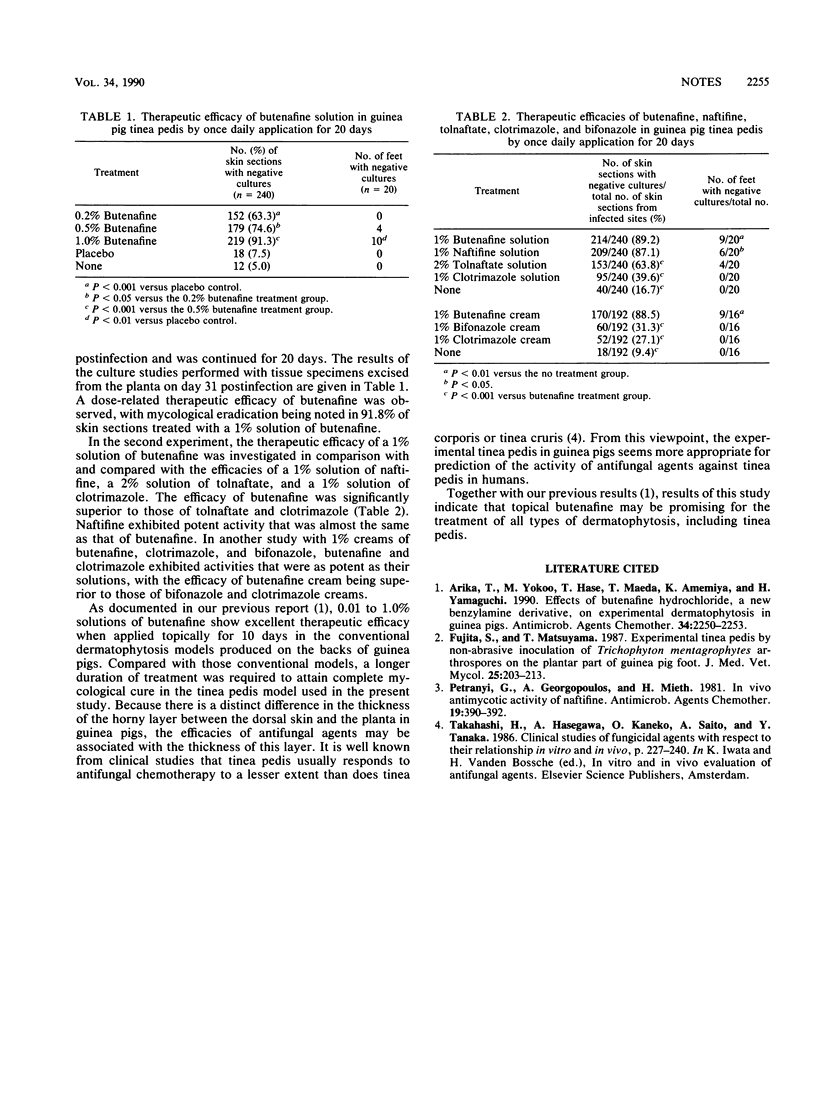
Abstract
Butenafine is a new antifungal benzylamine. The efficacy of butenafine was investigated in an experimental tinea pedis model in guinea pigs, which is pathologically similar to natural infections in humans. Butenafine (0.1 ml) in 0.2 to 1.0% solutions was applied to the site of infection. Treatment was started on day 10 postinfection and was continued for 20 days. Butenafine applied once daily exhibited excellent dose-related therapeutic efficacy. The efficacy of butenafine was significantly superior to those tolnaftate, clotrimazole, and bifonazole.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arika T., Yokoo M., Hase T., Maeda T., Amemiya K., Yamaguchi H. Effects of butenafine hydrochloride, a new benzylamine derivative, on experimental dermatophytosis in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2250–2253. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S., Matsuyama T. Experimental tinea pedis induced by non-abrasive inoculation of Trichophyton mentagrophytes arthrospores on the plantar part of a guinea pig foot. J Med Vet Mycol. 1987 Aug;25(4):203–213. doi: 10.1080/02681218780000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi G., Georgopoulos A., Mieth H. In vivo antimycotic activity of naftifine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):390–392. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


