Abstract
The effectiveness and safety of a short acting barbiturate, methohexital, was assessed for its use at the time of elective intubation in 18 newborn infants with severe respiratory or cardiac conditions. Evaluation included the speed of action and the degree of relaxation, sedation, and sleep in the first five minutes after administration. All newborn infants were intubated in a fully relaxed and somnolent state. In most infants recovery was completed within five minutes. A slight to moderate oxygen saturation drop was observed during the period of intubation, especially in patients with cyanotic heart disease. The side effects of the drug were twitching and a slight drop in blood pressure. In conclusion, methohexital seems to be a useful drug for short term anaesthesia in neonates, during which, short procedures like elective intubation can be safely performed. Keywords: methohexital; intubation; anaesthesia
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (91.2 KB).
Figure 1 .
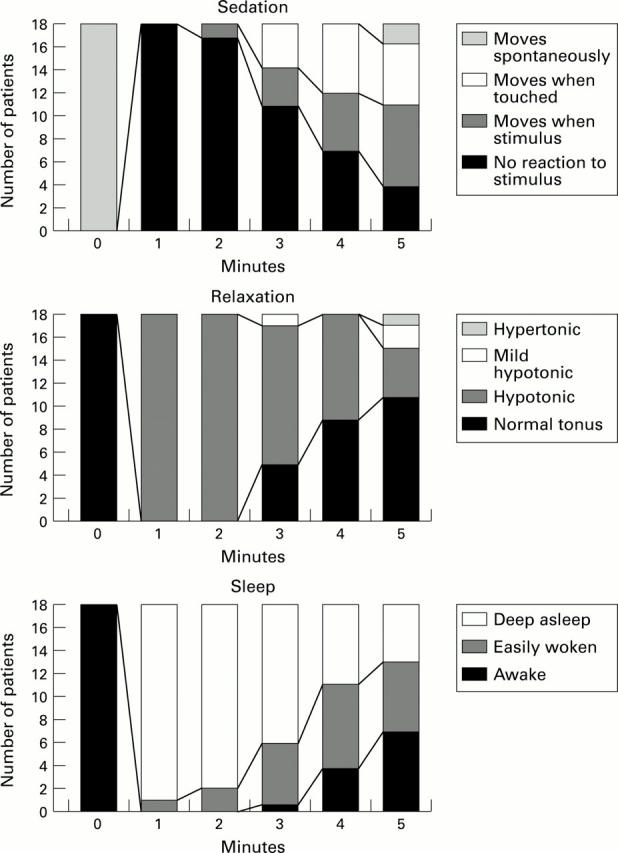
Effect of methohexital on sedation, relaxation, and sleep in neonates.
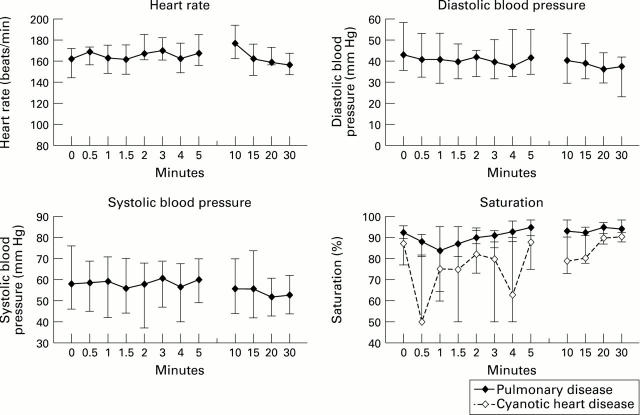
Figure 2 .
Median values, 25th and 75th interquartile ranges of heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure and oxygen saturation before, during, and after methohexital injection.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aun C. S., Sung R. Y., O'Meara M. E., Short T. G., Oh T. E. Cardiovascular effects of i.v. induction in children: comparison between propofol and thiopentone. Br J Anaesth. 1993 Jun;70(6):647–653. doi: 10.1093/bja/70.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey P. L., Wilbrink J., Zwanikken P., Pace N. L., Stanley T. H. Anesthetic induction with fentanyl. Anesth Analg. 1985 Jan;64(1):48–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrington K. J., Finer N. N., Etches P. C. Succinylcholine and atropine for premedication of the newborn infant before nasotracheal intubation: a randomized, controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 1989 Dec;17(12):1293–1296. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198912000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beskow A., Werner O., Westrin P. Faster recovery after anesthesia in infants after intravenous induction with methohexital instead of thiopental. Anesthesiology. 1995 Nov;83(5):976–979. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199511000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtin P., Daoud P., Jacqz-Aigrain E., Mussat P., Moriette G. Hypotension with midazolam and fentanyl in the newborn. Lancet. 1991 Jun 22;337(8756):1545–1546. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock M. K., Carter J. G., Moyers J. R., Stevens W. C. Rigidity and hypercarbia associated with high dose fentanyl induction of anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1981 May;60(5):362–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumrine R. S., Yodlowski E. H. Assessment of neuromuscular function in infants. Anesthesiology. 1981 Jan;54(1):29–32. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198101000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen R. H., Henry D. B. Cardiovascular changes in preterm neonates receiving isoflurane, halothane, fentanyl, and ketamine. Anesthesiology. 1986 Feb;64(2):238–242. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198602000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntlett I. S., Fisher D. M., Hertzka R. E., Kuhls E., Spellman M. J., Rudolph C. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl in neonatal humans and lambs: effects of age. Anesthesiology. 1988 Nov;69(5):683–687. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. I., Abraham E. C., Herrington C. A controlled investigation of propofol, thiopentone and methohexitone. Can J Anaesth. 1987 Sep;34(5):478–483. doi: 10.1007/BF03014354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunau R. V., Craig K. D. Pain expression in neonates: facial action and cry. Pain. 1987 Mar;28(3):395–410. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90073-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. B., Nahrwold M. L., de Rosayro A. M., Knight P. R., Jones R. M., Bolles R. E. Prevention of rigidity during fentanyl--oxygen induction of anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1981 Oct;55(4):452–454. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198110000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller A. Comparison of cardiovascular changes during anaesthesia and recovery from propofol-alfentanil-nitrous oxide and thiopentone-halothane-nitrous oxide anaesthesia in children undergoing otolaryngological surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1993 Nov;37(8):737–741. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1993.tb03800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacqz-Aigrain E., Daoud P., Burtin P., Maherzi S., Beaufils F. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam during continuous infusion in critically ill neonates. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;42(3):329–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00266357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacqz-Aigrain E., Wood C., Robieux I. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam in critically ill neonates. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;39(2):191–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00280059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong A. S., Brennan L., Bingham R., Morgan-Hughes J. An audit of induction of anaesthesia in neonates and small infants using pulse oximetry. Anaesthesia. 1992 Oct;47(10):896–899. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1992.tb03159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laycock G. J., McNicol L. R. Hypoxaemia during induction of anaesthesia--an audit of children who underwent general anaesthesia for routine elective surgery. Anaesthesia. 1988 Nov;43(11):981–984. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1988.tb05668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCollum J. S., Dundee J. W. Comparison of induction characteristics of four intravenous anaesthetic agents. Anaesthesia. 1986 Oct;41(10):995–1000. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1986.tb12740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar C., Bissonnette B. Awake intubation increases intracranial pressure without affecting cerebral blood flow velocity in infants. Can J Anaesth. 1994 Apr;41(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF03009904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murat I., Levron J. C., Berg A., Saint-Maurice C. Effects of fentanyl on baroreceptor reflex control of heart rate in newborn infants. Anesthesiology. 1988 May;68(5):717–722. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198805000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niv D., Davidovich S., Geller E., Urca G. Analgesic and hyperalgesic effects of midazolam: dependence on route of administration. Anesth Analg. 1988 Dec;67(12):1169–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeder J. C., Misvaer G. Comparison of propofol induction with thiopentone or methohexitone in short outpatient general anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1988 Nov;32(8):607–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1988.tb02796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosow C. E., Moss J., Philbin D. M., Savarese J. J. Histamine release during morphine and fentanyl anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1982 Feb;56(2):93–96. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198202000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runcie C. J., Mackenzie S. J., Arthur D. S., Morton N. S. Comparison of recovery from anaesthesia induced in children with either propofol or thiopentone. Br J Anaesth. 1993 Feb;70(2):192–195. doi: 10.1093/bja/70.2.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarnivaara L., Hiller A., Oikkonen M. QT interval, heart rate and arterial pressures using propofol, thiopentone or methohexitone for induction of anaesthesia in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1993 May;37(4):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1993.tb03740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamman F. L. Fentanyl-O2-N2O rigidity and pulmonary compliance. Anesth Analg. 1983 Mar;62(3):332–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrum S. F., Hannallah R. S., Verghese P. M., Welborn L. G., Norden J. M., Ruttiman U. Comparison of propofol and thiopental for rapid anesthesia induction in infants. Anesth Analg. 1994 Mar;78(3):482–485. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199403000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz C., Lenz G., Madee S., Schulze M. Fréquence des épisodes hypoxiques au cours de l'anesthésie générale de l'enfant. Cah Anesthesiol. 1989 Oct;37(6):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. H., Lerman J. Induction, maintenance and recovery characteristics of desflurane in infants and children. Can J Anaesth. 1992 Jan;39(1):6–13. doi: 10.1007/BF03008665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truog R., Anand K. J. Management of pain in the postoperative neonate. Clin Perinatol. 1989 Mar;16(1):61–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen M., Iisalo E., Kanto J., Tikkanen J. Comparison between propofol and thiopentone for induction of anaesthesia in children. Anaesthesia. 1988 Aug;43(8):696–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1988.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westrin P. Methohexital dissolved in lipid emulsion for intravenous induction of anesthesia in infants and children. Anesthesiology. 1992 Jun;76(6):917–921. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199206000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]