Abstract
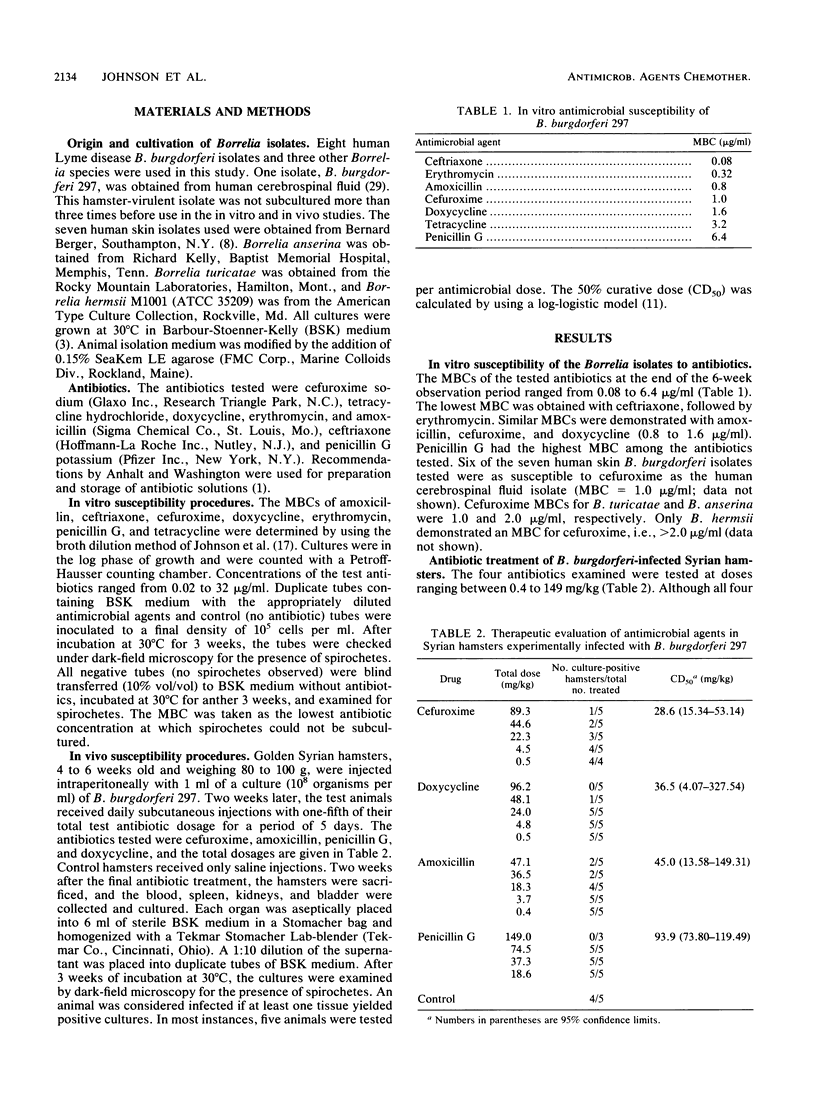
The in vitro and in vivo susceptibilities of the Lyme disease pathogen Borrelia burgdorferi to cefuroxime were compared with those of several other antibiotics commonly used to treat this disease. Cefuroxime demonstrated a higher MBC in vitro (1.0 microgram/ml) than ceftriaxone (0.08 microgram/ml) or erythromycin (0.32 microgram/ml), but the MBC was similar to that of amoxicillin (0.8 microgram/ml) and doxycycline (1.6 micrograms/ml). B. burgdorferi was considerably less susceptible to tetracycline (3.2 micrograms/ml) and penicillin G (6.4 micrograms/ml). Of the three other Borrelia species tested, two (Borrelia turicatae and Borrelia anserina) also demonstrated susceptibility to cefuroxime, while the third (Borrelia hermsii) was less susceptible. Results obtained with four antimicrobial agents in the in vivo hamster model parallel the antibiotic susceptibilities in the in vitro study. The three antibiotics with similar MBCs in vitro, i.e., cefuroxime, doxycycline, and amoxicillin, demonstrated comparable activities in preventing borreliosis in B. burgdorferi-challenged hamsters (50% curative doses = 28.6, 36.5 and 45.0 mg/kg, respectively). Penicillin G, which demonstrated the highest MBC in vitro, had very weak protective activity in the hamster model system. These results indicate that the in vitro and in vivo activities of cefuroxime against B. burgdorferi are comparable to those of several oral antibiotics currently being used in the treatment of early Lyme disease and suggest that the oral form of this cephalosporin may be an effective alternative therapy for this disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Laboratory aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):399–414. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. The diagnosis of Lyme disease: rewards and perils. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Apr 1;110(7):501–502. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-7-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. An animal model for Lyme arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:264–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Johnson R. C. Clinical and microbiologic findings in six patients with erythema migrans of Lyme disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Dec;21(6):1188–1191. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Kaplan M. H., Rothenberg I. R., Barbour A. G. Isolation and characterization of the Lyme disease spirochete from the skin of patients with erythema chronicum migrans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Sep;13(3):444–449. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Halperin J. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J. Treatment of late Lyme borreliosis--randomised comparison of ceftriaxone and penicillin. Lancet. 1988 May 28;1(8596):1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J., Halperin J. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Seronegative Lyme disease. Dissociation of specific T- and B-lymphocyte responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Hindersson P., Pedersen N. S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.338-346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C., White T. J., Shelburne C. E. Detection of antigens in urine of mice and humans infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.58-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M., Girard D. In-vitro and in-vivo susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi to azithromycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25 (Suppl A):33–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.suppl_a.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, to four antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. E., Klein G. C., Schmid G. P., Feeley J. C. Susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete to seven antimicrobial agents. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):549–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mursic V. P., Wilske B., Schierz G., Holmburger M., Süss E. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):424–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02013102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G., Süss E., Gross B. Comparative antimicrobial activity of the new macrolides against Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;8(7):651–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01968150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Museteanu C., Zimmer G., Mossmann H., Simon M. M. The severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mouse. A laboratory model for the analysis of Lyme arthritis and carditis. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1427–1432. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A., England D. M., Konick L. Induction of lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2336–2342. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2336-2342.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Hutchinson G. J., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Craft J. E., DeSanna E. T., Malawista S. E. Treatment of the early manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):22–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Hutchinson G. J., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Craft J. E., DeSanna E. T., Malawista S. E. Treatment of the early manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):22–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



