Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (81.1 KB).
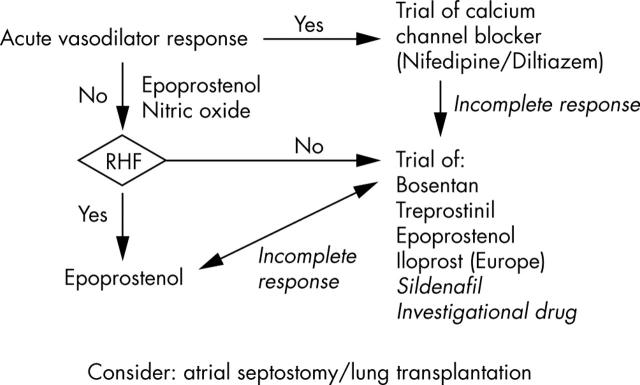
Figure 1.
Algorithm of the treatment of paediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension.
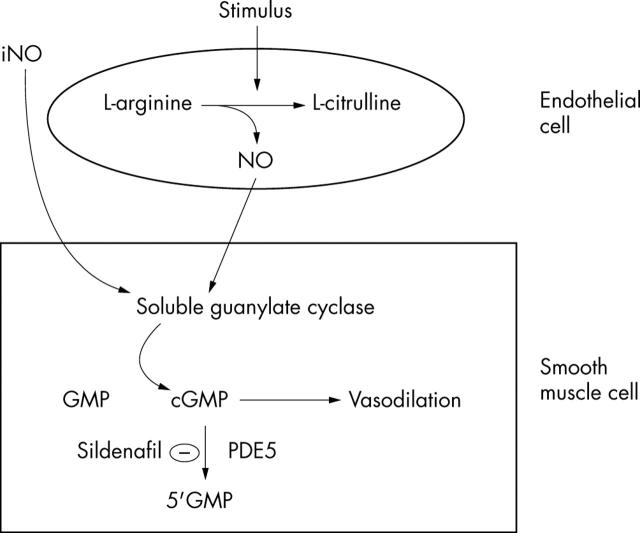
Figure 2.
Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) bypasses the damaged endothelium seen in pulmonary hypertensive disorders.
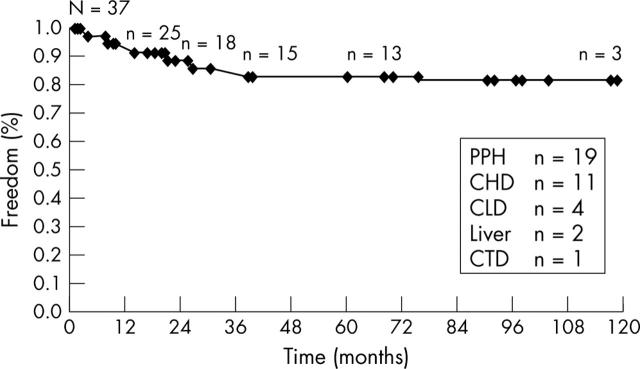
Figure 3.
Kaplan-Meier curves of long term prostacyclin treatment in children with pulmonary hypertension at The Children's Hospital Heart Institute/Paediatric Heart Lung Center, Denver, Colorado. PPH, primary pulmonary hypertension; CHD, congenital heart disease; CLD, chronic lung disease; Liver, liver disease; CTD, connective tissue disease.
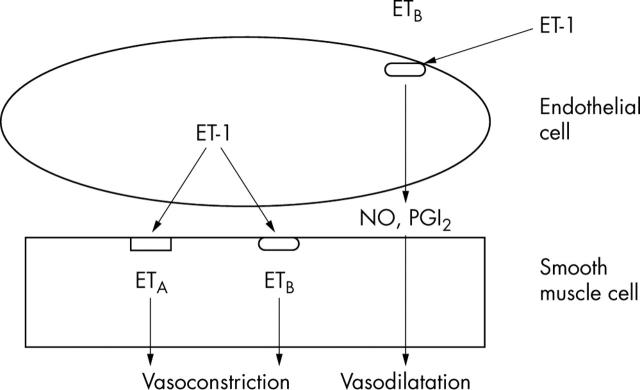
Figure 4.
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a potent vasoactive peptide produced primarily in the vascular endothelial cell, but also may be produced by smooth muscle cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atz A. M., Adatia I., Lock J. E., Wessel D. L. Combined effects of nitric oxide and oxygen during acute pulmonary vasodilator testing. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Mar;33(3):813–819. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atz A. M., Adatia I., Wessel D. L. Rebound pulmonary hypertension after inhalation of nitric oxide. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996 Dec;62(6):1759–1764. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(96)00542-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atz A. M., Wessel D. L. Inhaled nitric oxide in the neonate with cardiac disease. Semin Perinatol. 1997 Oct;21(5):441–455. doi: 10.1016/s0146-0005(97)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atz A. M., Wessel D. L. Sildenafil ameliorates effects of inhaled nitric oxide withdrawal. Anesthesiology. 1999 Jul;91(1):307–310. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199907000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atz Andrew M., Lefler Amy K., Fairbrother David L., Uber Walter E., Bradley Scott M. Sildenafil augments the effect of inhaled nitric oxide for postoperative pulmonary hypertensive crises. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002 Sep;124(3):628–629. doi: 10.1067/mtc.2002.125265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger W. R., Channick R. N., Kerr K. M., Fedullo P. F. Evaluation of patients with suspected chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999 Apr;11(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/s1043-0679(99)70011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J., Maislin G., Fishman A. P. Vasodilator therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension in children. Circulation. 1999 Mar 9;99(9):1197–1208. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.9.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J. Recent advances in the treatment of pediatric pulmonary artery hypertension. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1999 Apr;46(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst Robyn J., Ivy Dunbar, Dingemanse Jasper, Widlitz Allison, Schmitt Kelly, Doran Aimee, Bingaman Deborah, Nguyen Ngoc, Gaitonde Michael, van Giersbergen Paul L. M. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of bosentan in pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Apr;73(4):372–382. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9236(03)00005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst Robyn J., Langleben David, Frost Adaani, Horn Evelyn M., Oudiz Ronald, Shapiro Shelley, McLaughlin Vallerie, Hill Nicholas, Tapson Victor F., Robbins Ivan M. Sitaxsentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003 Nov 20;169(4):441–447. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200307-957OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst Robyn J., McGoon Michael, McLaughlin Vallerie, Tapson Victor, Rich Stuart, Rubin Lewis, Wasserman Karlman, Oudiz Ronald, Shapiro Shelley, Robbins Ivan M. Beraprost therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Jun 18;41(12):2119–2125. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman Erika Berman, Barst Robyn J. Eisenmenger's syndrome: current management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2002 Sep-Oct;45(2):129–138. doi: 10.1053/pcad.2002.127492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berner M., Beghetti M., Spahr-Schopfer I., Oberhansli I., Friedli B. Inhaled nitric oxide to test the vasodilator capacity of the pulmonary vascular bed in children with long-standing pulmonary hypertension and congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Mar 1;77(7):532–535. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)89353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucek Mark M., Edwards Leah B., Keck Berkeley M., Trulock Elbert P., Taylor David O., Mohacsi Paul J., Hertz Marshall I. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Sixth Official Pediatric Report--2003. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2003 Jun;22(6):636–652. doi: 10.1016/s1053-2498(03)00184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channick R. N., Newhart J. W., Johnson F. W., Williams P. J., Auger W. R., Fedullo P. F., Moser K. M. Pulsed delivery of inhaled nitric oxide to patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: an ambulatory delivery system and initial clinical tests. Chest. 1996 Jun;109(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1378/chest.109.6.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabby M. L., Canter C. E., Moller J. H., Bridges N. D. Hemodynamic data and survival in children with pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997 Aug;30(2):554–560. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlem Peter, van Aalderen Wim M. C., de Neef Marjorie, Dijkgraaf Marcel G. W., Bos Albert P. Randomized controlled trial of aerosolized prostacyclin therapy in children with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2004 Apr;32(4):1055–1060. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000120055.52377.bf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A., Bossuyt A., Dab I. Acute effects of oxygen, nifedipine, and diltiazem in patients with cystic fibrosis and mild pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;6(1):53–59. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950060113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor J. W., Bridges N. D., Clark B. J., Spray T. L. Update on lung transplantation in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1998 Jun;10(3):256–261. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199806000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geggel R. L., Dozor A. J., Fyler D. C., Reid L. M. Effect of vasodilators at rest and during exercise in young adults with cystic fibrosis and chronic cor pulmonale. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):531–536. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghofrani Hossein Ardeschir, Wiedemann Ralph, Rose Frank, Schermuly Ralph T., Olschewski Horst, Weissmann Norbert, Gunther Andreas, Walmrath Dieter, Seeger Werner, Grimminger Friedrich. Sildenafil for treatment of lung fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002 Sep 21;360(9337):895–900. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy D. D., Griebel J. L., Kinsella J. P., Abman S. H. Acute hemodynamic effects of pulsed delivery of low flow nasal nitric oxide in children with pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr. 1998 Sep;133(3):453–456. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy D. D., Kinsella J. P., Wolfe R. R., Abman S. H. Atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide in children with pulmonary hypertension after surgical repair of congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Jan 1;77(1):102–105. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)89147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy D. D., Kinsella J. P., Ziegler J. W., Abman S. H. Dipyridamole attenuates rebound pulmonary hypertension after inhaled nitric oxide withdrawal in postoperative congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998 Apr;115(4):875–882. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70369-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy D. Dunbar, Doran Aimee, Claussen Lori, Bingaman Deborah, Yetman Anji. Weaning and discontinuation of epoprostenol in children with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension receiving concomitant bosentan. Am J Cardiol. 2004 Apr 1;93(7):943–946. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.12.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy D. Dunbar, Parker Donna, Doran Aimee, Parker Donna, Kinsella John P., Abman Steven H. Acute hemodynamic effects and home therapy using a novel pulsed nasal nitric oxide delivery system in children and young adults with pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2003 Oct 1;92(7):886–890. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(03)00910-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Higenbottam T. W., Cremona G., Akamine S., Demoncheaux E. A., Smith A. P., Siddons T. E. Minimizing the inhaled dose of NO with breath-by-breath delivery of spikes of concentrated gas. Circulation. 1998 Dec 1;98(22):2429–2432. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.22.2429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max M., Rossaint R. Inhaled prostacyclin in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Pediatr. 1999 Dec;158 (Suppl 1):S23–S26. doi: 10.1007/pl00014316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis Evangelos, Tymchak Wayne, Lien Dale, Webster Linda, Hashimoto Kyoko, Archer Stephen. Oral sildenafil is an effective and specific pulmonary vasodilator in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: comparison with inhaled nitric oxide. Circulation. 2002 May 21;105(20):2398–2403. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000016641.12984.dc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. H., Wheeler L., Lane K. B., Loyd E., Gaddipati R., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Loyd J. E. Mutation in the gene for bone morphogenetic protein receptor II as a cause of primary pulmonary hypertension in a large kindred. N Engl J Med. 2001 Aug 2;345(5):319–324. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108023450502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschewski Horst, Simonneau Gerald, Galiè Nazzareno, Higenbottam Timothy, Naeije Robert, Rubin Lewis J., Nikkho Sylvia, Speich Rudolf, Hoeper Marius M., Behr Jürgen. Inhaled iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2002 Aug 1;347(5):322–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl Jeffrey M., Nelson David P., Raake Jenni L., Manning Peter B., Schwartz Steven M., Koons Lisa, Shanley Thomas P., Wong Hector R., Duffy Jodie Y. Inhaled nitric oxide increases endothelin-1 levels: a potential cause of rebound pulmonary hypertension. Crit Care Med. 2002 Jan;30(1):89–93. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200201000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepke-Zaba J., Higenbottam T. W., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Stone D., Wallwork J. Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1991 Nov 9;338(8776):1173–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast B., Newby D. E., Wilson L. E., Webb D. J., Mankad P. S. Early therapeutic experience with the endothelin antagonist BQ-123 in pulmonary hypertension after congenital heart surgery. Heart. 1999 Oct;82(4):505–508. doi: 10.1136/hrt.82.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Pulmonary hypertension: pathophysiology as a basis for clinical decision making. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1999 Nov;18(11):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/s1053-2498(99)00015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimensberger P. C., Spahr-Schopfer I., Berner M., Jaeggi E., Kalangos A., Friedli B., Beghetti M. Inhaled nitric oxide versus aerosolized iloprost in secondary pulmonary hypertension in children with congenital heart disease: vasodilator capacity and cellular mechanisms. Circulation. 2001 Jan 30;103(4):544–548. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.4.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig E. B., Kerstein D., Barst R. J. Long-term prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension with associated congenital heart defects. Circulation. 1999 Apr 13;99(14):1858–1865. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.14.1858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin Lewis J., Badesch David B., Barst Robyn J., Galie Nazzareno, Black Carol M., Keogh Anne, Pulido Tomas, Frost Adaani, Roux Sebastien, Leconte Isabelle. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2002 Mar 21;346(12):896–903. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval J., Bauerle O., Gomez A., Palomar A., Martínez Guerra M. L., Furuya M. E. Primary pulmonary hypertension in children: clinical characterization and survival. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Feb;25(2):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)00391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval J., Gaspar J., Pulido T., Bautista E., Martínez-Guerra M. L., Zeballos M., Palomar A., Gómez A. Graded balloon dilation atrial septostomy in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. A therapeutic alternative for patients nonresponsive to vasodilator treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Aug;32(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Neick Ingram, Hartenstein Paulina, Li Jia, Stiller Brigitte, Nagdyman Nicole, Hübler Michael, Butrous Ghazwan, Petros Andy, Lange Peter, Redington Andrew N. Intravenous sildenafil is a potent pulmonary vasodilator in children with congenital heart disease. Circulation. 2003 Sep 9;108 (Suppl 1):II167–II173. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000087384.76615.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Neick Ingram, Li Jia, Reader Jayne A., Shekerdemian Lara, Redington Andrew N., Penny Daniel J. The endothelin antagonist BQ123 reduces pulmonary vascular resistance after surgical intervention for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002 Sep;124(3):435–441. doi: 10.1067/mtc.2002.121492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneau Gerald, Barst Robyn J., Galie Nazzareno, Naeije Robert, Rich Stuart, Bourge Robert C., Keogh Anne, Oudiz Ronald, Frost Adaani, Blackburn Shelmer D. Continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil, a prostacyclin analogue, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Mar 15;165(6):800–804. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.6.2106079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon Olivier, Humbert Marc, Nunes Hilario, Parent Florence, Garcia Gilles, Hervé Philippe, Rainisio Maurizio, Simonneau Gérald. Long-term intravenous epoprostenol infusion in primary pulmonary hypertension: prognostic factors and survival. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Aug 21;40(4):780–788. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima Kyoko, Stevenson William G. Ventricular tachycardia associated with myocardial infarct scar: a spectrum of therapies for a single patient. Circulation. 2002 Jul 9;106(2):176–179. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000019361.34897.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THILENIUS O. G., NADAS A. S., JOCKIN H. PRIMARY PULMONARY VASCULAR OBSTRUCTION IN CHILDREN. Pediatrics. 1965 Jul;36:75–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trembath Richard C., Harrison Rachel. Insights into the genetic and molecular basis of primary pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr Res. 2003 Mar 5;53(6):883–888. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000061565.22500.E7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuder R. M., Cool C. D., Geraci M. W., Wang J., Abman S. H., Wright L., Badesch D., Voelkel N. F. Prostacyclin synthase expression is decreased in lungs from patients with severe pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Jun;159(6):1925–1932. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.159.6.9804054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D. L., Adatia I., Giglia T. M., Thompson J. E., Kulik T. J. Use of inhaled nitric oxide and acetylcholine in the evaluation of pulmonary hypertension and endothelial function after cardiopulmonary bypass. Circulation. 1993 Nov;88(5 Pt 1):2128–2138. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.5.2128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widlitz A., Barst R. J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in children. Eur Respir J. 2003 Jan;21(1):155–176. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00088302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]