Abstract
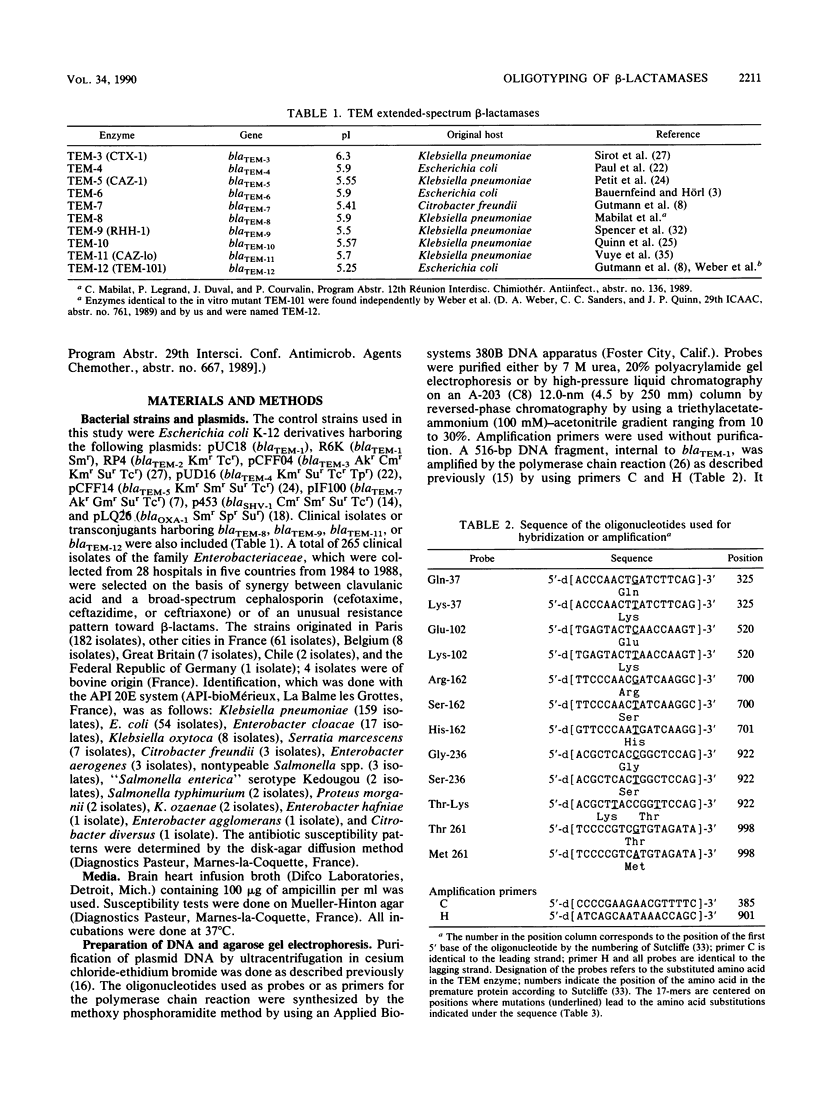
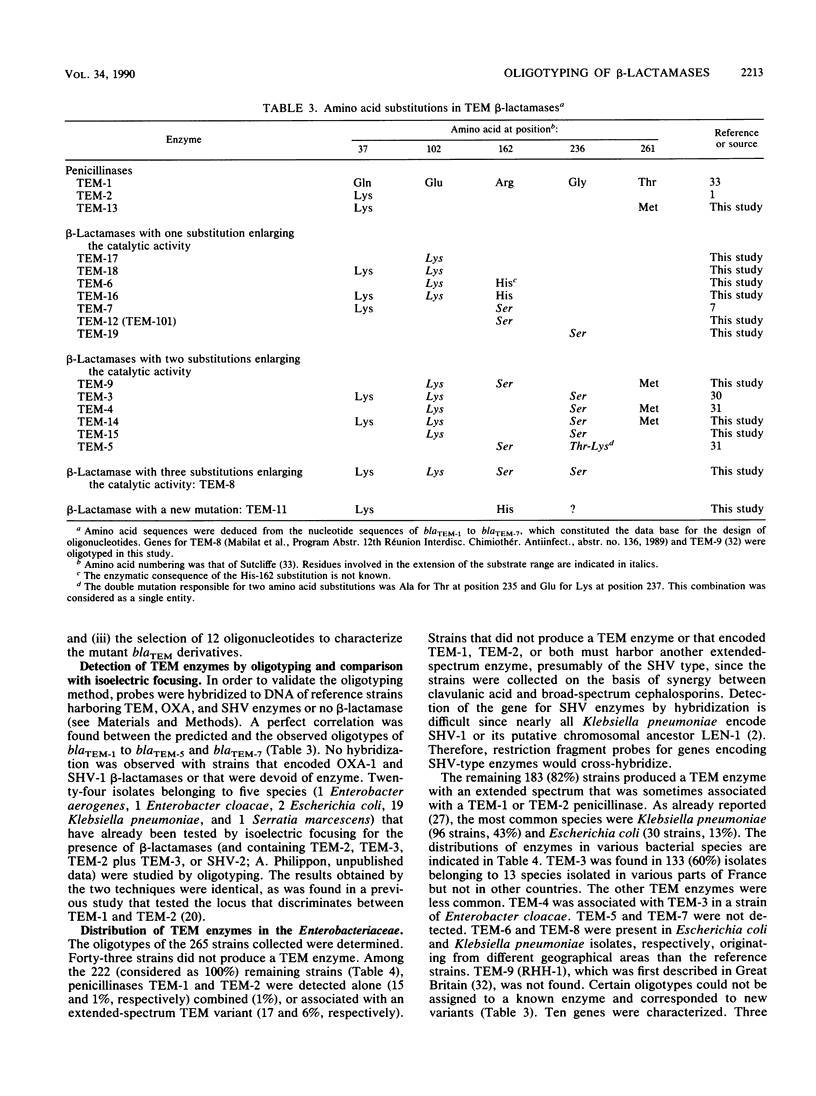
Based on the DNA sequences of blaTEM-1 and blaTEM-2, which encode parental penicillinases TEM-1 and TEM-2, respectively, and blaTEM-3, blaTEM-4, blaTEM-5, blaTEM-6, and blaTEM-7, which encode extended-spectrum beta-lactamases, we designed heptadecanucleotides to discriminate point mutations in five loci. Determination of the hybridization profiles by colony hybridization with this selection of probes, termed "oligotyping," allowed characterization of the TEM variants present in 265 clinical isolates of the family Enterobacteriaceae that exhibit synergism between a penicillinase inhibitor and broad-spectrum cephaslosporins. Among the 222 strains harboring TEM enzymes, Klebsiella pneumoniae (48%) and Escherichia coli (21%) were predominant, and TEM-3 was the most common enzyme (60%). Penicillinases TEM-1 and TEM-2 were detected alone (15 and 1%, respectively), combined (1%), or associated with another TEM beta-lactamase (17 and 6%, respectively). Fourteen variants, including seven new enzymes, were detected. One, TEM-13, was a new penicillinase with the same isoelectric point and substrate range as TEM-2 but differed by a single amino acid substitution, whereas the others, TEM-14 to TEM-19, were extended-spectrum beta-lactamases that consisted of novel combinations of known amino acid substitutions. Different TEM variants were found to coexist within the same cells. A patient could harbor two or three different strains that encoded the same enzyme or two indistinguishable isolates that produced distinct TEM beta-lactamases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Scott G. K. Partial amino acid sequence of penicillinase coded by Escherichia coli plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa Y., Ohta M., Kido N., Fujii Y., Komatsu T., Kato N. Close evolutionary relationship between the chromosomally encoded beta-lactamase gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the TEM beta-lactamase gene mediated by R plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Buisson C., Legrand P., Philippon A., Montravers F., Ansquer M., Duval J. Transferable enzymatic resistance to third-generation cephalosporins during nosocomial outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):302–306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90891-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buré A., Legrand P., Arlet G., Jarlier V., Paul G., Philippon A. Dissemination in five French hospitals of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K25 harbouring a new transferable enzymatic resistance to third generation cephalosporins and aztreonam. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):780–782. doi: 10.1007/BF01975048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. T., Clowes R. C. Variations between the nucleotide sequences of Tn1, Tn2, and Tn3 and expression of beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):913–916. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.913-916.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collatz E., Tran Van Nhieu G., Billot-Klein D., Williamson R., Gutmann L. Substitution of serine for arginine in position 162 of TEM-type beta-lactamases extends the substrate profile of mutant enzymes, TEM-7 and TEM-101, to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F., Tran Van Nhieu G., Lu T., Carlet J., Collatz E., Williamson R. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-7) involved in resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):860–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Shah P., Krcmery V., Antal M., Mitsuhashi S. Transferable resistance to cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole and cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01641355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Le Goffic F., Andrillon J. Etude cinétique de deux beta lactamases responsables d'un møeme phénotype. Biochimie. 1974;56(8):1025–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Goussard S., Sougakoff W., Spencer R. C., Courvalin P. Direct sequencing of the amplified structural gene and promoter for the extended-broad-spectrum beta-lactamase TEM-9 (RHH-1) of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Plasmid. 1990 Jan;23(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A. Beta-lactamases. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jan;40(1):18–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Bissonnette L., Roy P. H. Precise insertion of antibiotic resistance determinants into Tn21-like transposons: nucleotide sequence of the OXA-1 beta-lactamase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7378–7382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Paul G. C., Philippon A. M., Roy P. H. Oligonucleotide probes (TEM-1, OXA-1) versus isoelectric focusing in beta-lactamase characterization of 114 resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):397–399. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Rossi J. J., Bazin R., Roy P. H. Oligonucleotide probes for the detection of TEM-1 and TEM-2 beta-lactamase genes and their transposons. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Mar;33(3):205–211. doi: 10.1139/m87-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul G. C., Gerbaud G., Bure A., Philippon A. M., Pangon B., Courvalin P. TEM-4, a new plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase that hydrolyzes broad-spectrum cephalosporins in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1958–1963. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul G., Barthélémy M., Philippon A., Peduzzi J., Gilly L., Labia R., Névot P. Immunological comparison of constitutive beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria by neutralization in zymogram gels: properties of anti-TEM-1 and anti-TEM-2 sera. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;139(4):435–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Gerbaud G., Sirot D., Courvalin P., Sirot J. Molecular epidemiology of TEM-3 (CTX-1) beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):219–224. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Sirot D. L., Chanal C. M., Sirot J. L., Labia R., Gerbaud G., Cluzel R. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae more resistant to ceftazidime than to other broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):626–630. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Miyashiro D., Sahm D., Flamm R., Bush K. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-10) conferring selective resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot J., Chanal C., Petit A., Sirot D., Labia R., Gerbaud G. Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae producing novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases markedly active against third-generation cephalosporins: epidemiologic studies. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):850–859. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Petit A., Goussard S., Sirot D., Bure A., Courvalin P. Characterization of the plasmid genes blaT-4 and blaT-5 which encode the broad-spectrum beta-lactamases TEM-4 and TEM-5 in enterobacteriaceae. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Wheat P. F., Winstanley T. G., Cox D. M., Plested S. J. Novel beta-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring unusual resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):919–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuye A., Verschraegen G., Claeys G. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli resistant to ceftazidime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):757–761. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


