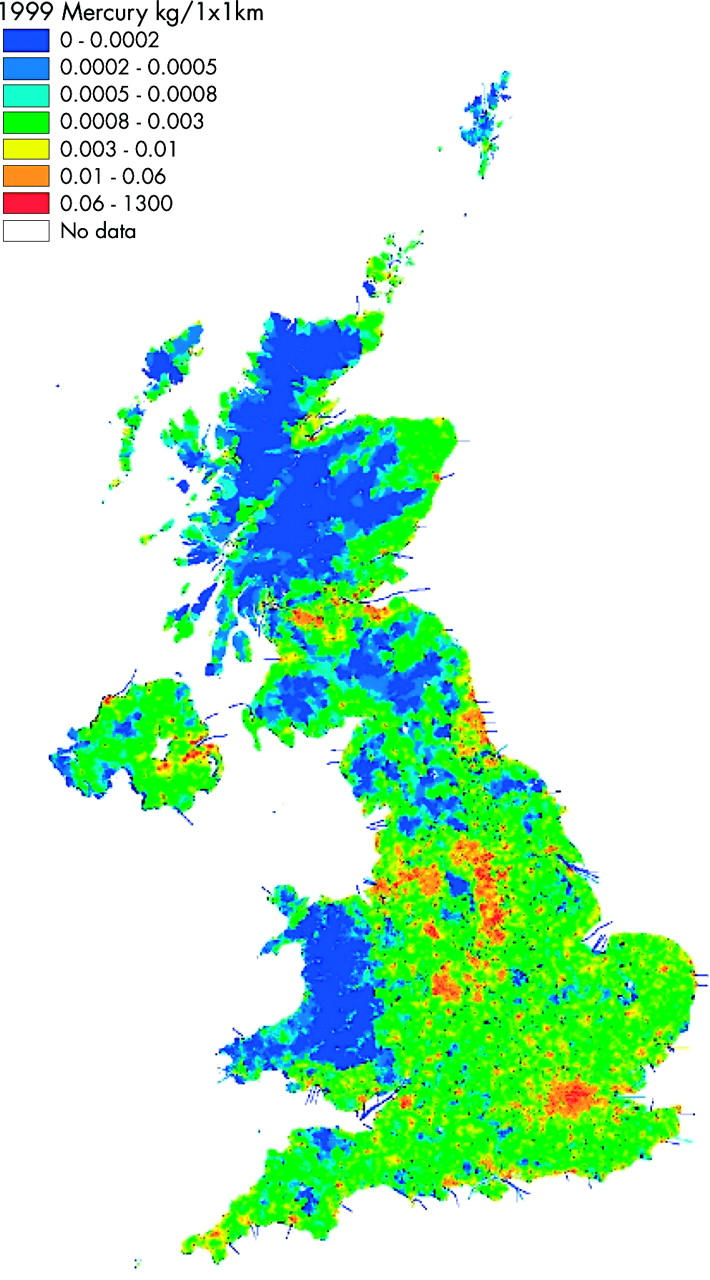
Emissions of mercury in the UK in 1999 including data within the 12 mile coastal limit.
Figure 2 .
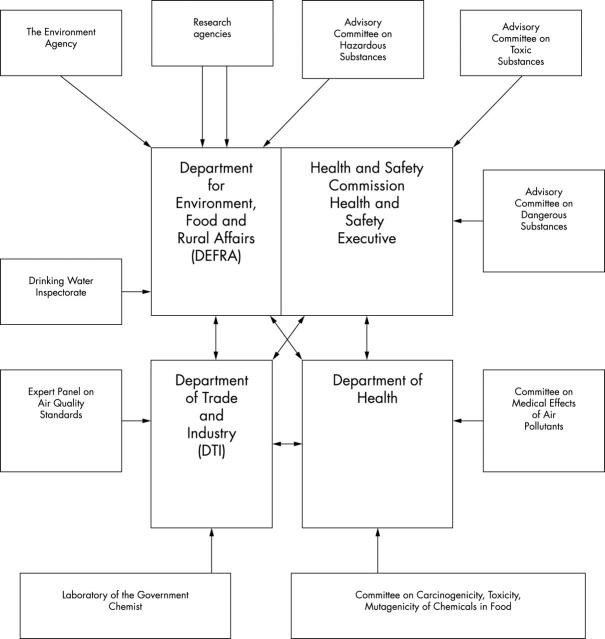
Main source of advice for the UK government on substances hazardous to human health and the environment.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett Julia R. On a growth curve: children's environmental health centers. Environ Health Perspect. 2002 Oct;110(10):A570–A572. doi: 10.1289/ehp.110-a570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearer C. F. How are children different from adults? Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Sep;103 (Suppl 6):7–12. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearer C. F. The special and unique vulnerability of children to environmental hazards. Neurotoxicology. 2000 Dec;21(6):925–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger D., Leviton A., Waternaux C., Needleman H., Rabinowitz M. Longitudinal analyses of prenatal and postnatal lead exposure and early cognitive development. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1037–1043. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A., Fierens S. The Belgian PCB/dioxin incident: a critical review of health risks evaluations. Int J Toxicol. 2002 Sep-Oct;21(5):333–340. doi: 10.1080/10915810290096540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield Richard L., Henderson Charles R., Jr, Cory-Slechta Deborah A., Cox Christopher, Jusko Todd A., Lanphear Bruce P. Intellectual impairment in children with blood lead concentrations below 10 microg per deciliter. N Engl J Med. 2003 Apr 17;348(16):1517–1526. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson P. W., Myers G. J., Cox C., Axtell C., Shamlaye C., Sloane-Reeves J., Cernichiari E., Needham L., Choi A., Wang Y. Effects of prenatal and postnatal methylmercury exposure from fish consumption on neurodevelopment: outcomes at 66 months of age in the Seychelles Child Development Study. JAMA. 1998 Aug 26;280(8):701–707. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.8.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott P., Arnold R., Barltrop D., Thornton I., House I. M., Henry J. A. Clinical lead poisoning in England: an analysis of routine sources of data. Occup Environ Med. 1999 Dec;56(12):820–824. doi: 10.1136/oem.56.12.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber Dan. Toxicology. Overhaul of CDC panel revives lead safety debate. Science. 2002 Oct 25;298(5594):732–732. doi: 10.1126/science.298.5594.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean P., Weihe P., White R. F., Debes F., Araki S., Yokoyama K., Murata K., Sørensen N., Dahl R., Jørgensen P. J. Cognitive deficit in 7-year-old children with prenatal exposure to methylmercury. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1997 Nov-Dec;19(6):417–428. doi: 10.1016/s0892-0362(97)00097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg J. The health effects of fossil fuel derived particles. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Feb;86(2):79–83. doi: 10.1136/adc.86.2.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins B. G., Douglas J. G. The new BTS/SIGN asthma guidelines: where evidence leads the way. Thorax. 2003 Feb;58(2):98–99. doi: 10.1136/thorax.58.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper Kim, She Jianwen. Lessons from the polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs): precautionary principle, primary prevention, and the value of community-based body-burden monitoring using breast milk. Environ Health Perspect. 2003 Jan;111(1):109–114. doi: 10.1289/ehp.5438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. L. Contending with contradictory data in a risk assessment context: the case of methylmercury. Neurotoxicology. 2001 Oct;22(5):667–675. doi: 10.1016/s0161-813x(01)00040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser J. Toxicology. Mercury report backs strict rules. Science. 2000 Jul 21;289(5478):371–372. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5478.371a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazantzis G., Al-Mufti A. W., Al-Jawad A., Al-Shahwani Y., Majid M. A., Mahmoud R. M., Soufi M., Tawfiq K., Ibrahim M. A., Dabagh H. Epidemiology of organomercury poisoning in Iraq. II. Relationship of mercury levels in blood and hair to exposure and to clinical findings. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53 (Suppl):37–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman-Esseboom C., Weisglas-Kuperus N., de Ridder M. A., Van der Paauw C. G., Tuinstra L. G., Sauer P. J. Effects of polychlorinated biphenyl/dioxin exposure and feeding type on infants' mental and psychomotor development. Pediatrics. 1996 May;97(5):700–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanphear B. P., Dietrich K., Auinger P., Cox C. Cognitive deficits associated with blood lead concentrations <10 microg/dL in US children and adolescents. Public Health Rep. 2000 Nov-Dec;115(6):521–529. doi: 10.1093/phr/115.6.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky Theodore I., Schneider Jay S. Lead neurotoxicity in children: basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Brain. 2003 Jan;126(Pt 1):5–19. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffredo C. A., Silbergeld E. K., Ferencz C., Zhang J. Association of transposition of the great arteries in infants with maternal exposures to herbicides and rodenticides. Am J Epidemiol. 2001 Mar 15;153(6):529–536. doi: 10.1093/aje/153.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mably T. A., Bjerke D. L., Moore R. W., Gendron-Fitzpatrick A., Peterson R. E. In utero and lactational exposure of male rats to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. 3. Effects on spermatogenesis and reproductive capability. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 May;114(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90103-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer Brian, Brown Phil, Linder Meadow. Moving further upstream: from toxics reduction to the precautionary principle. Public Health Rep. 2002 Nov-Dec;117(6):574–586. doi: 10.1093/phr/117.6.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman H. L., Gunnoe C., Leviton A., Reed R., Peresie H., Maher C., Barrett P. Deficits in psychologic and classroom performance of children with elevated dentine lead levels. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 29;300(13):689–695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903293001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patandin S., Lanting C. I., Mulder P. G., Boersma E. R., Sauer P. J., Weisglas-Kuperus N. Effects of environmental exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins on cognitive abilities in Dutch children at 42 months of age. J Pediatr. 1999 Jan;134(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease W., Vandenberg J., Hooper K. Comparing alternative approaches to establishing regulatory levels for reproductive toxicants: DBCP as a case study. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Feb;91:141–155. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9191141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S. Molecular biology of the Ah receptor and its role in carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett. 2001 Mar 31;120(1-3):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(01)00301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler Richard H., Blank Imre, Varga Natalia, Robert Fabien, Hau Jörg, Guy Philippe A., Robert Marie-Claude, Riediker Sonja. Acrylamide from Maillard reaction products. Nature. 2002 Oct 3;419(6906):449–450. doi: 10.1038/419449a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyasu Takashi, Okada Morimichi, Imura Ryusuke, Sakamoto Hayao. Vertical variations in the concentration of mercury in soils around Sakurajima Volcano, Southern Kyushu, Japan. Sci Total Environ. 2003 Mar 20;304(1-3):221–230. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreugdenhil Hestien J. I., Slijper Froukje M. E., Mulder Paul G. H., Weisglas-Kuperus Nynke. Effects of perinatal exposure to PCBs and dioxins on play behavior in Dutch children at school age. Environ Health Perspect. 2002 Oct;110(10):A593–A598. doi: 10.1289/ehp.021100593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward Elizabeth M., Schulte Paul A., Bayard Steve, Blair Aaron, Brandt-Rauf Paul, Butler Mary Ann, Dankovic David, Hubbs Ann F., Jones Carol, Karstadt Myra. Priorities for development of research methods in occupational cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 2003 Jan;111(1):1–12. doi: 10.1289/ehp.111-1241299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]