Abstract
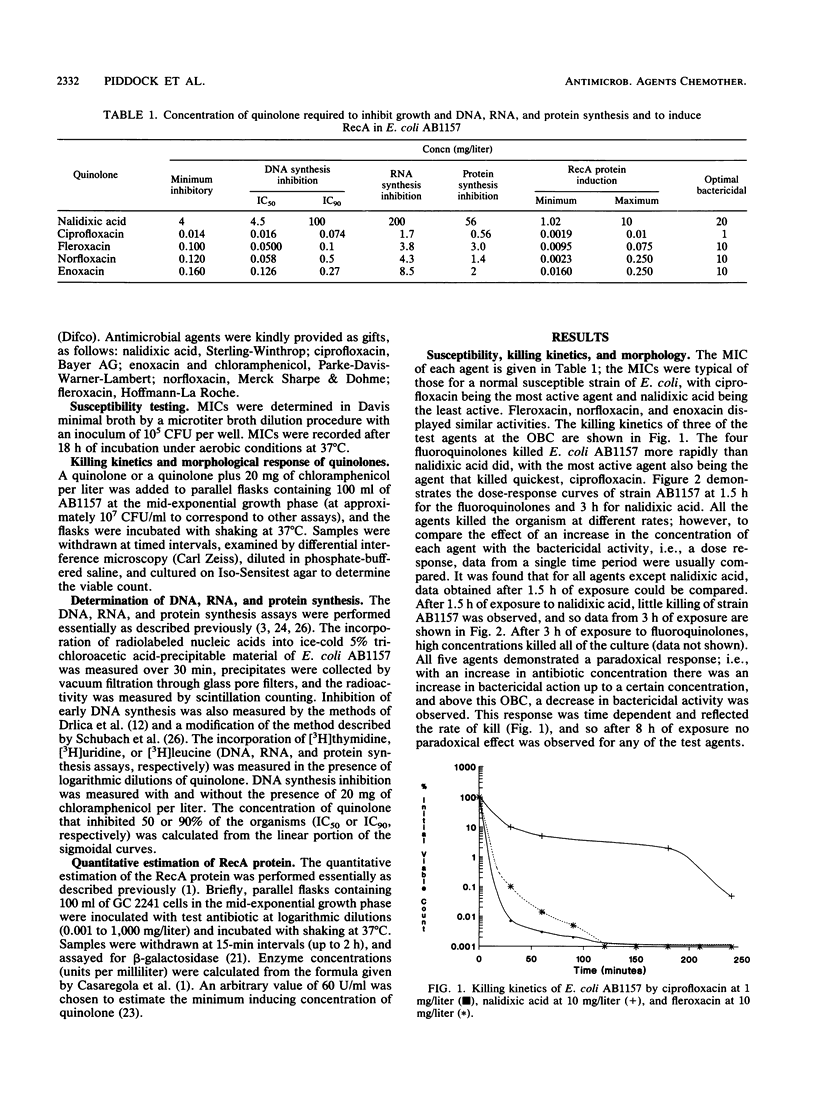
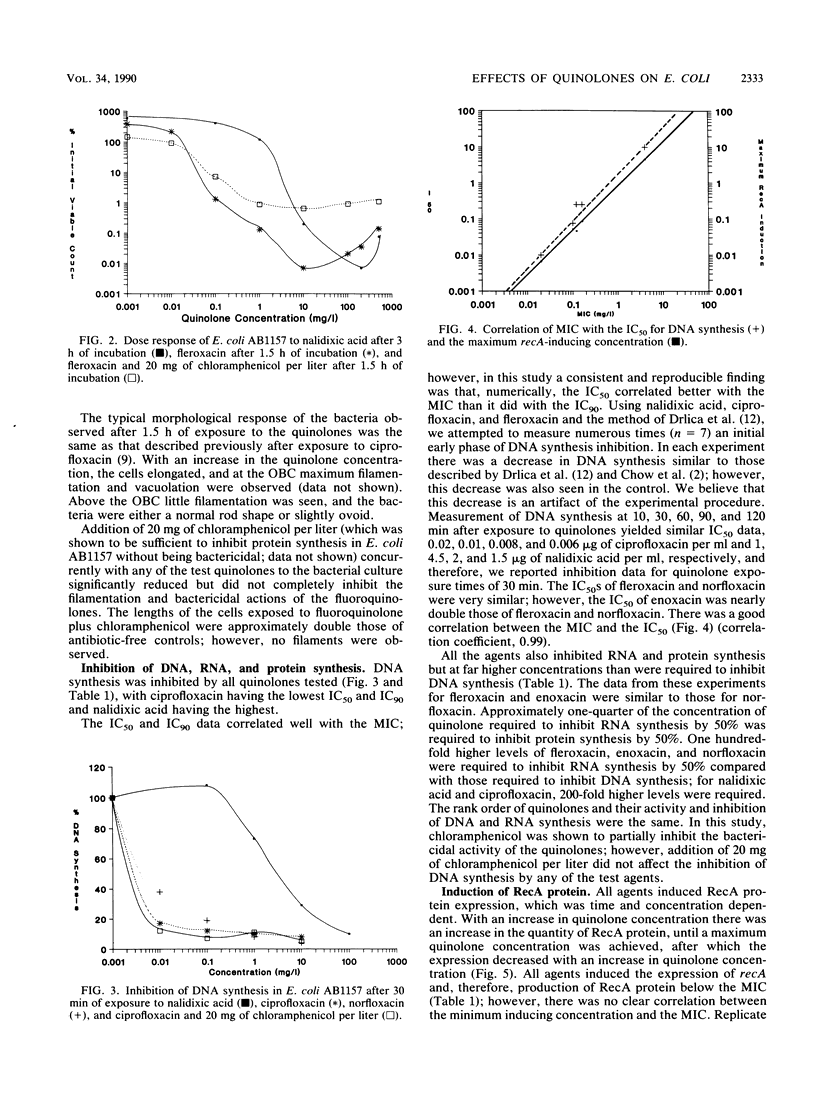
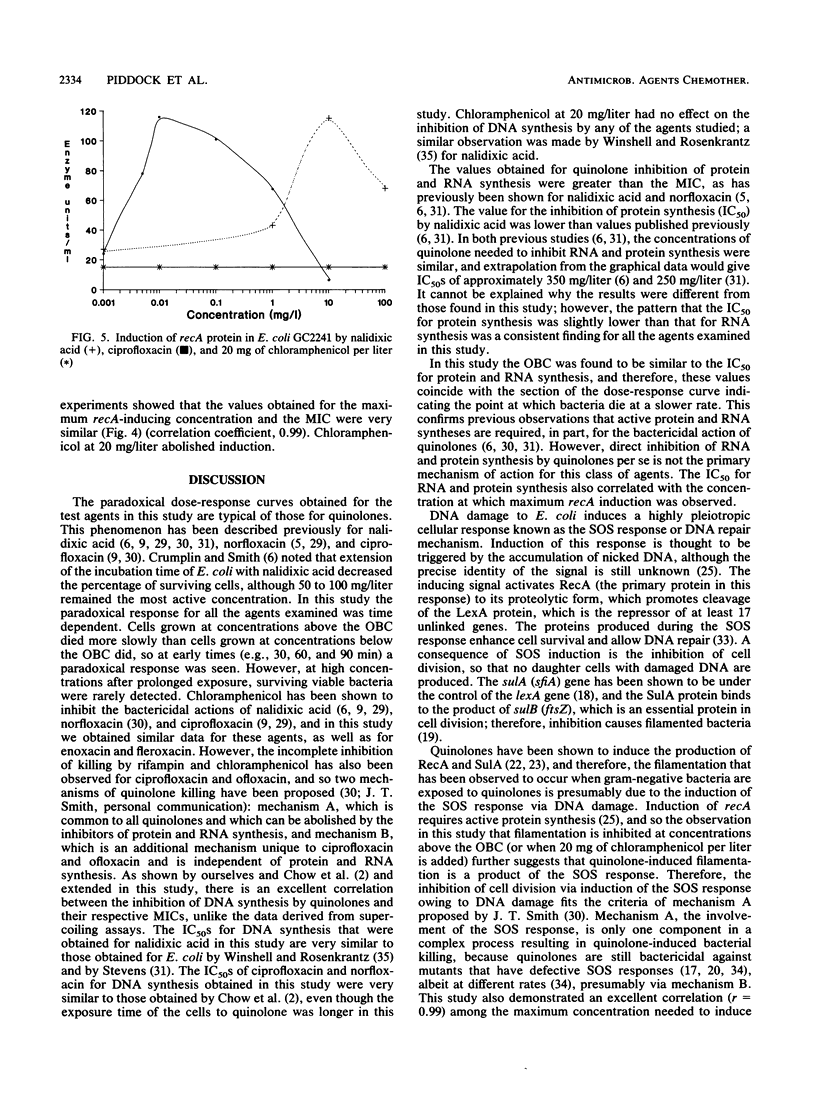
The effects of nalidixic acid and four fluoroquinolones on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in the presence and absence of 20 mg of chloramphenicol per liter were examined by comparing the killing kinetics, MIC, morphological response, and maximum concentration to induce recA in Escherichia coli. All agents demonstrated paradoxical killing kinetics, in that above an optimum concentration the rate of bactericidal action was slower. Filamentation of E. coli AB1157 was observed with all quinolones up to the optimum bactericidal concentration. Addition of chloramphenicol reduced the bactericidal activity, inhibited filamentation, and abolished recA induction, but it had no effect on DNA synthesis inhibition by any of the agents. Excellent correlation was obtained between the concentration required to inhibit DNA synthesis by 50%, the MIC, the maximum concentration to induce recA, and the optimum bactericidal concentration. Evidence from this study and previously published data suggest that the primary mechanism of action of quinolones is independent of the SOS response and does not require active protein synthesis; however, induction of recA and SOS responses is consequential and enhances cell death.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casaregola S., D'Ari R., Huisman O. Quantitative evaluation of recA gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):430–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00334135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. T., Dougherty T. J., Fraimow H. S., Bellin E. Y., Miller M. H. Association between early inhibition of DNA synthesis and the MICs and MBCs of carboxyquinolone antimicrobial agents for wild-type and mutant [gyrA nfxB(ompF) acrA] Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. The requirement for potassium for bacteriophage T4 protein and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtright J. B., Turowski D. A., Sonstein S. A. Alteration of bacterial DNA structure, gene expression, and plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance following exposure to enoxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21 (Suppl B):1–18. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Kenwright M., Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13 (Suppl B):9–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_b.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Smith J. T. Nalidixic acid and bacterial chromosome replication. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):643–645. doi: 10.1038/260643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Smith J. T. Nalidixic acid: an antibacterial paradox. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):251–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitz W. H., Cook T. M., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. 3. Conditions required for lethality. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.768-773.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver J. M., Wise R. Morphological and biochemical changes in Escherichia coli after exposure to ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):31–41. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagala J. M., Hanna L. D., Heifetz C. L., Hutt M. P., Mich T. F., Sanchez J. P., Solomon M. New structure-activity relationships of the quinolone antibacterials using the target enzyme. The development and application of a DNA gyrase assay. J Med Chem. 1986 Mar;29(3):394–404. doi: 10.1021/jm00153a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Engle E. C., Manes S. H. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: possibility of two levels of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6879–6883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. Model for regulation of Escherichia coli DNA repair functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Ng E. Y., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of action of and resistance to ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högberg T., Khanna I., Drake S. D., Mitscher L. A., Shen L. L. Structure-activity relationships among DNA gyrase inhibitors. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,2-dihydro-4, 4-dimethyl-1-oxo-2-naphthalenecarboxylic acids as 1-carba bioisosteres of oxolinic acid. J Med Chem. 1984 Mar;27(3):306–310. doi: 10.1021/jm00369a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Howard B. M., Ratcliffe N. T., Smith J. T. 4-quinolones and the SOS response. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):139–144. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguin E., Lutkenhaus J., D'Ari R. Reversibility of SOS-associated division inhibition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.733-738.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Rogers L. H., Hill W. E. Survival of recombination-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli during incubation with nalidixic acid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1195–1198. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1195-1198.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Culebras E., Moreno F., Baquero F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):631–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roozen K. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Curtiss R., 3rd Synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in plasmid-containing minicells of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):21–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.21-33.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Defais M. Signal of induction of recA protein in E. coli. Mutat Res. 1984 Feb;131(2):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Whitmer J. D., Davern C. I. Genetic control of DNA initiation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Mitscher L. A., Sharma P. N., O'Donnell T. J., Chu D. W., Cooper C. S., Rosen T., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: a cooperative drug--DNA binding model. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3886–3894. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T. The mode of action of 4-quinolones and possible mechanisms of resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):21–29. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P. J. Bactericidal effect against Escherichia coli of nalidixic acid and four structurally related compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):535–542. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters R. N., Piddock L. J., Wise R. The effect of mutations in the SOS response on the kinetics of quinolone killing. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Dec;24(6):863–873. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winshell E. B., Rosenkranz H. S. Nalidixic Acid and the Metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1168–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1168-1175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Furutani Y., Inoue S., Ohue T., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. New nalidixic acid resistance mutations related to deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


