Abstract
Background: Gaviscon Infant (GI) has been recommended for gastro-oesophageal reflux (GOR) in infants. Its efficacy has not been examined with a physiologically appropriate denominator to define the degree of GOR.
Aim: To investigate the influence of Gaviscon Infant on GOR in infants using combined pH and intraluminal impedance measurement.
Methods: Twenty infants (mean age 163.5 days, range 34–319 days) exclusively bottle fed, with symptoms clinically suggestive of GOR, underwent 24 hour studies of intra-oesophageal 6 channel impedance and dual channel pH monitoring, during which six random administrations (3+3) of Gaviscon Infant (625 mg in 225 ml milk) or placebo (mannitol and Solvito N, 625 mg in 225 ml milk) were given in a double blind fashion. Impedance/pH reflux data were recorded and analysed blind by one observer.
Results: The median number of reflux events/hour (1.58 v 1.68), acid reflux events/hour (0.26 v 0.43), minimum distal or proximal pH, total acid clearance time per hour (time with pH below pH 4), and total reflux duration per hour were not significantly different after GI than after placebo. Reflux height was marginally lower after GI (median 66.6% v 77.3% oesophageal length) compared with placebo.
Conclusions: Results showed a marginal but significant difference between Gaviscon Infant and placebo in average reflux height, and raises questions regarding any perceived clinical benefit of its use.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (150.6 KB).
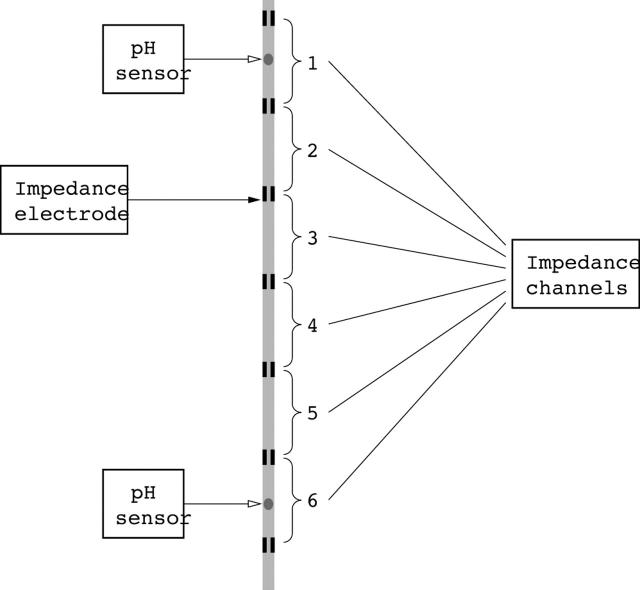
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the impedance catheter with seven impedance electrodes set at 1.5 cm intervals and comprising six measuring segments (impedance channels). Distal and proximal pH electrodes were also incorporated to detect the pH of the refluxate at approximately 2 cm above the lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) and in the upper oesophagus.
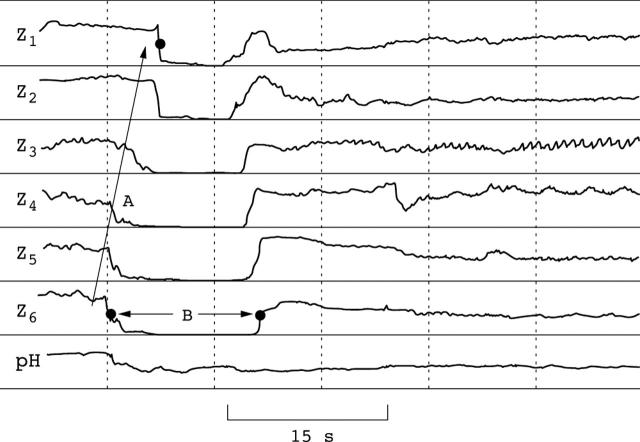
Figure 2.
Impedance pattern typically observed during a reflux episode. In this example only the distal pH channel is shown which is located approximately 1.5 cm above the LOS. The retrograde oesophageal flow is indicated by arrow A. In this example the reflux reaches the proximal (highest, Z1) channel. The reflux duration is indicated by arrow B. The pH of the reflux can be derived from the pH channel and the acid clearance is the time taken for the pH channel wave to reach pH 4.
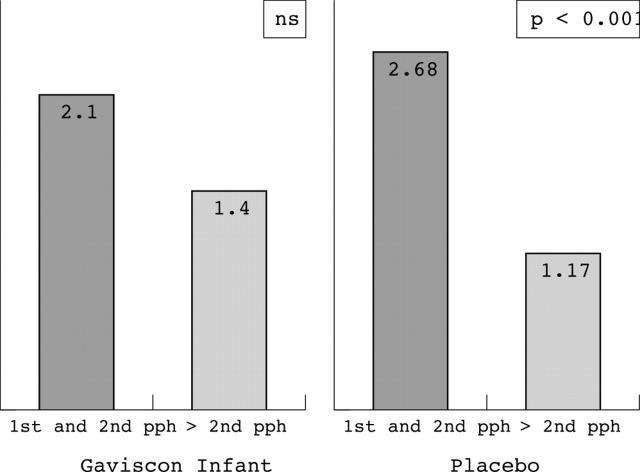
Figure 3.
After treatment with Gaviscon Infant, while the number of reflux events per hour was lower from 2 hours after feeding, compared with the first two hours after feeding, the difference in the number of reflux episodes per hour was not statistically significant. After treatment with placebo, the number of reflux events per hour was markedly lower from 2 hours after feeding, compared with the first two hours after feeding, and the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.001). pph, postprandial hour.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A standardized protocol for the methodology of esophageal pH monitoring and interpretation of the data for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux. Working Group of the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992 May;14(4):467–471. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199205000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender G. N., Makuch R. S. Double-contrast barium examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract with nonendoscopic biopsy: findings in 100 patients. Radiology. 1997 Feb;202(2):355–359. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.2.9015056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. W. Silent gastro-oesophageal reflux: how much do we miss? Arch Dis Child. 1992 Nov;67(11):1325–1327. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.11.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buts J. P., Barudi C., Otte J. B. Double-blind controlled study on the efficacy of sodium alginate (Gaviscon) in reducing gastroesophageal reflux assessed by 24 h continuous pH monitoring in infants and children. Eur J Pediatr. 1987 Mar;146(2):156–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02343223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRE I. J. The natural history of the partial thoracic stomach (hiatus hernia) in children. Arch Dis Child. 1959 Aug;34:344–353. doi: 10.1136/adc.34.176.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Luyer B., Mougenot J. F., Mashako L., Chapoy P., Olives J. P., Morali A., Chevallier B., Ginies J. L., Dupont C., Dagorne M. Etude clinique multicentrique de l'alginate de sodium dans le traitement des régurgitations du nourrisson. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1992 Dec;39(10):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Daggy B. P., Brodie D. A., Jacoby H. I. Review article: alginate-raft formulations in the treatment of heartburn and acid reflux. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Jun;14(6):669–690. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd R. W., Wren J., Evans S., Lander M., Ong T. H. Gastroesophageal reflux in children. Clinical profile, course and outcome with active therapy in 126 cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1987 Feb;26(2):55–60. doi: 10.1177/000992288702600201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson M. Disorders of the oesophagus and stomach in infants. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997 Sep;11(3):547–571. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3528(97)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas Y., Belli D., Benhamou P., Cadranel S., Cezard J. P., Cucchiara S., Dupont C., Faure C., Gottrand F., Hassall E. A critical appraisal of current management practices for infant regurgitation--recommendations of a working party. Eur J Pediatr. 1997 May;156(5):343–357. doi: 10.1007/s004310050613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas Y., Goyvaerts H., Helven R., Sacre L. Gastroesophageal reflux, as measured by 24-hour pH monitoring, in 509 healthy infants screened for risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatrics. 1991 Oct;88(4):834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco N., Pope C. E., 2nd, Gannan R. M., Roberts P., Hill L. D. Measurement of esophageal reflux by scintigraphy. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Nov;29(11):977–982. doi: 10.1007/BF01311246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weldon A. P., Robinson M. J. Trial of gaviscon in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux of infancy. Aust Paediatr J. 1972 Oct;8(5):279–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1972.tb01837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl T. G., Silny J., Schenke S., Peschgens T., Heimann G., Skopnik H. Gastroesophageal reflux and respiratory phenomena in infants: status of the intraluminal impedance technique. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999 Apr;28(4):423–428. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199904000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl Tobias G., Moroder Christoph, Trachterna Morten, Thomson Mike, Silny Jiri, Heimann Gerhard, Skopnik Heino. Esophageal pH monitoring and impedance measurement: a comparison of two diagnostic tests for gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002 May;34(5):519–523. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200205000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ajuriaguerra M., Radvanyi-Bouvet M. F., Huon C., Moriette G. Gastroesophageal reflux and apnea in prematurely born infants during wakefulness and sleep. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Oct;145(10):1132–1136. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160100064024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]