Abstract
Aims: To test the suitability of a simple once daily (OD) gentamicin regimen for use in young infants where routine therapeutic drug monitoring is not possible.
Methods: In an open, randomised, controlled trial, infants with suspected severe sepsis admitted to a Kenyan, rural district hospital received a novel, OD gentamicin regimen or routine multi-dose (MD) regimens.
Results: A total of 297 infants (over 40% ⩽7 days) were randomised per protocol; 292 contributed at least some data for analysis of pharmacological endpoints. One hour after the first dose, 5% (7/136) and 28% (35/123) of infants in OD and MD arms respectively had plasma gentamicin concentrations <4 µg/ml (a surrogate of treatment inadequacy). Geometric mean gentamicin concentrations at this time were 9.0 µg/ml (95% CI 8.3 to 9.9) and 4.7 µg/ml (95% CI 4.2 to 5.3) respectively. By the fourth day, pre-dose concentrations ⩾2 µg/ml (a surrogate of potential treatment toxicity) were found in 6% (5/89) and 24% (21/86) of infants respectively. Mortality was similar in both groups and clinically insignificant, although potential gentamicin induced renal toxicity was observed in <2% infants.
Conclusions: A "two, four, six, eight" OD gentamicin regime, appropriate for premature infants and those in the first days and weeks of life, seems a suitable, safe prescribing guide in resource poor settings.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (214.7 KB).
Figure 1.
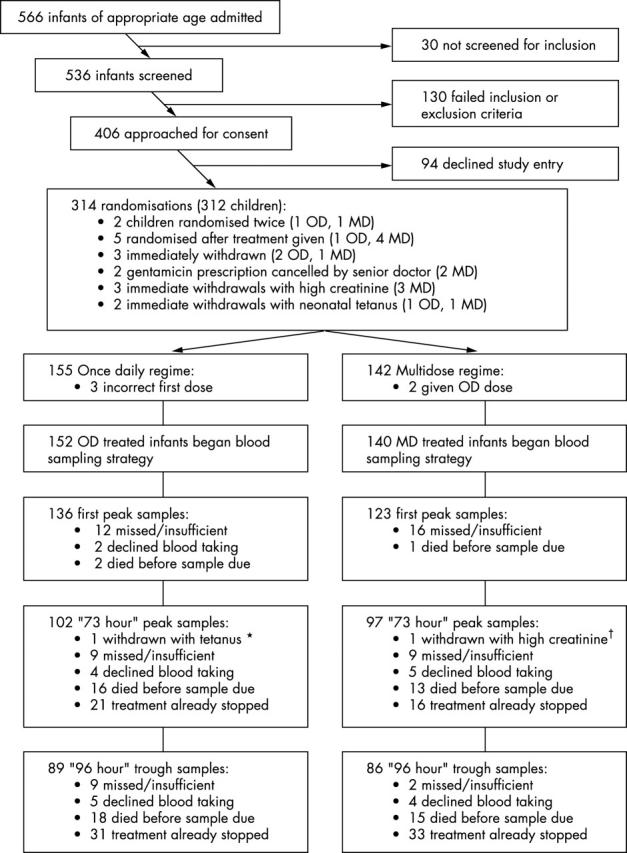
Trial profile. *Diagnosed six hours after admission. †Admission creatinine result obtained late, met exclusion criteria.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal Ghanshyam, Rastogi Alok, Pyati Suma, Wilks Angela, Pildes Rosita S. Comparison of once-daily versus twice-daily gentamicin dosing regimens in infants > or = 2500 g. J Perinatol. 2002 Jun;22(4):268–274. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M. Z., Goetz M. B. A meta-analysis of the relative efficacy and toxicity of single daily dosing versus multiple daily dosing of aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis. 1997 May;24(5):796–809. doi: 10.1093/clinids/24.5.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assael B. M., Gianni V., Marini A., Peneff P., Sereni F. Gentamicin dosage in preterm and term neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Nov;52(11):883–886. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.11.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey T. C., Little J. R., Littenberg B., Reichley R. M., Dunagan W. C. A meta-analysis of extended-interval dosing versus multiple daily dosing of aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis. 1997 May;24(5):786–795. doi: 10.1093/clinids/24.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang A. T., Bang R. A., Baitule S. B., Reddy M. H., Deshmukh M. D. Effect of home-based neonatal care and management of sepsis on neonatal mortality: field trial in rural India. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1955–1961. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)03046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Ioannidis J. P., Cappelleri J. C., Lau J. Single or multiple daily doses of aminoglycosides: a meta-analysis. BMJ. 1996 Feb 10;312(7027):338–345. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7027.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell H. Single or multiple daily doses of aminoglycosides. More details needed of treatment in neonates and young children. BMJ. 1996 Aug 24;313(7055):490–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.313.7055.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. K., Raber S. R., Rodvold K. A., Areff D. National survey of extended-interval aminoglycoside dosing. Clin Infect Dis. 2000 Mar;30(3):433–439. doi: 10.1086/313692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy S. Unlicensed and off label drug use for paediatric patients. Optimal dosing schedules with gentamicin are needed for premature neonates. BMJ. 1998 Jul 18;317(7152):204–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Low D. C., Bissenden J. G. Gentamicin dosage for the newborn. Lancet. 1986 Mar 1;1(8479):508–509. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92974-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisman D. N., Kaye K. M. Once-daily dosing of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000 Jun;14(2):475–487. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5520(05)70259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayani K. C., Hatzopoulos F. K., Frank A. L., Thummala M. R., Hantsch M. J., Schatz B. M., John E. G., Vidyasagar D. Pharmacokinetics of once-daily dosing of gentamicin in neonates. J Pediatr. 1997 Jul;131(1 Pt 1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(97)70127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isemann B. T., Kotagal U. R., Mashni S. M., Luckhaupt E. J., Johnson C. J. Optimal gentamicin therapy in preterm neonates includes loading doses and early monitoring. Ther Drug Monit. 1996 Oct;18(5):549–555. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy M. K., Nicolau D. P., Nightingale C. H., Quintiliani R. The pharmacodynamics of aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Jul;27(1):23–27. doi: 10.1086/514620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. P., Jewesson P. J. A critical reevaluation of the "therapeutic range" of aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):320–339. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N., Thomas M. L. Intravenous administration of kanamycin and gentamicin in newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1977 Oct;60(4):463–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miron D. Once daily dosing of gentamicin in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001 Dec;20(12):1169–1173. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200112000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulhall A., de Louvois J., Hurley R. Incidence of potentially toxic concentrations of gentamicin in the neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Nov;58(11):897–900. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.11.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. E., Davey P. G. Once-daily aminoglycoside dosing. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):346–347. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., MacGowan A. P. Once-daily aminoglycoside dosing. Lancet. 1993 Apr 3;341(8849):895–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd P. T., Hughes E. A., Placzek M. M., Hodes D. T. Reference ranges for plasma creatinine during the first month of life. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Mar;58(3):212–215. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.3.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopnik H., Wallraf R., Nies B., Tröster K., Heimann G. Pharmacokinetics and antibacterial activity of daily gentamicin. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Jan;67(1 Spec No):57–61. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.1_spec_no.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szefler S. J., Wynn R. J., Clarke D. F., Buckwald S., Shen D., Schentag J. J. Relationship of gentamicin serum concentrations to gestational age in preterm and term neonates. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):312–315. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thureen P. J., Reiter P. D., Gresores A., Stolpman N. M., Kawato K., Hall D. M. Once- versus twice-daily gentamicin dosing in neonates >/=34 Weeks' gestation: cost-effectiveness analyses. Pediatrics. 1999 Mar;103(3):594–598. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.3.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Alba Romero C., Gómez Castillo E., Manzanares Secades C., Rodriguez López J., Arreaza López L., Saenz Valiente P. Once daily gentamicin dosing in neonates. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998 Dec;17(12):1169–1171. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199812000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


