Abstract
Background: It is widely believed that hydrostatic reduction of intussusception is less successful in children with prolonged symptoms prior to presentation.
Aim: To prospectively evaluate success in relation to duration of symptoms.
Methods: Prospective study in which children, regardless of symptom duration, underwent an attempt at hydrostatic reduction.
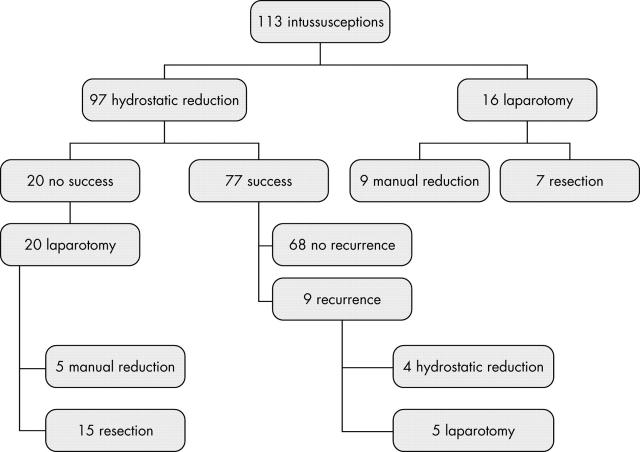
Results: Of 113 children presenting with intussusception, 16 had peritonitis and required immediate laparotomy. A hydrostatic reduction was attempted in 97 and was successful in 77 (79%). There were 26 successful reductions with symptoms <12 hours (81%), 30 with symptoms for 12–24 hours (81%), and 21 with symptoms >24 hours (75%).
Conclusion: The success rate with hydrostatic reduction was not significantly influenced by symptom duration.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (45.7 KB).
Figure 1.
Summary of results.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daneman A., Alton D. J. Intussusception. Issues and controversies related to diagnosis and reduction. Radiol Clin North Am. 1996 Jul;34(4):743–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneman Alan, Navarro Oscar. Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol. 2002 Nov 19;33(2):79–85. doi: 10.1007/s00247-002-0832-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. F., McCabe A. J., Raine P. A. M. The ins and outs of intussusception: history and management over the past fifty years. J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Jul;38(7 Suppl):60–64. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(03)00080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiore J. W. Intussusception. Semin Pediatr Surg. 1999 Nov;8(4):214–220. doi: 10.1016/s1055-8586(99)70029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrikson Susan, Blane Caroline E., Koujok Khaldoun, Strouse Peter J., DiPietro Michael A., Goodsitt Mitchell M. The effect of screening sonography on the positive rate of enemas for intussusception. Pediatr Radiol. 2002 Dec 12;33(3):190–193. doi: 10.1007/s00247-002-0848-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim H. K., Bae S. H., Lee K. H., Seo G. S., Yoon G. S. Assessment of reducibility of ileocolic intussusception in children: usefulness of color Doppler sonography. Radiology. 1994 Jun;191(3):781–785. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.3.8184064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro O., Dugougeat F., Kornecki A., Shuckett B., Alton D. J., Daneman A. The impact of imaging in the management of intussusception owing to pathologic lead points in children. A review of 43 cases. Pediatr Radiol. 2000 Sep;30(9):594–603. doi: 10.1007/s002470000261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe J. F., Fong S., Cheong I., O'Connell P. Plain film diagnosis of intussusception: prevalence of the target sign. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 Mar;158(3):619–621. doi: 10.2214/ajr.158.3.1739006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnen J. A., Festen C., van Roosmalen R. P. Intussusception: factors related to treatment. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Aug;65(8):871–873. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.8.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. A., Babyn P., Alton D. J. Plain abdominal radiography in suspected intussusception: a reassessment. Pediatr Radiol. 1994;24(1):17–20. doi: 10.1007/BF02017652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmit P., Rohrschneider W. K., Christmann D. Intestinal intussusception survey about diagnostic and nonsurgical therapeutic procedures. Pediatr Radiol. 1999 Oct;29(10):752–761. doi: 10.1007/s002470050689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson C. A., Seibert J. J., Strain J. D., Glasier C. M., Leithiser R. E., Jr, Iqbal V. Intussusception: clinical and radiographic factors influencing reducibility. Pediatr Radiol. 1989;20(1-2):57–60. doi: 10.1007/BF02010635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. W., Stephens B., Vane D. W., Grosfeld J. L. Intussusception: current management in infants and children. Surgery. 1987 Oct;102(4):704–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto L. G., Morita S. Y., Boychuk R. B., Inaba A. S., Rosen L. M., Yee L. L., Young L. L. Stool appearance in intussusception: assessing the value of the term "currant jelly". Am J Emerg Med. 1997 May;15(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0735-6757(97)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]