Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (70.7 KB).
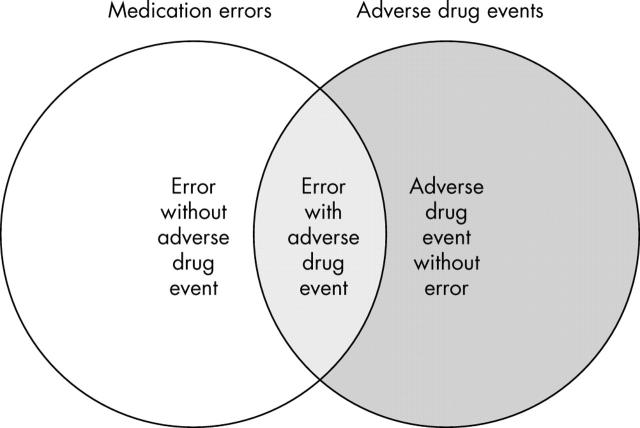
Figure 1.
Diagram illustrating the distinction between adverse drug events and medication errors.
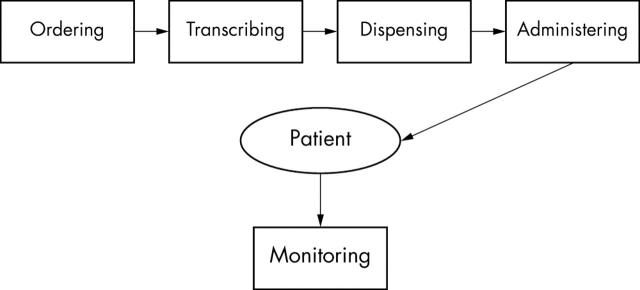
Figure 2.
Series of steps from ordering to patient receiving medication with a paper based ordering system.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnhold R. G., Adebonojo F. O., Callas E. R., Callas J., Carte E., Stein R. C. Patients and prescriptions. Comprehension and compliance with medical instructions in a suburban pediatric practice. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1970 Nov;9(11):648–651. doi: 10.1177/000992287000901107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Cullen D. J., Laird N., Petersen L. A., Small S. D., Servi D., Laffel G., Sweitzer B. J., Shea B. F., Hallisey R. Incidence of adverse drug events and potential adverse drug events. Implications for prevention. ADE Prevention Study Group. JAMA. 1995 Jul 5;274(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Leape L. L., Cullen D. J., Laird N., Petersen L. A., Teich J. M., Burdick E., Hickey M., Kleefield S., Shea B. Effect of computerized physician order entry and a team intervention on prevention of serious medication errors. JAMA. 1998 Oct 21;280(15):1311–1316. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.15.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendon Robert J., DesRoches Catherine M., Brodie Mollyann, Benson John M., Rosen Allison B., Schneider Eric, Altman Drew E., Zapert Kinga, Herrmann Melissa J., Steffenson Annie E. Views of practicing physicians and the public on medical errors. N Engl J Med. 2002 Dec 12;347(24):1933–1940. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa022151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordun L. A., Butt W. Drug errors in intensive care. J Paediatr Child Health. 1992 Aug;28(4):309–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1992.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coté C. J., Karl H. W., Notterman D. A., Weinberg J. A., McCloskey C. Adverse sedation events in pediatrics: analysis of medications used for sedation. Pediatrics. 2000 Oct;106(4):633–644. doi: 10.1542/peds.106.4.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coté C. J., Notterman D. A., Karl H. W., Weinberg J. A., McCloskey C. Adverse sedation events in pediatrics: a critical incident analysis of contributing factors. Pediatrics. 2000 Apr;105(4 Pt 1):805–814. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.4.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folli H. L., Poole R. L., Benitz W. E., Russo J. C. Medication error prevention by clinical pharmacists in two children's hospitals. Pediatrics. 1987 May;79(5):718–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortescue Elizabeth B., Kaushal Rainu, Landrigan Christopher P., McKenna Kathryn J., Clapp Margaret D., Federico Frank, Goldmann Donald A., Bates David W. Prioritizing strategies for preventing medication errors and adverse drug events in pediatric inpatients. Pediatrics. 2003 Apr;111(4 Pt 1):722–729. doi: 10.1542/peds.111.4.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heubi J. E., Barbacci M. B., Zimmerman H. J. Therapeutic misadventures with acetaminophen: hepatoxicity after multiple doses in children. J Pediatr. 1998 Jan;132(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth Mark T., Fichtl Richard E., Behta Maryam, Raisch Dennis W., Mendez-Rico Elena, Adams Alexa, Greifer Melanie, Bostwick Susan, Greenwald Bruce M. Incidence and impact of adverse drug events in pediatric inpatients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003 Jan;157(1):60–65. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. B., Butta J. K., Donohue P. K., Glenn D. J., Holtzman N. A. Discharging patients with prescriptions instead of medications: sequelae in a teaching hospital. Pediatrics. 1996 Apr;97(4):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal R., Bates D. W., Landrigan C., McKenna K. J., Clapp M. D., Federico F., Goldmann D. A. Medication errors and adverse drug events in pediatric inpatients. JAMA. 2001 Apr 25;285(16):2114–2120. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.16.2114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. James, Paice Naomi, Rangrej Jagadish, Forestell Gregory J., Swartz Ron. The effect of computerized physician order entry on medication errors and adverse drug events in pediatric inpatients. Pediatrics. 2003 Sep;112(3 Pt 1):506–509. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.3.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren G., Barzilay Z., Greenwald M. Tenfold errors in administration of drug doses: a neglected iatrogenic disease in pediatrics. Pediatrics. 1986 Jun;77(6):848–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozer Eran, Scolnik Dennis, Keays Tara, Shi Kevin, Luk Tracy, Koren Gideon. Large errors in the dosing of medications for children. N Engl J Med. 2002 Apr 11;346(15):1175–1176. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200204113461518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozer Eran, Scolnik Dennis, Macpherson Alison, Keays Tara, Shi Kevin, Luk Tracy, Koren Gideon. Variables associated with medication errors in pediatric emergency medicine. Pediatrics. 2002 Oct;110(4):737–742. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leape L. L., Cullen D. J., Clapp M. D., Burdick E., Demonaco H. J., Erickson J. I., Bates D. W. Pharmacist participation on physician rounds and adverse drug events in the intensive care unit. JAMA. 1999 Jul 21;282(3):267–270. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann Christoph U., Conner Kim G., Cox Jeanne M. Preventing provider errors: online total parenteral nutrition calculator. Pediatrics. 2004 Apr;113(4):748–753. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. R., Rimsza M. E., Bay R. C. Parents can dose liquid medication accurately. Pediatrics. 1997 Sep;100(3 Pt 1):330–333. doi: 10.1542/peds.100.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel Philippe, Quenon Jean Luc, de Sarasqueta Anne Marie, Scemama Olivier. Comparison of three methods for estimating rates of adverse events and rates of preventable adverse events in acute care hospitals. BMJ. 2004 Jan 24;328(7433):199–199. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7433.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil A. C., Petersen L. A., Cook E. F., Bates D. W., Lee T. H., Brennan T. A. Physician reporting compared with medical-record review to identify adverse medical events. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Sep 1;119(5):370–376. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-5-199309010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. M., Baker D. W., Williams M. V., Nurss J. R. The test of functional health literacy in adults: a new instrument for measuring patients' literacy skills. J Gen Intern Med. 1995 Oct;10(10):537–541. doi: 10.1007/BF02640361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts Amy L., Barr Frederick E., Gregory David F., Wright Lorianne, Patel Neal R. Computerized physician order entry and medication errors in a pediatric critical care unit. Pediatrics. 2004 Jan;113(1 Pt 1):59–63. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor Monja L., Pastore Jennifer, Gerstle Justin T., Langer Jacob C. Incidence of medical error and adverse outcomes on a pediatric general surgery service. J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Sep;38(9):1361–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(03)00396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju T. N., Kecskes S., Thornton J. P., Perry M., Feldman S. Medication errors in neonatal and paediatric intensive-care units. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):374–376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reason J. Human error: models and management. BMJ. 2000 Mar 18;320(7237):768–770. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7237.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark Darin C. Bar codes and drug administration. Am J Nurs. 2004 Jan;104(1):63–66. doi: 10.1097/00000446-200401000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. M., Wallace J., Paton J. Y. Medication errors in a paediatric teaching hospital in the UK: five years operational experience. Arch Dis Child. 2000 Dec;83(6):492–497. doi: 10.1136/adc.83.6.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H. O., Brodowy B. A. Implementation and evaluation of an automated dispensing system. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1995 Apr 15;52(8):823–828. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/52.8.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor James A., Brownstein Dena, Christakis Dimitri A., Blackburn Susan, Strandjord Thomas P., Klein Eileen J., Shafii Jaleh. Use of incident reports by physicians and nurses to document medical errors in pediatric patients. Pediatrics. 2004 Sep;114(3):729–735. doi: 10.1542/peds.2003-1124-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincer M. J., Murray J. M., Yuill A., Allen A. C., Evans J. R., Stinson D. A. Drug errors and incidents in a neonatal intensive care unit. A quality assurance activity. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Jun;143(6):737–740. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150180119032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh Kathleen E., Miller Marlene R., Vinci Robert J., Bauchner Howard. Pediatric resident education about medical errors. Ambul Pediatr. 2004 Nov-Dec;4(6):514–517. doi: 10.1367/A04-009R1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]