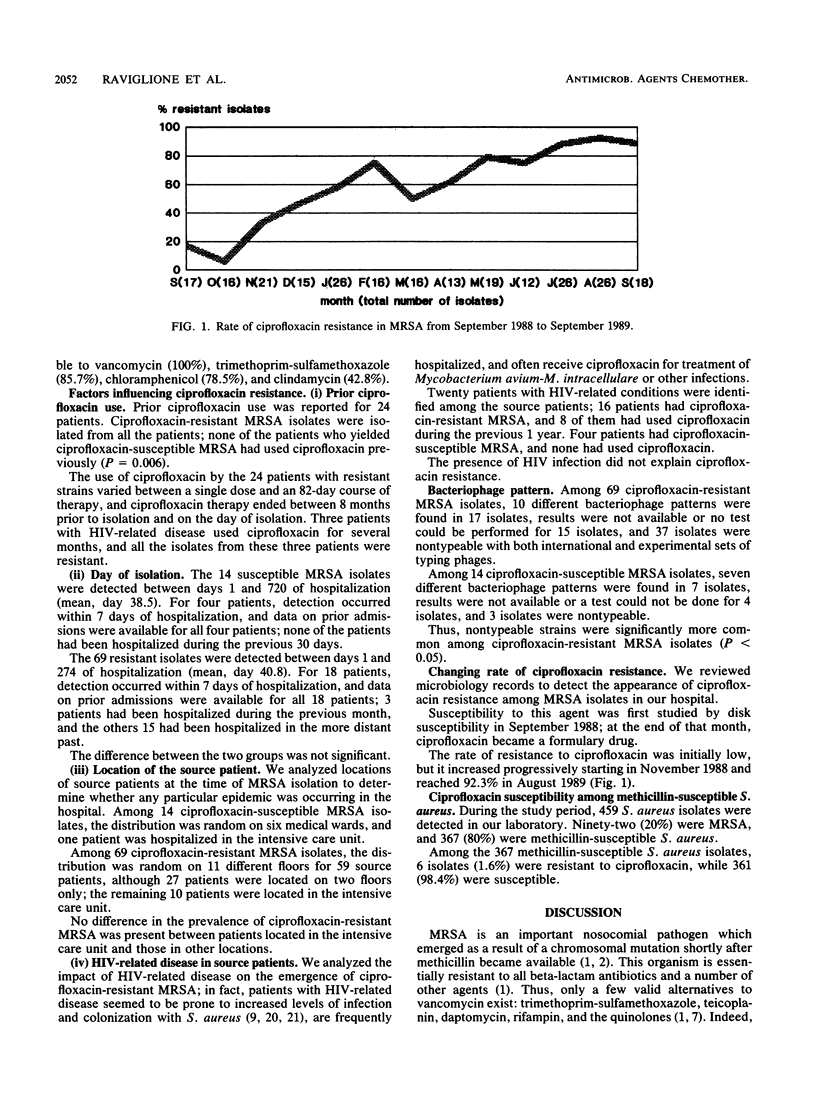
Abstract
Use of ciprofloxacin as an alternative to vancomycin for treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection has been paralleled by the emergence of resistant strains. This phenomenon has also been noticed in our hospital. To confirm our observation, methicillin and ciprofloxacin susceptibilities were tested by disk diffusion and broth microdilution techniques. We studied 83 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained from various sources over a 4-month period. Ciprofloxacin resistance (MIC, greater than 2 micrograms/ml) was detected in 69 isolates (83%). Prior use of ciprofloxacin was reported for 24 of 69 patients with ciprofloxacin-resistant strains and 0 of 14 patients with ciprofloxacin-susceptible strains. The day of detection during the hospital stay and the location of the source patient were not significantly different between resistant and susceptible strains. Bacteriophage typing showed a higher occurrence of nontypeable strains among ciprofloxacin-resistant strains (54%). Review of our microbiology register showed a progressive increase in the rate of resistance to ciprofloxacin during the first year of use, with initial rates being about 10% and recent rates being higher than 80%. On the other hand, methicillin-susceptible S. aureus remained uniformly susceptible to ciprofloxacin (98.4%). We conclude that prior use of ciprofloxacin is an important factor for the selection of ciprofloxacin-resistant strains and that ciprofloxacin has limited usefulness against methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumfitt W., Hamilton-Miller J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1188–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):173–186. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth G. J., Lothian J. L., Williams J. D. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: report of an outbreak in a London teaching hospital. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Jan;11(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S. J. Staphylococcal sepsis. The changing pattern of disease and therapy. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):100–104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Guerrero M., Rouse M., Henry N., Wilson W. Ciprofloxacin therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):747–751. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejzor B., Bokkenheuser V. D. Performance of the prompt system in identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):267–268. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.267-268.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: detection methods and treatment of infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):995–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Gellermann H., Chambers H. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and recurrent staphylococcal infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and AIDS-related complex. Am J Med. 1988 Aug;85(2):172–176. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Barriere S. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety R. Ciprofloxacin versus vancomycin in the therapy of experimental methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):527–530. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley S. G., Bertram M. A., Young L. S. Activity of ciprofloxacin against resistant clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Mar;17(3):281–286. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maple P. A., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. World-wide antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1989 Mar 11;1(8637):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhouse E. C., Mulvihill T. E., Jones L., Mooney D., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T. The in-vitro activity of some antimicrobial agents against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Mar;15(3):291–295. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Ruane P. J., Johnston L., Wong P., Wheelock J. P., MacDonald K., Reinhardt J. F., Johnson C. C., Statner B., Blomquist I. Ciprofloxacin for eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy E. A., Barbaro D., Luby J. P., Mackowiak P. A. Ciprofloxacin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviglione M. C., Battan R., Pablos-Mendez A., Aceves-Casillas P., Mullen M. P., Taranta A. Infections associated with Hickman catheters in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1989 Jun;86(6 Pt 2):780–786. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviglione M. C., Mariuz P., Pablos-Mendez A., Battan R., Ottuso P., Taranta A. High Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage rate in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS-related complex. Am J Infect Control. 1990 Apr;18(2):64–69. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(90)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Jones D., Perry W., Baradet T., Mayr E., Rampersad C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in New York City hospitals: inter-hospital spread of resistant strains of type 88. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):536–538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.536-538.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to quinolones. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):335–336. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.335-336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalit I., Berger S. A., Gorea A., Frimerman H. Widespread quinolone resistance among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in a general hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):593–594. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N. Staphylococcus aureus. The persistent pathogen (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 May 31;310(22):1437–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405313102206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr Bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin against amikacin- and cefotaxime-resistant gram-negative bacilli and methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1098–1100. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H., Tecson-Tumang F. Ciprofloxacin therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections or colonizations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Itoh-Yamashita N., Konno M. Cloning and expression of the norA gene for fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1535–1539. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westblom T. U., Abele B., Blount R., Hyslop D. L. Successful oral treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis using ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1988 Dec;85(6):884–884. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Bacterial resistance to quinolones: mechanisms and clinical importance. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S960–S968. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods G. L., Yam P. Evaluation of MicroScan MIC panels for detection of oxacillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):816–820. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.816-820.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



