Abstract
Background: Postural drainage chest physiotherapy in infants with cystic fibrosis (CF) exacerbates gastro-oesophageal reflux (GOR) and may contribute to a more rapid deterioration in lung function.
Aims: To compare standard postural drainage chest physiotherapy (SPT) and a modified physiotherapy regimen (MPT) without head-down tilt, with regard to GOR, arousal state, and cardiorespiratory function.
Methods: Twenty infants with CF underwent 30 hour oesophageal pH monitoring, during which four chest physiotherapy sessions were administered (day 1: MPT–SPT; day 2: SPT–MPT). Arousal state, heart rate, and oxygen saturation were documented for each of the physiotherapy positions (supine, prone, right lateral, and left lateral with (SPT) or without (MPT) 30° head-down tilt).
Results: Significantly more reflux episodes occurred during SPT than during MPT, but there were no significant differences in median episode duration or fractional reflux time. During SPT, left lateral positioning was associated with fewer reflux episodes compared to other positions. During supine and prone positioning, more reflux episodes occurred during SPT than during MPT. Infants were significantly more likely to be awake or cry during SPT. There was a significant association between crying and reflux episodes for SPT. Non-nutritive sucking was associated with a significant reduction in reflux episodes during SPT. Oxygen saturation during SPT was significantly lower during crying and other waking, and non-nutritive sucking during SPT was associated with a significant increase in oxygen saturation.
Conclusions: SPT is associated with GOR, distressed behaviour, and lower oxygen saturation.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (298.6 KB).
Figure 1 .
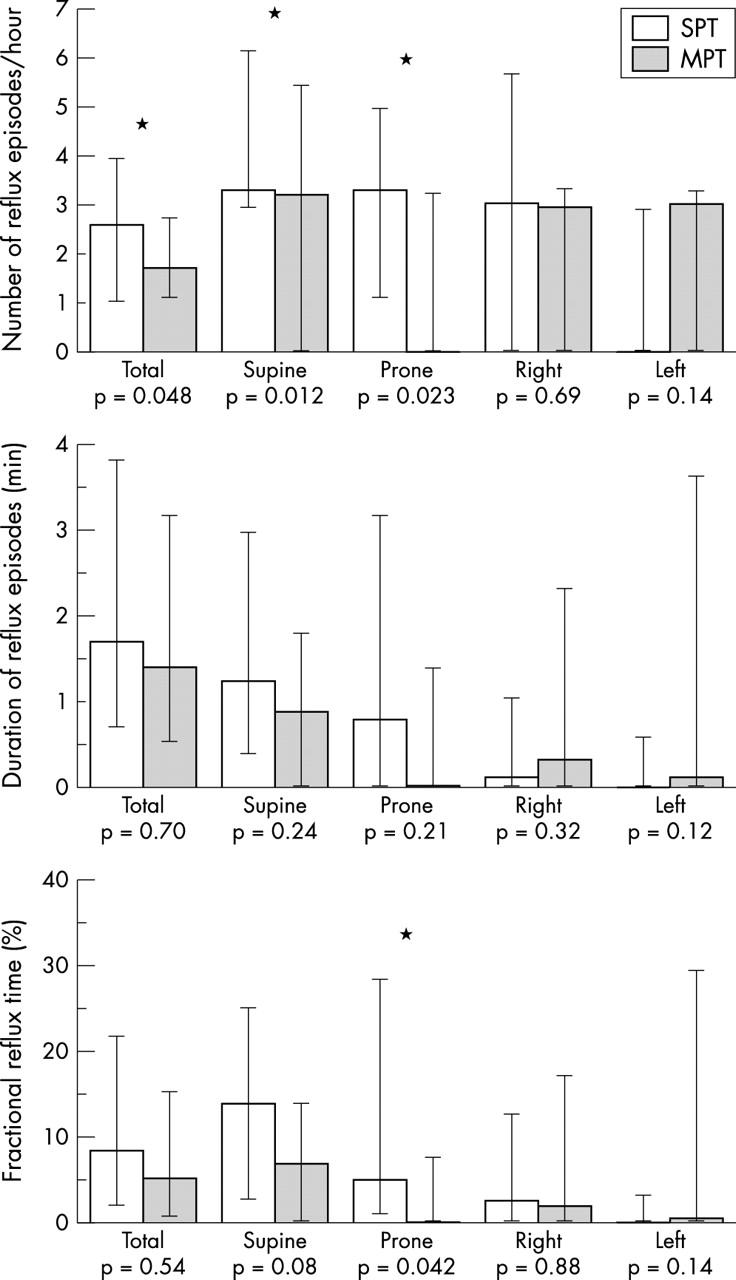
Median number of reflux episodes per hour, median duration of reflux episodes, and median fractional reflux time during chest physiotherapy in each of four positions carried out using either a standard postural drainage technique (SPT), or a modified regimen without head-down tilt (MPT). Twenty patients were studied twice in each of four positions during both physiotherapy regimens. Error bars show interquartile range. *Wilcoxon signed rank test: p < 0.05.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Button B. M., Heine R. G., Catto-Smith A. G., Phelan P. D., Olinsky A. Postural drainage and gastro-oesophageal reflux in infants with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Feb;76(2):148–150. doi: 10.1136/adc.76.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button B. M., Heine R. G., Catto-Smith A. G., Phelan P. D. Postural drainage in cystic fibrosis: is there a link with gastro-oesophageal reflux? J Paediatr Child Health. 1998 Aug;34(4):330–334. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1754.1998.00236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button Brenda M., Heine Ralf G., Catto-Smith Anthony G., Olinsky Anthony, Phelan Peter D., Ditchfield Michael R., Story Ian. Chest physiotherapy in infants with cystic fibrosis: to tip or not? A five-year study. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003 Mar;35(3):208–213. doi: 10.1002/ppul.10227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cucchiara S., Santamaria F., Andreotti M. R., Minella R., Ercolini P., Oggero V., de Ritis G. Mechanisms of gastro-oesophageal reflux in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1991 May;66(5):617–622. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPietro J. A., Cusson R. M., Caughy M. O., Fox N. A. Behavioral and physiologic effects of nonnutritive sucking during gavage feeding in preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 1994 Aug;36(2):207–214. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199408000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M., Kelstrup M., Andersen J. B., Kinoshita T., Falk P., Støvring S., Gøthgen I. Improving the ketchup bottle method with positive expiratory pressure, PEP, in cystic fibrosis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;65(6):423–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigelson J., Sauvegrain J. Refux gastro-oesophagien dans la mucoviscidose. Nouv Presse Med. 1975 Nov 8;4(38):2729–2730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feranchak A. P., Orenstein S. R., Cohn J. F. Behaviors associated with onset of gastroesophageal reflux episodes in infants. Prospective study using split-screen video and pH probe. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1994 Nov;33(11):654–662. doi: 10.1177/000992289403301104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles D. R., Wagener J. S., Accurso F. J., Butler-Simon N. Short-term effects of postural drainage with clapping vs autogenic drainage on oxygen saturation and sputum recovery in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1995 Oct;108(4):952–954. doi: 10.1378/chest.108.4.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine R. G., Button B. M., Olinsky A., Phelan P. D., Catto-Smith A. G. Gastro-oesophageal reflux in infants under 6 months with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1998 Jan;78(1):44–48. doi: 10.1136/adc.78.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara H., Dent J., Davidson G. Mechanisms responsible for gastroesophageal reflux in children. Gastroenterology. 1997 Aug;113(2):399–408. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9247456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T., McNicholas W. T., FitzGerald M. X. Hypoxaemia during chest physiotherapy in patients with cystic fibrosis. Ir J Med Sci. 1986 Oct;155(10):345–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02960715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers W. F., Herbst J. J. Effectiveness of positioning therapy for gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatrics. 1982 Jun;69(6):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein David M. Heads up! clear those airways! Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003 Mar;35(3):160–161. doi: 10.1002/ppul.10228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein S. R. Crying does not exacerbate gastroesophageal reflux in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992 Jan;14(1):34–37. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199201000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein S. R. Effect of nonnutritive sucking on infant gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatr Res. 1988 Jul;24(1):38–40. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198807000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein S. R. Prone positioning in infant gastroesophageal reflux: is elevation of the head worth the trouble? J Pediatr. 1990 Aug;117(2 Pt 1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80527-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein S. R., Shalaby T. M., Cohn J. F. Reflux symptoms in 100 normal infants: diagnostic validity of the infant gastroesophageal reflux questionnaire. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1996 Dec;35(12):607–614. doi: 10.1177/000992289603501201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein S. R., Whitington P. F., Orenstein D. M. The infant seat as treatment for gastroesophageal reflux. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 29;309(13):760–763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309293091304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paludetto R., Robertson S. S., Hack M., Shivpuri C. R., Martin R. J. Transcutaneous oxygen tension during nonnutritive sucking in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1984 Oct;74(4):539–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinelli J., Symington A. Non-nutritive sucking for promoting physiologic stability and nutrition in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001071–CD001071. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao S. Y., Chang Y. J., Lannon H., Yarandi H. Meta-analysis of the effects of nonnutritive sucking on heart rate and peripheral oxygenation: research from the past 30 years. Issues Compr Pediatr Nurs. 1997 Jan-Mar;20(1):11–24. doi: 10.3109/01460869709026874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snel A., Barnett C. P., Cresp T. L., Haslam R. R., Davidson G. P., Malbert T. H., Dent J., Omari T. I. Behavior and gastroesophageal reflux in the premature neonate. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000 Jan;30(1):18–21. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200001000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel C. T., Byrne W. J., Ament M. E., Euler A. R. Correlation of esophageal lengths in children with height: application to the Tuttle test without prior esophageal manometry. J Pediatr. 1979 Jan;94(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. M., McCloud P., Cameron D. J. Posture and gastro-oesophageal reflux: a case for left lateral positioning. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Mar;76(3):254–258. doi: 10.1136/adc.76.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treloar D. M. The effect of nonnutritive sucking on oxygenation in healthy, crying full-term infants. Appl Nurs Res. 1994 May;7(2):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0897-1897(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas Y., De Wolf D., Deneyer M., Sacre L. Incidence of gastroesophageal reflux in sleep, awake, fasted, and postcibal periods in asymptomatic and symptomatic infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Mar-Apr;7(2):177–180. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas Y., Sacre-Smits L. Seventeen-hour continuous esophageal pH monitoring in the newborn: evaluation of the influence of position in asymptomatic and symptomatic babies. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985 Jun;4(3):356–361. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198506000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


