Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (75.2 KB).
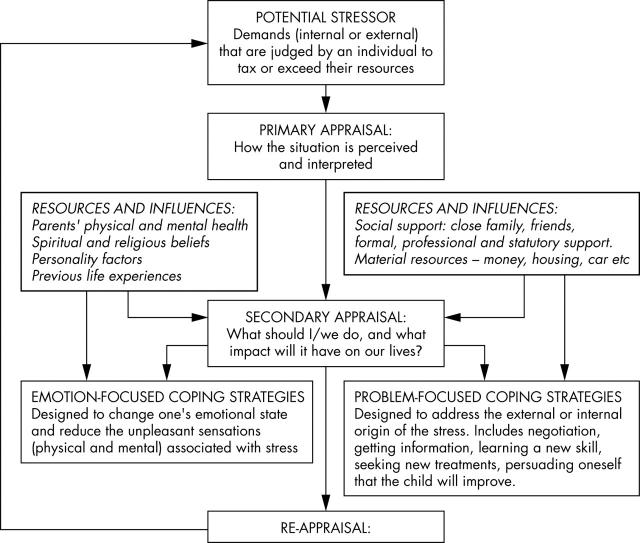
Figure 1.
Stress and Coping Model, based on Lazarus and Folkman11 and Beresford10 (with permission of J Child Psychol Psychiatry).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ablon J. Parents' responses to their child's diagnosis of neurofibromatosis 1. Am J Med Genet. 2000 Jul 17;93(2):136–142. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20000717)93:2<136::aid-ajmg11>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ablon J. The Parents' Auxiliary of Little People of America: a self-help model of social support for families of short-statured children. Prev Hum Serv. 1982 Spring;1(3):31–46. doi: 10.1300/J293v01n03_04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainbinder J. G., Blanchard L. W., Singer G. H., Sullivan M. E., Powers L. K., Marquis J. G., Santelli B. A qualitative study of Parent to Parent support for parents of children with special needs. Consortium to evaluate Parent to Parent. J Pediatr Psychol. 1998 Apr;23(2):99–109. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/23.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton P. L., Böll V., Everett J. M., Kelly A. M., Meredith K. H., Payne T. G. Beyond child development centres: care coordination for children with disabilities. Child Care Health Dev. 1997 Jan;23(1):29–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.1997.839839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton P. L., Minchom P. E. Models of parent partnership and child development centres. Child Care Health Dev. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):27–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.1991.tb00676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aytch L. S., Hammond R., White C. Seizures in infants and young children: an exploratory study of family experiences and needs for information and support. J Neurosci Nurs. 2001 Oct;33(5):278–285. doi: 10.1097/01376517-200110000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresford B. A. Resources and strategies: how parents cope with the care of a disabled child. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;35(1):171–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1994.tb01136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. B., Weiss J. O. A professional partnership with genetic support groups. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Jan;29(1):21–33. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco P. A., Kohen H., Shapland C. Parents-as-teachers: design and establishment of a training programme for paediatric residents. Med Educ. 1999 Sep;33(9):695–701. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2923.1999.00334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. R. The needs of parents with chronically sick children: a literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2001 Nov;36(4):600–607. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2001.02013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander S. R., Watkins C. E., Jr Therapeutic aspects of support groups for parents of the mentally retarded. Int J Group Psychother. 1985 Jan;35(1):65–78. doi: 10.1080/00207284.1985.11491405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. F., Radin M. B., McConnell B. Parent-to-parent support: a critical component of health care services for families. Issues Compr Pediatr Nurs. 1992 Jan-Mar;15(1):55–67. doi: 10.3109/01460869209078240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr S. M., McIntosh J. B. Coping when a child has a disability: exploring the impact of parent-to-parent support. Child Care Health Dev. 2000 Jul;26(4):309–322. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.2000.00149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G., Stewart D., King S., Law M. Organizational characteristics and issues affecting the longevity of self-help groups for parents of children with special needs. Qual Health Res. 2000 Mar;10(2):225–241. doi: 10.1177/104973200129118381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M., King S., Stewart D., King G. The perceived effects of parent-led support groups for parents of children with disabilities. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 2001;21(2-3):29–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell Wendy, Sloper Patricia. Information that informs rather than alienates families with disabled children: developing a model of good practice. Health Soc Care Community. 2002 Mar;10(2):74–81. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2524.2002.00344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain H. Coping with a child with disabilities from the parents' perspective: the function of information. Child Care Health Dev. 1999 Jul;25(4):299–312. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.1999.00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahi Jugnoo S., Manaras Irene, Tuomainen Helena, Hundt Gillian Lewando. Meeting the needs of parents around the time of diagnosis of disability among their children: evaluation of a novel program for information, support, and liaison by key workers. Pediatrics. 2004 Oct;114(4):e477–e482. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-0240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins J. A. Self-help groups for parents. Pediatr Nurs. 1987 Nov-Dec;13(6):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M., Pistrang N., Barker C. The benefits of mutual support groups for parents of children with disabilities. Am J Community Psychol. 2001 Feb;29(1):113–132. doi: 10.1023/A:1005253514140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallard P., Dickinson F. Groups for parents of pre-school children with severe disabilities. Child Care Health Dev. 1994 May-Jun;20(3):197–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.1994.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winch A. E., Christoph J. M. Parent-to-parent links: building networks for parents of hospitalized children. Child Health Care. 1988 Fall;17(2):93–97. doi: 10.1207/s15326888chc1702_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. H., McMenamy J. M., Perrin E. C. Parent advisory groups in pediatric practices: parents' and professionals' perceptions. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001 Jun;155(6):692–698. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.155.6.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]