Abstract
Aims: To investigate the natural history and incidence of autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT) in paediatric patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Methods: Since 1990, annual screening for thyroid disease has been performed in children and adolescents with T1D. Antibodies against thyroperoxidase (anti-TPO) and thyroglobulin (anti-TG) as well as TSH were measured in 659 patients (54.3% boys). In 126 patients, anti-TPO and anti-TG levels were followed at yearly intervals from onset up to five years of T1D. Anti-TPO above 30 U/ml and anti-TG above 20 U/ml were considered positive, values above 100 U/ml as significantly raised and indicative of AIT. L-thyroxine treatment was started if TSH was higher than 4.5 µU/ml and/or thyroid gland enlargement on thyroid ultrasound was present.
Results: At initial screening, 15.4% of patients had raised anti-TPO and 14.4% anti-TG. Girls had more frequently raised antibodies than boys. Sixty two patients (9.4%, 61% girls) required treatment with L-thyroxine. The cumulative incidence (SE) of AIT after 10 years of diabetes was 0.14 (0.02), being significantly higher in females (0.18 (0.03)), particularly after the age of 12 years. At T1D onset, positive anti-TPO and anti-TG were present in 21 of 126 patients (16.7%), each. All patients with significantly increased values of anti-TPO (n = 17, 148–5340 U/ml) and anti-TG (n = 11, 140–2000 U/ml) at T1D onset remained positive during the following five years.
Conclusions: For early detection of autoimmune thyroiditis in children with T1D, measurement of anti-TPO and TSH at T1D onset and in yearly intervals after the age of 12 years is recommended.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (105.6 KB).
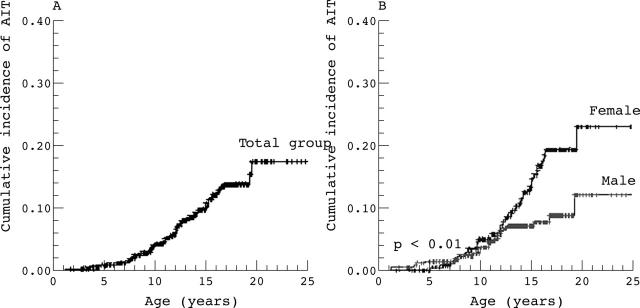
Figure 1.
Cumulative incidence (probability) of autoimmune thyroiditis according to the age of 659 children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: (A) in the total group, (B) stratified to gender of patients.
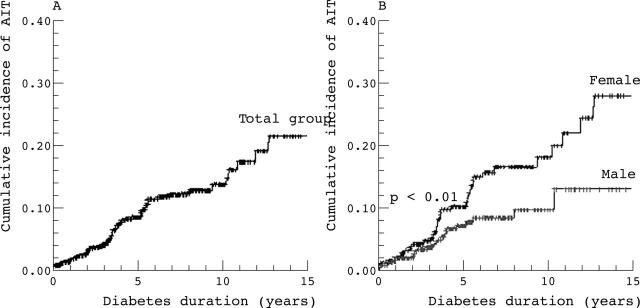
Figure 2.
Cumulative incidence (probability) of autoimmune thyroiditis according to the duration of type 1 diabetes in 659 children and adolescents: (A) in the total group, (B) stratified to gender of patients.
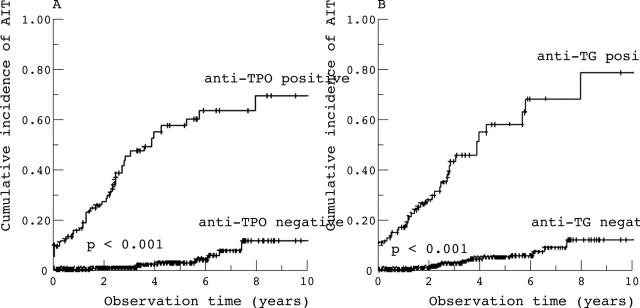
Figure 3.
Cumulative incidence (probability) of autoimmune thyroiditis in 637 patients with type 1 diabetes according to the presence of antibodies against (A) thyroperoxidase (anti-TPO) and (B) thyroglobulin (anti-TG).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acerini C. L., Ahmed M. L., Ross K. M., Sullivan P. B., Bird G., Dunger D. B. Coeliac disease in children and adolescents with IDDM: clinical characteristics and response to gluten-free diet. Diabet Med. 1998 Jan;15(1):38–44. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199801)15:1<38::AID-DIA520>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badenhoop K., Walfish P. G., Rau H., Fischer S., Nicolay A., Bogner U., Schleusener H., Usadel K. H. Susceptibility and resistance alleles of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DQA1 and HLA DQB1 are shared in endocrine autoimmune disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Jul;80(7):2112–2117. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.7.7608264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. P., Garg S. K., Cockerham R. S., Wilcox W. D., Walravens P. A. Thyroid hormone replacement and growth of children with subclinical hypothyroidism and diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990 May;7(4):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin C. C., Shanahan F. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and coeliac disease. Lancet. 1997 Apr 12;349(9058):1096–1097. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)09153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan C. M., Daniels G. H. Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 1996 Jul 11;335(2):99–107. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199607113350206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman Janice S., Steenkiste Ann R., Burke James P., Songini Marco. Type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis: together at last. Diabetes Care. 2003 Nov;26(11):3192–3193. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.11.3192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzese A., Buono P., Mascolo M., Leo A. L., Valerio G. Thyroid autoimmunity starting during the course of type 1 diabetes denotes a subgroup of children with more severe diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000 Aug;23(8):1201–1202. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.8.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen D., Bennedbaek F. N., Hansen L. K., Hoier-Madsen M., Jacobsen B. B., Hegedüs L. Thyroid function, morphology and autoimmunity in young patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999 Jun;140(6):512–518. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1400512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holl R. W., Bohm B., Loos U., Grabert M., Heinze E., Homoki J. Thyroid autoimmunity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Effect of age, gender and HLA type. Horm Res. 1999;52(3):113–118. doi: 10.1159/000023446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlston R. S., Tomlinson I. P., Ford D., Seal S., Marossy A. M., Ferguson A., Holmes G. K., Hosie K. B., Howdle P. D., Jewell D. P. Linkage analysis of candidate regions for coeliac disease genes. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Aug;6(8):1335–1339. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.8.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz M., Liesenkötter K. P., Stach B., Willgerodt H., Stäblein W., Singendonk W., Jäger-Roman E., Litzenbörger H., Ehnert B., Grüters A. The prevalence of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies and autoimmune thyroiditis in children and adolescents in an iodine replete area. Eur J Endocrinol. 2003 Mar;148(3):301–307. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1480301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karvonen M., Pitkäniemi M., Pitkäniemi J., Kohtamäki K., Tajima N., Tuomilehto J. Sex difference in the incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: an analysis of the recent epidemiological data. World Health Organization DIAMOND Project Group. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1997 Dec;13(4):275–291. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0895(199712)13:4<275::aid-dmr197>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordonouri Olga, Klinghammer Albrecht, Lang Egbert B., Grüters-Kieslich Annette, Grabert Matthias, Holl Reinhard W. Thyroid autoimmunity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a multicenter survey. Diabetes Care. 2002 Aug;25(8):1346–1350. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.8.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. D., Elliott R. B. Early environmental events as a cause of IDDM. Evidence and implications. Diabetes. 1994 Jul;43(7):843–850. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.7.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesenkötter K. P., Kiebler A., Stach B., Willgerodt H., Grüters A. Small thyroid volumes and normal iodine excretion in Berlin schoolchildren indicate full normalization of iodine supply. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1997;105 (Suppl 4):46–50. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorini R., d'Annunzio G., Vitali L., Scaramuzza A. IDDM and autoimmune thyroid disease in the pediatric age group. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Mar;9 (Suppl 1):89–94. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1996.9.s1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcocci C., Vitti P., Cetani F., Catalano F., Concetti R., Pinchera A. Thyroid ultrasonography helps to identify patients with diffuse lymphocytic thyroiditis who are prone to develop hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jan;72(1):209–213. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCanlies E., O'Leary L. A., Foley T. P., Kramer M. K., Burke J. P., Libman A., Swan J. S., Steenkiste A. R., Mccarthy B. J., Trucco M. Hashimoto's thyroiditis and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: differences among individuals with and without abnormal thyroid function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 May;83(5):1548–1551. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.5.4769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn A., Di Michele S., Di Luzio R., Tumini S., Chiarelli F. The effect of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic control in children and adolescents with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2002 Jan;19(1):70–73. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. C. Natural course of 'subclinical' hypothyroidism in childhood and adolescence. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996 Mar;150(3):293–297. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1996.02170280063012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naluai A. T., Nilsson S., Samuelsson L., Gudjónsdóttir A. H., Ascher H., Ek J., Hallberg B., Kristiansson B., Martinsson T., Nerman O. The CTLA4/CD28 gene region on chromosome 2q33 confers susceptibility to celiac disease in a way possibly distinct from that of type 1 diabetes and other chronic inflammatory disorders. Tissue Antigens. 2000 Oct;56(4):350–355. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2000.560407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocecco M., Ventura A. Coeliac disease and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a causal association? Acta Paediatr. 1995 Dec;84(12):1432–1433. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radetti G., Paganini C., Gentili L., Bernasconi S., Betterle C., Borkenstein M., Cvijovic K., Kadrnka-Lovrencic M., Krzisnik C., Battelino T. Frequency of Hashimoto's thyroiditis in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 1995 Jun;32(2):121–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00569570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumník Z., Kolousková S., Cinek O., Kotalová R., Vavrinec J., Snajderová M. HLA-DQA1*05-DQB1*0201 positivity predisposes to coeliac disease in Czech diabetic children. Acta Paediatr. 2000 Dec;89(12):1426–1430. doi: 10.1080/080352500456589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunbridge W. M., Brewis M., French J. M., Appleton D., Bird T., Clark F., Evered D. C., Evans J. G., Hall R., Smith P. Natural history of autoimmune thyroiditis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jan 24;282(6260):258–262. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6260.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda Hironori, Howson Joanna M. M., Esposito Laura, Heward Joanne, Snook Hywel, Chamberlain Giselle, Rainbow Daniel B., Hunter Kara M. D., Smith Annabel N., Di Genova Gianfranco. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature. 2003 Apr 30;423(6939):506–511. doi: 10.1038/nature01621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerio G., Maiuri L., Troncone R., Buono P., Lombardi F., Palmieri R., Franzese A. Severe clinical onset of diabetes and increased prevalence of other autoimmune diseases in children with coeliac disease diagnosed before diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2002 Oct 19;45(12):1719–1722. doi: 10.1007/s00125-002-0923-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderpump Mark P. J., Tunbridge W. Michael G. Epidemiology and prevention of clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism. Thyroid. 2002 Oct;12(10):839–847. doi: 10.1089/105072502761016458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]