Abstract
Aims: To assess prevalence of the insulin resistance syndrome (IRS: obesity, abnormal glucose homoeostasis, dyslipidaemia, and hypertension) in obese UK children and adolescents of different ethnicities and to assess whether fasting data is sufficient to identify IRS in childhood obesity.
Methods: A total of 103 obese (BMI >95th centile) children and adolescents 2–18 years of age referred for assessment underwent an oral glucose tolerance test, measurement of fasting lipids, and blood pressure determination. Main outcome measures were prevalence of components of IRS by modified WHO criteria, with IRS defined as ⩾3 components (including obesity).
Results: There were 67 girls (65%). BMI z-score ranged from 1.65 to 6.15, with 72% having a z-score ⩾3.0. Abnormal glucose homoeostasis was identified in 46% (hyperinsulinism in 40%, impaired fasting glucose in 0.8%, impaired glucose tolerance in 11%). No subjects had silent type 2 diabetes. Dyslipidaemia was identified in 30% and hypertension in 32%. Thirty one per cent had obesity alone, 36% had two components, 28% had three, and 5% had all four components. Birth weight, BMI, and family history of IRS were not associated with risk of IRS. Higher age increased the risk of IRS; however the syndrome was seen in 30% of children under 12 years. The use of fasting glucose and insulin data for identifying IRS had a sensitivity of 88% and specificity of 100%.
Conclusions: One third of obese children and adolescents have the IRS; however type 2 diabetes is rare. Obese children with the IRS may form a high risk group to whom scarce intervention resources should be targeted. Further work is needed to develop appropriate screening programmes for IRS components in significantly obese children.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (74.8 KB).
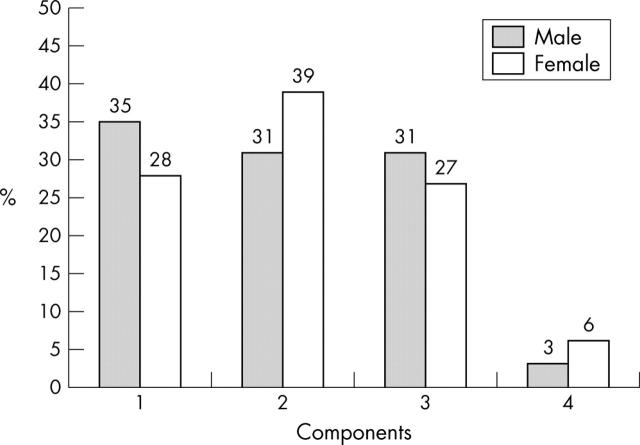
Figure 1.
Number of IRS components by sex (including obesity).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti K. G., Zimmet P. Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998 Jul;15(7):539–553. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::AID-DIA668>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand Sonia S., Razak Fahad, Vuksan Vlad, Gerstein Hertzel C., Malmberg Klas, Yi Qilong, Teo Koon K., Yusuf Salim. Diagnostic strategies to detect glucose intolerance in a multiethnic population. Diabetes Care. 2003 Feb;26(2):290–296. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao W., Srinivasan S. R., Wattigney W. A., Berenson G. S. Persistence of multiple cardiovascular risk clustering related to syndrome X from childhood to young adulthood. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Arch Intern Med. 1994 Aug 22;154(16):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenson G. S., Srinivasan S. R. Consideration of serum cholesterol in risk factor profiling for all young individuals. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2001 Oct;11 (Suppl 5):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black N. Evidence based policy: proceed with care. BMJ. 2001 Aug 4;323(7307):275–279. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7307.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevale Schianca Gian Piero, Rossi Antonello, Sainaghi Pier Paolo, Maduli Elisabetta, Bartoli Ettore. The significance of impaired fasting glucose versus impaired glucose tolerance: importance of insulin secretion and resistance. Diabetes Care. 2003 May;26(5):1333–1337. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.5.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Srinivasan S. R., Elkasabany A., Berenson G. S. Cardiovascular risk factors clustering features of insulin resistance syndrome (Syndrome X) in a biracial (Black-White) population of children, adolescents, and young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1999 Oct 1;150(7):667–674. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a010069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. J., Bellizzi M. C., Flegal K. M., Dietz W. H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000 May 6;320(7244):1240–1243. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. J., Freeman J. V., Preece M. A. Body mass index reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jul;73(1):25–29. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decsi Tamás, Molnár Dénes. Insulin resistance syndrome in children : pathophysiology and potential management strategies. Paediatr Drugs. 2003;5(5):291–299. doi: 10.2165/00128072-200305050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. J., Smith A., Betts P. R., Crowne E. C., Shield J. P. H. Type 2 diabetes in obese white children. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Mar;86(3):207–208. doi: 10.1136/adc.86.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagot-Campagna A., Pettitt D. J., Engelgau M. M., Burrows N. R., Geiss L. S., Valdez R., Beckles G. L., Saaddine J., Gregg E. W., Williamson D. F. Type 2 diabetes among North American children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review and a public health perspective. J Pediatr. 2000 May;136(5):664–672. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2000.105141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowell S. L., Maudsley G., Maguire P., Leinster S. J., Bligh J. Student assessment in undergraduate medical education in the United Kingdom, 1998. Med Educ. 2000 Sep;34 (Suppl 1):1–49. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2000.0340s1001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. S., Dietz W. H., Srinivasan S. R., Berenson G. S. The relation of overweight to cardiovascular risk factors among children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 1999 Jun;103(6 Pt 1):1175–1182. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.6.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. S., Khan L. K., Dietz W. H., Srinivasan S. R., Berenson G. S. Relationship of childhood obesity to coronary heart disease risk factors in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2001 Sep;108(3):712–718. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. S., Mansfield M. W., Barrett J. H., Grant P. J. Heritability of features of the insulin resistance syndrome in a community-based study of healthy families. Diabet Med. 2002 Dec;19(12):994–999. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich John E. Contributions of insulin-resistance and insulin-secretory defects to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003 Apr;78(4):447–456. doi: 10.4065/78.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goran M. I., Gower B. A. Longitudinal study on pubertal insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2001 Nov;50(11):2444–2450. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.11.2444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goran Michael I., Bergman Richard N., Cruz Martha L., Watanabe Richard. Insulin resistance and associated compensatory responses in african-american and Hispanic children. Diabetes Care. 2002 Dec;25(12):2184–2190. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.12.2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Romero F., Rodríguez-Morán M. Glucose intolerance is predicted by the high Fasting Insulin-to-Glucose ratio. Diabetes Metab. 2001 Apr;27(2 Pt 1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman T. B., Briefel R. R., Carroll M. D., Rifkind B. M., Cleeman J. I., Maurer K. R., Johnson C. L. Distributions and trends of serum lipid levels among United States children and adolescents ages 4-19 years: data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Prev Med. 1998 Nov-Dec;27(6):879–890. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1998.0376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinchcliffe R. Medical examiner variability. J Laryngol Otol. 1997 Jan;111(1):8–14. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100136321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson Linda, Aitken Peter, Hayes Tom. Are medical postgraduate certification processes valid? A systematic review of the published evidence. Med Educ. 2002 Jan;36(1):73–91. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2002.01120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Invitti Cecilia, Guzzaloni Gabriele, Gilardini Luisa, Morabito Francesco, Viberti Giancarlo. Prevalence and concomitants of glucose intolerance in European obese children and adolescents. Diabetes Care. 2003 Jan;26(1):118–124. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly B. 'The professor has submitted her questions and thus we may proceed to set the examination paper'. Med Educ. 2000 Jan;34(1):7–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2000.00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Nambi S. S., Mather K., Baron A. D., Follmann D. A., Sullivan G., Quon M. J. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Jul;85(7):2402–2410. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.7.6661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khera N., Stroobant J., Primhak R. A., Gupta R., Davies H. Training the ideal hospital doctor: the specialist registrars' perspective. Med Educ. 2001 Oct;35(10):957–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichner P., Sisler G. C., Harper D. A study of the reliability of the clinical oral examination in psychiatry. Can J Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;29(5):394–397. doi: 10.1177/070674378402900506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little D. Learning disabilities, medical students, and common sense. Acad Med. 1999 Jun;74(6):622–623. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199906000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzar S. The English language and Arabic medical students. Med Educ. 1999 May;33(5):394–395. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.1999.0416b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., DeFronzo R. A. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care. 1999 Sep;22(9):1462–1470. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.9.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. R., Hosker J. P., Rudenski A. S., Naylor B. A., Treacher D. F., Turner R. C. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985 Jul;28(7):412–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00280883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. A., Barton B. A., Biro F. M., Daniels S. R., Sprecher D. L. Overweight, fat patterning, and cardiovascular disease risk factors in black and white boys. J Pediatr. 1999 Oct;135(4):451–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newble D. I., Hoare J., Sheldrake P. F. The selection and training of examiners for clinical examinations. Med Educ. 1980 Sep;14(5):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.1980.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newble David. Techniques for measuring clinical competence: objective structured clinical examinations. Med Educ. 2004 Feb;38(2):199–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2004.01755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston-Whyte E., Fraser R., McKinley R., Hastings A., Cookson J., Alun-Jones T. Hospital clinicians' views on training as examiners for undergraduate regulatory clinical examinations. Med Educ. 2000 Nov;34(11):964–964. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2000.0818f.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M. R., Webb L. C., Houston W. M. Correcting performance-rating errors in oral examinations. Eval Health Prof. 1991 Mar;14(1):100–122. doi: 10.1177/016327879101400107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. J., Wilson M. L., Summerbell C. D., Wilson D. C. Obesity: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment; evidence based answers to common questions. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Jun;86(6):392–394. doi: 10.1136/adc.86.6.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C., Sarangi S., Southgate L., Wakeford R., Wass V. Oral examinations-equal opportunities, ethnicity, and fairness in the MRCGP. BMJ. 2000 Feb 5;320(7231):370–375. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7231.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinaiko A. R., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Steinberger J., Moran A., Luepker R., Rocchini A. P., Prineas R. J. Insulin resistance syndrome in childhood: associations of the euglycemic insulin clamp and fasting insulin with fatness and other risk factors. J Pediatr. 2001 Nov;139(5):700–707. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.118535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Ranjana, Fisch Gene, Teague Barbara, Tamborlane William V., Banyas Bruna, Allen Karin, Savoye Mary, Rieger Vera, Taksali Sara, Barbetta Gina. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002 Mar 14;346(11):802–810. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan Sathanur R., Myers Leann, Berenson Gerald S. Predictability of childhood adiposity and insulin for developing insulin resistance syndrome (syndrome X) in young adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Diabetes. 2002 Jan;51(1):204–209. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.1.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate P., Foulkes J., Neighbour R., Campion P., Field S. Assessing physicians' interpersonal skills via videotaped encounters: a new approach for the Royal College of General Practitioners Membership examination. J Health Commun. 1999 Apr-Jun;4(2):143–152. doi: 10.1080/108107399127011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. S., Mellsop G., Callender K., Crawshaw J., Ellis P. M., Hall A., MacDonald J., Silfverskiold P., Romans-Clarkson S. The oral examination: a study of academic and non-academic factors. Med Educ. 1993 Sep;27(5):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.1993.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortolero S. R., Goff D. C., Jr, Nichaman M. Z., Labarthe D. R., Grunbaum J. A., Hanis C. L. Cardiovascular risk factors in Mexican-American and non-Hispanic white children: The Corpus Christi Child Heart Study. Circulation. 1997 Jul 15;96(2):418–423. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.2.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweed M., Cookson J. The face validity of a final professional clinical examination. Med Educ. 2001 May;35(5):465–473. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2001.00895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwaifo Gabriel I., Fallon Erica M., Chin Jeff, Elberg Jane, Parikh Shamik J., Yanovski Jack A. Indices of insulin action, disposal, and secretion derived from fasting samples and clamps in normal glucose-tolerant black and white children. Diabetes Care. 2002 Nov;25(11):2081–2087. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.11.2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent Francesca, Little D'Anna, Bertollini Roberto, Nemer Leda E., Barbone Fabio, Tamburlini Giorgio. Burden of disease attributable to selected environmental factors and injury among children and adolescents in Europe. Lancet. 2004 Jun 19;363(9426):2032–2039. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeford R., Southgate L., Wass V. Improving oral examinations: selecting, training, and monitoring examiners for the MRCGP. Royal College of General Practitioners. BMJ. 1995 Oct 7;311(7010):931–935. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7010.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wass Val, Roberts Celia, Hoogenboom Ron, Jones Roger, Van der Vleuten Cees. Effect of ethnicity on performance in a final objective structured clinical examination: qualitative and quantitative study. BMJ. 2003 Apr 12;326(7393):800–803. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7393.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. A., Polliack M. R., Tabenkin H., Kahan E. Variations among examiners in family medicine residency board oral examinations. Med Educ. 2000 Jan;34(1):13–17. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2000.00408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whincup Peter H., Gilg Julie A., Papacosta Olia, Seymour Carol, Miller George J., Alberti K. G. M. M., Cook Derek G. Early evidence of ethnic differences in cardiovascular risk: cross sectional comparison of British South Asian and white children. BMJ. 2002 Mar 16;324(7338):635–635. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7338.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson Tim J., Frampton Christopher M., Thompson-Fawcett Mark, Egan Tony. Objectivity in objective structured clinical examinations: checklists are no substitute for examiner commitment. Acad Med. 2003 Feb;78(2):219–223. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200302000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams Christine L., Hayman Laura L., Daniels Stephen R., Robinson Thomas N., Steinberger Julia, Paridon Stephen, Bazzarre Terry. Cardiovascular health in childhood: A statement for health professionals from the Committee on Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young (AHOY) of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2002 Jul 2;106(1):143–160. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000019555.61092.9e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. M., Lever R., Harden R. M., Robertson J. I. Examination of clinical examiners. Lancet. 1969 Jan 4;1(7584):37–40. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90998-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaphe John, Street Simon. How do examiners decide?: a qualitative study of the process of decision making in the oral examination component of the MRCGP examination. Med Educ. 2003 Sep;37(9):764–771. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.2003.01606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young-Hyman D., Schlundt D. G., Herman L., De Luca F., Counts D. Evaluation of the insulin resistance syndrome in 5- to 10-year-old overweight/obese African-American children. Diabetes Care. 2001 Aug;24(8):1359–1364. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.8.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vleuten C. P., van Luyk S. J., van Ballegooijen A. M., Swanson D. B. Training and experience of examiners. Med Educ. 1989 May;23(3):290–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.1989.tb01547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]