Abstract
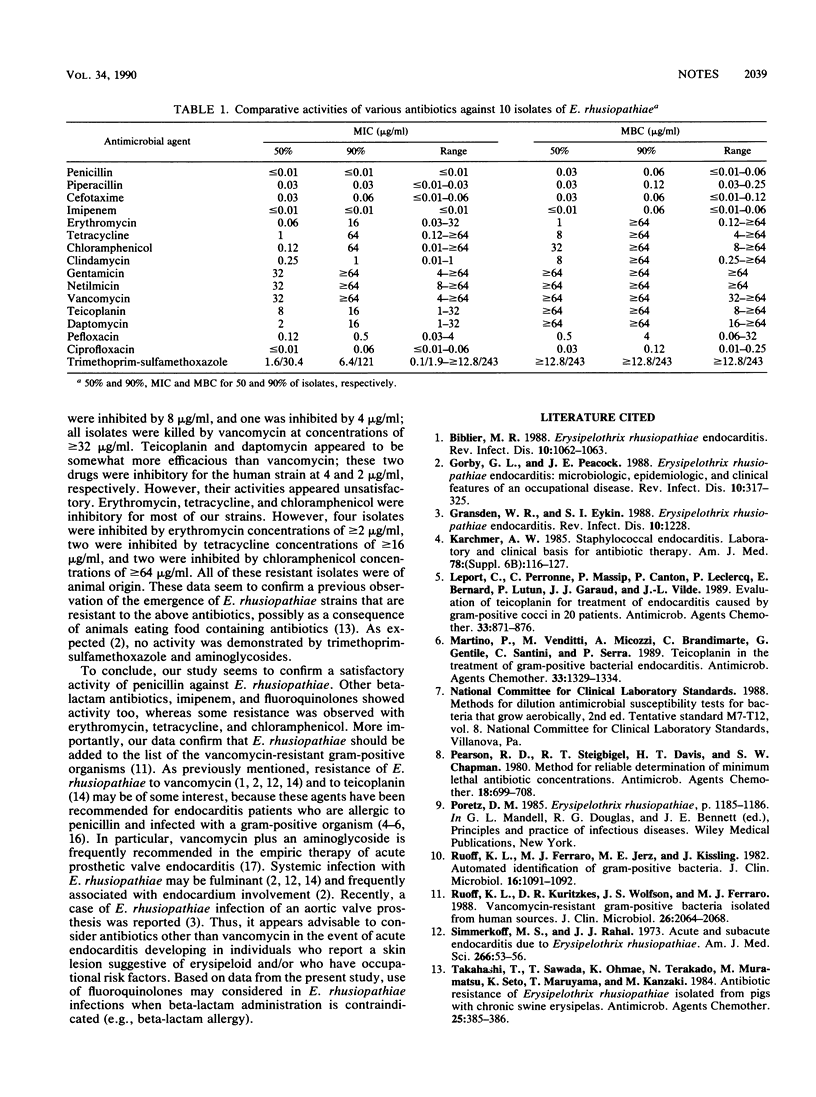
The in vitro susceptibilities of 10 isolates of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae to 16 antimicrobial agents were determined. Penicillin and imipenem were the most active agents, followed by piperacillin, cefotaxime, ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and clindamycin. Some resistance was observed with erythromycin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol. Activity was poor or absent with vancomycin, teicoplanin, daptomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, gentamicin, and netilmicin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibler M. R. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):1062–1063. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorby G. L., Peacock J. E., Jr Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis: microbiologic, epidemiologic, and clinical features of an occupational disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):317–325. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Eykyn S. J. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Nov-Dec;10(6):1228–1228. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.6.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W. Staphylococcal endocarditis. Laboratory and clinical basis for antibiotic therapy. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 28;78(6B):116–127. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90374-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leport C., Perronne C., Massip P., Canton P., Leclercq P., Bernard E., Lutun P., Garaud J. J., Vilde J. L. Evaluation of teicoplanin for treatment of endocarditis caused by gram-positive cocci in 20 patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):871–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino P., Venditti M., Micozzi A., Brandimarte C., Gentile G., Santini C., Serra P. Teicoplanin in the treatment of gram-positive-bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1329–1334. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J., Jerz M. E., Kissling J. Automated identification of gram-positive bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kuritzkes D. R., Wolfson J. S., Ferraro M. J. Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria isolated from human sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2064–2068. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2064-2068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simerkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr Acute and subacute endocarditis due to Erysipelothrix rhusopathiae. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Jul;266(1):53–57. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197307000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Sawada T., Ohmae K., Terakado N., Muramatsu M., Seto K., Maruyama T., Kanzaki M. Antibiotic resistance of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated from pigs with chronic swine erysipelas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):385–386. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venditti M., Gelfusa V., Castelli F., Brandimarte C., Serra P. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;9(1):50–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01969536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Geraci J. E. Treatment of streptococcal infective endocarditis. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 28;78(6B):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Jaumin P. M., Danielson G. K., Giuliani E. R., Washington JA I. I., Geraci J. E. Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):751–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


