Abstract
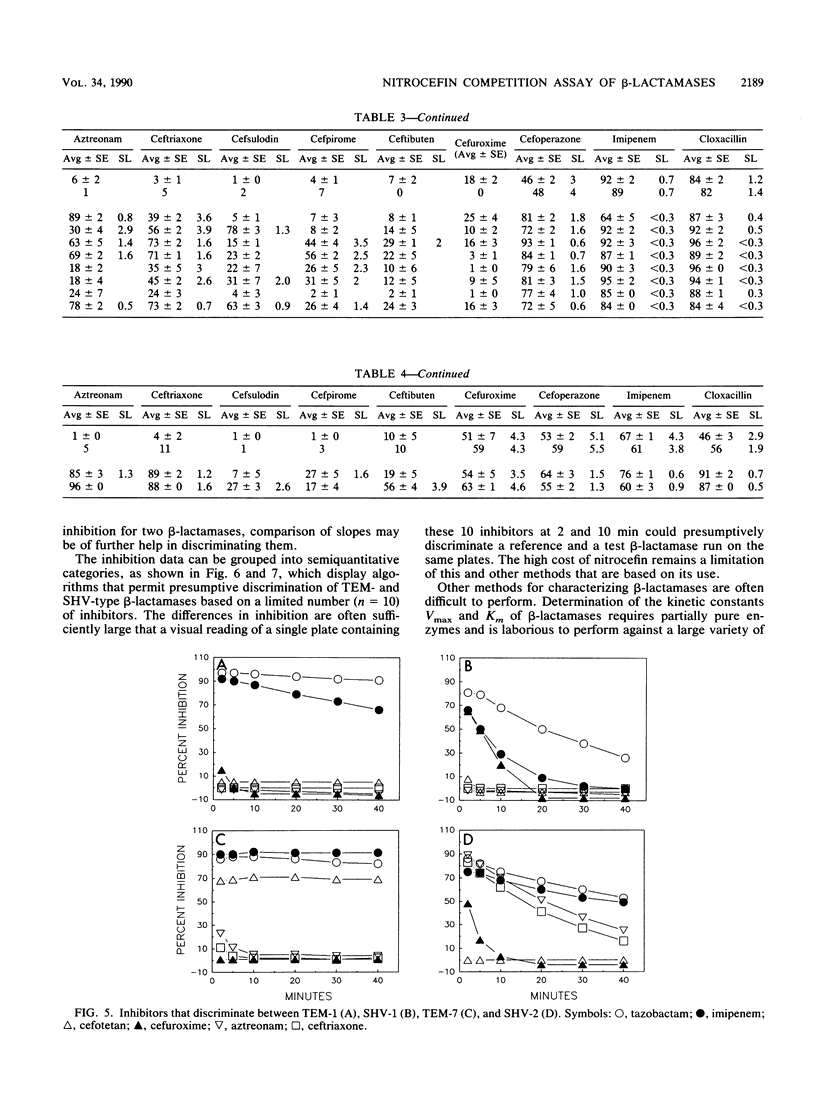
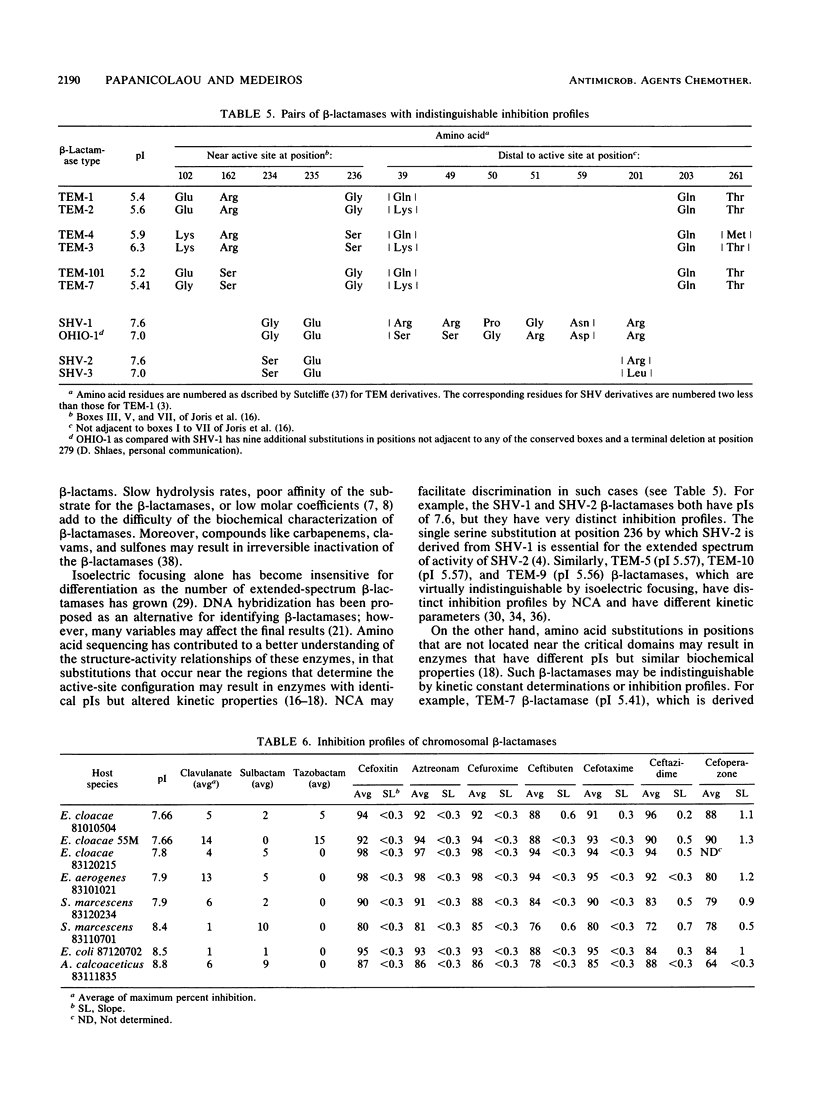
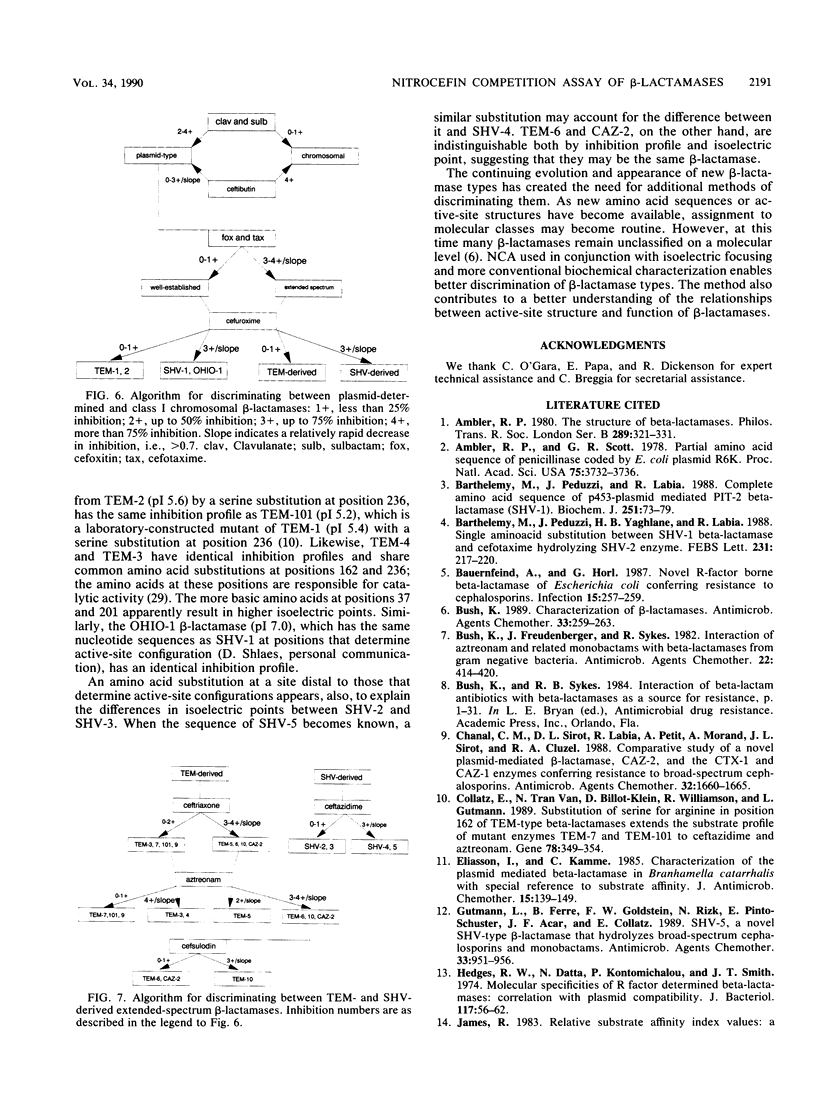
We describe a nitrocefin competition assay for determining inhibition profiles as a useful adjunct to existing biochemical methods for the discrimination of beta-lactamases. The hydrolysis rate of nitrocefin was measured with a plate photometer as the change in A480 over 45 min in the presence of 17 inhibitors. Fourteen well-established beta-lactamases and 13 extended-spectrum beta-lactamases were tested. Correlations with data from isoelectric focusing and amino acid sequencing suggested that the inhibition profile reflects alterations in the active-site configuration of beta-lactamases. The method was especially useful in measuring the relative affinities of beta-lactamases against poorly hydrolyzed substrates and in screening large numbers of isolates for the detection of new beta-lactamase types.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Scott G. K. Partial amino acid sequence of penicillinase coded by Escherichia coli plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Peduzzi J., Labia R. Complete amino acid sequence of p453-plasmid-mediated PIT-2 beta-lactamase (SHV-1). Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):73–79. doi: 10.1042/bj2510073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Péduzzi J., Ben Yaghlane H., Labia R. Single amino acid substitution between SHV-1 beta-lactamase and cefotaxime-hydrolyzing SHV-2 enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanal C. M., Sirot D. L., Labia R., Petit A., Morand A., Sirot J. L., Cluzel R. A. Comparative study of a novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase, CAZ-2, and the CTX-1 and CAZ-1 enzymes conferring resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1660–1665. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collatz E., Tran Van Nhieu G., Billot-Klein D., Williamson R., Gutmann L. Substitution of serine for arginine in position 162 of TEM-type beta-lactamases extends the substrate profile of mutant enzymes, TEM-7 and TEM-101, to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson I., Kamme C. Characterization of the plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in Branhamella catarrhalis, with special reference to substrate affinity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Feb;15(2):139–149. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Ferré B., Goldstein F. W., Rizk N., Pinto-Schuster E., Acar J. F., Collatz E. SHV-5, a novel SHV-type beta-lactamase that hydrolyzes broad-spectrum cephalosporins and monobactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N., Kontomichalou P., Smith J. T. Molecular specificities of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.56-62.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ghuysen J. M., Dive G., Renard A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Kelly J. A., Boyington J. C., Moews P. C. The active-site-serine penicillin-recognizing enzymes as members of the Streptomyces R61 DD-peptidase family. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2500313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Guionie M., Barthélémy M. Properties of three carbenicillin-hydrolysing beta-lactamases (CARB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of a new enzyme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Morand A., Tiwari K., Sirot J., Sirot D., Petit A. Interactions of new plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases with third-generation cephalosporins. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):885–891. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R. C., Medeiros A. A., Jacoby G. A. Molecular cloning and DNA homology of plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A. Beta-lactamases. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jan;40(1):18–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Cohenford M., Jacoby G. A. Five novel plasmid-determined beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):715–719. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas M. H., Jarlier V., Honore N., Philippon A., Cole S. T. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding SHV-3 beta-lactamase responsible for transferable cefotaxime resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Dec;33(12):2096–2100. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.12.2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul G. C., Gerbaud G., Bure A., Philippon A. M., Pangon B., Courvalin P. TEM-4, a new plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase that hydrolyzes broad-spectrum cephalosporins in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1958–1963. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Labia R., Jacoby G. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1131–1136. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péduzzi J., Barthélémy M., Tiwari K., Mattioni D., Labia R. Structural features related to hydrolytic activity against ceftazidime of plasmid-mediated SHV-type CAZ-5 beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Dec;33(12):2160–2163. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.12.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Miyashiro D., Sahm D., Flamm R., Bush K. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-10) conferring selective resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Medeiros A. A., Kron M. A., Currie-McCumber C., Papa E., Vartian C. V. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae from Ohio. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):220–224. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot J., Labia R., Thabaut A. Klebsiella pneumoniae strains more resistant to ceftazidime than to other third-generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Oct;20(4):611–612. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.4.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Wheat P. F., Winstanley T. G., Cox D. M., Plested S. J. Novel beta-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring unusual resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):919–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecoli C., Prevost F. E., Ververis J. J., Medeiros A. A., O'Leary G. P., Jr Comparison of polyacrylamide and agarose gel thin-layer isoelectric focusing for the characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):186–189. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


