Abstract
AIM—To investigate changes in various cardiorespiratory variables with inhaled nitric oxide (NO), as part of a randomised controlled trial. METHODS—Infants were treated with inhaled NO for 72 hours. Changes in oxygenation were assessed using the oxygenation index (OI). Serial changes in pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) were assessed using the Doppler derived acceleration time to right ventricular ejection time ratio (AT:RVET). Doppler measurements of right ventricular output, pulmonary blood flow, and systolic PAP was performed in a subset of infants. RESULTS—Twenty infants received inhaled NO and 22 acted as controls. Infants were treated at a median dose of 5 (range 5 to 20) ppm. There was a fall in median OI by 17% in treated infants within 30 minutes of treatment. The fall in OI in treated infants was significantly different from the response in controls until 96 hours. Infants treated with inhaled NO showed a rapid response with a median rise in AT:RVET of 0.04 (range −0.06 to 0.12) within 30 minutes. The change in AT:RVET was significantly different from controls until 4 hours. Median systolic PAP also fell in treated infants by 6.1 (range −14.4 to −4.4) mm Hg within 1 hour. Changes in OI were significantly associated with changes in PBF (r = 0.44), but not with changes in AT:RVET. CONCLUSION—Treatment with inhaled NO rapidly improves oxygenation and lowers PAP in preterm infants. However, these effects are transient and treatment does not influence long term outcome. Keywords: Inhaled nitric oxide; pulmonary artery pressure; oxygenation index
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (136.0 KB).
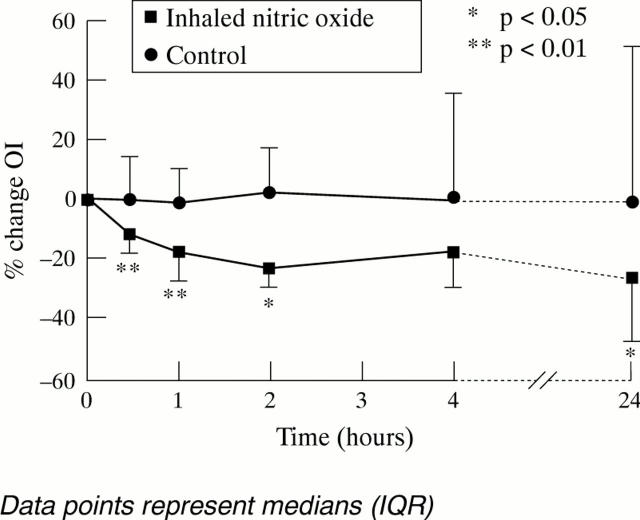
Figure 1 .
Percentage change in OI with inhaled NO up to 24 hours
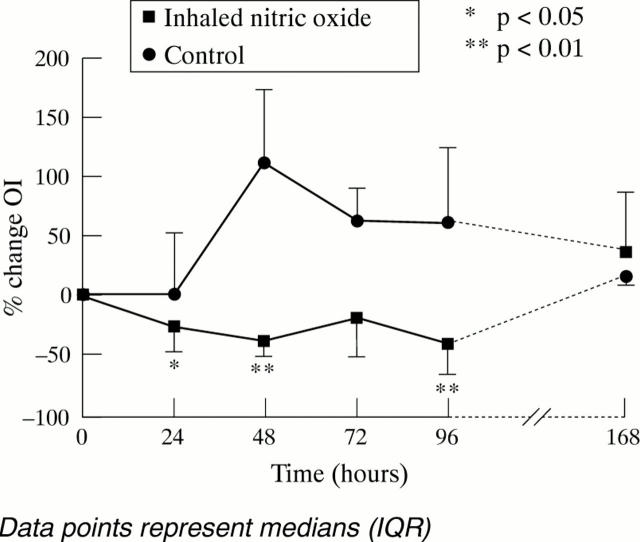
Figure 2 .
Percentage change in OI with inhaled NO up to 168 hours
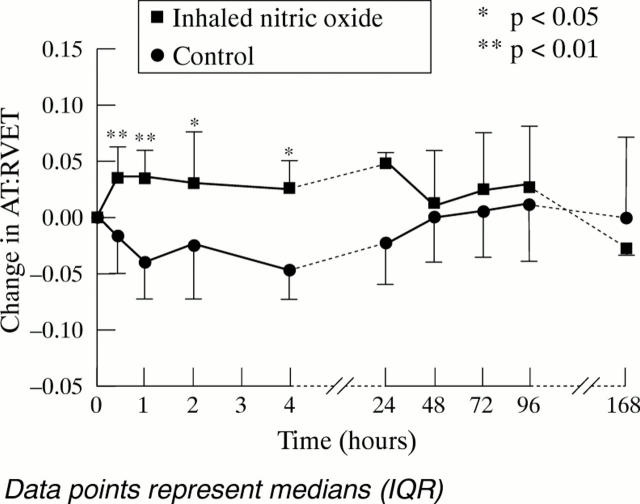
Figure 3 .
Changes in AT:RVET with inhaled NO
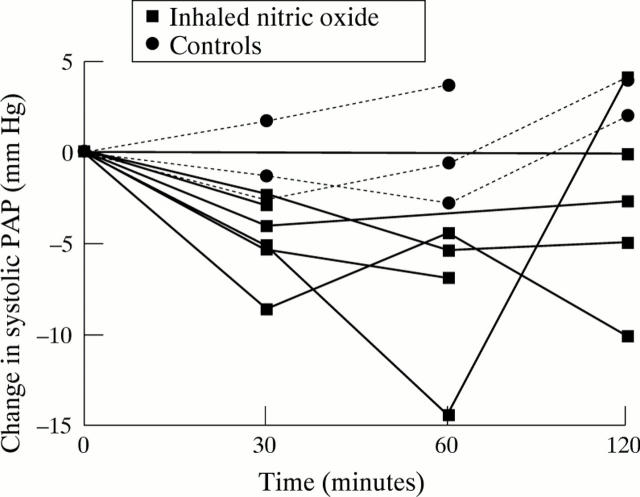
Figure 4 .
Individual changes in systolic PAP with inhaled NO
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abman S. H., Griebel J. L., Parker D. K., Schmidt J. M., Swanton D., Kinsella J. P. Acute effects of inhaled nitric oxide in children with severe hypoxemic respiratory failure. J Pediatr. 1994 Jun;124(6):881–888. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abman S. H., Kinsella J. P. Inhaled nitric oxide for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: the physiology matters! Pediatrics. 1995 Dec;96(6):1153–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abman S. H., Kinsella J. P. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy of pulmonary hypertension and respiratory failure in premature and term neonates. Adv Pharmacol. 1995;34:457–474. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barefield E. S., Karle V. A., Phillips J. B., 3rd, Carlo W. A. Inhaled nitric oxide in term infants with hypoxemic respiratory failure. J Pediatr. 1996 Aug;129(2):279–286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(96)70255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Calculating correlation coefficients with repeated observations: Part 1--Correlation within subjects. BMJ. 1995 Feb 18;310(6977):446–446. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6977.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. J., Archer L. N. Doppler assessment of pulmonary artery pressure and extrapulmonary shunting in the acute phase of hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jan;66(1 Spec No):6–11. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.1_spec_no.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. Shunts in patients with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1993 Nov;92(5):737–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fineman J. R., Soifer S. J., Heymann M. A. Regulation of pulmonary vascular tone in the perinatal period. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:115–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer N. N., Etches P. C., Kamstra B., Tierney A. J., Peliowski A., Ryan C. A. Inhaled nitric oxide in infants referred for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: dose response. J Pediatr. 1994 Feb;124(2):302–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(94)70324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foubert L., Fleming B., Latimer R., Jonas M., Oduro A., Borland C., Higenbottam T. Safety guidelines for use of nitric oxide. Lancet. 1992 Jun 27;339(8809):1615–1616. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91886-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach H., Rossaint R., Pappert D., Falke K. J. Time-course and dose-response of nitric oxide inhalation for systemic oxygenation and pulmonary hypertension in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;23(8):499–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1993.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Jarvenpaa A. L., Boynton B., Mannino F., Gluck L., Moore T., Edwards D. Exogenous human surfactant for treatment of severe respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized prospective clinical trial. J Pediatr. 1985 Jun;106(6):963–969. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heal C. A., Spencer S. A. Methaemoglobinaemia with high-dose nitric oxide administration. Acta Paediatr. 1995 Nov;84(11):1318–1319. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högman M., Frostell C., Arnberg H., Hedenstierna G. Bleeding time prolongation and NO inhalation. Lancet. 1993 Jun 26;341(8861):1664–1665. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90802-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer P., Evans N. Re-evaluation of the left atrial to aortic root ratio as a marker of patent ductus arteriosus. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1994 Mar;70(2):F112–F117. doi: 10.1136/fn.70.2.f112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karamanoukian H. L., Glick P. L., Zayek M., Steinhorn R. H., Zwass M. S., Fineman J. R., Morin F. C., 3rd Inhaled nitric oxide in congenital hypoplasia of the lungs due to diaphragmatic hernia or oligohydramnios. Pediatrics. 1994 Nov;94(5):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. P., Abman S. H. Recent developments in the pathophysiology and treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. J Pediatr. 1995 Jun;126(6):853–864. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. P., Ivy D. D., Abman S. H. Inhaled nitric oxide improves gas exchange and lowers pulmonary vascular resistance in severe experimental hyaline membrane disease. Pediatr Res. 1994 Sep;36(3):402–408. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199409000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. P., McQueston J. A., Rosenberg A. A., Abman S. H. Hemodynamic effects of exogenous nitric oxide in ovine transitional pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):H875–H880. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.3.H875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. P., Neish S. R., Shaffer E., Abman S. H. Low-dose inhalation nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992 Oct 3;340(8823):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92687-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosturakis D., Goldberg S. J., Allen H. D., Loeber C. Doppler echocardiographic prediction of pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Apr 1;53(8):1110–1115. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnqvist P. A., Winberg P., Lundell B., Selldén H., Olsson G. L. Inhaled nitric oxide in neonates and children with pulmonary hypertension. Acta Paediatr. 1994 Nov;83(11):1132–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb18265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani G., Barefield E. S., Carlo W. A. The role of nitric oxide in the treatment of neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1996 Apr;8(2):118–125. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199604000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. I., Tang S. F., Keech A., Celermajer D. S. Rebound pulmonary hypertension on withdrawal from inhaled nitric oxide. Lancet. 1995 Jul 1;346(8966):51–52. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92681-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliowski A., Finer N. N., Etches P. C., Tierney A. J., Ryan C. A. Inhaled nitric oxide for premature infants after prolonged rupture of the membranes. J Pediatr. 1995 Mar;126(3):450–453. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Jr, Fineman J. R., Morin F. C., 3rd, Shaul P. W., Rimar S., Schreiber M. D., Polin R. A., Zwass M. S., Zayek M. M., Gross I. Inhaled nitric oxide and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. The Inhaled Nitric Oxide Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 Feb 27;336(9):605–610. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199702273360902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Jr, Lang P., Bigatello L. M., Vlahakes G. J., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide in congenital heart disease. Circulation. 1993 Feb;87(2):447–453. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Polaner D. M., Lang P., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992 Oct 3;340(8823):818–819. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92686-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossaint R., Falke K. J., López F., Slama K., Pison U., Zapol W. M. Inhaled nitric oxide for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 11;328(6):399–405. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302113280605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozé J. C., Storme L., Zupan V., Morville P., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Mercier J. C. Echocardiographic investigation of inhaled nitric oxide in newborn babies with severe hypoxaemia. Lancet. 1994 Jul 30;344(8918):303–305. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. W., Nycyk J., Shaw B. N. Prediction of chronic neonatal lung disease on day 4 of life. Eur J Pediatr. 1996 Aug;155(8):668–671. doi: 10.1007/BF01957150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skimming J. W., DeMarco V. G., Cassin S. The effects of nitric oxide inhalation on the pulmonary circulation of preterm lambs. Pediatr Res. 1995 Jan;37(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. R., Boys R. J., Heads A., Hey E. N., Hunter S. Estimation of pulmonary arterial pressure in the newborn: study of the repeatability of four Doppler echocardiographic techniques. Pediatr Cardiol. 1996 Nov-Dec;17(6):360–369. doi: 10.1007/s002469900080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yock P. G., Popp R. L. Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):657–662. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellers T., Gutgesell H. P. Noninvasive estimation of pulmonary artery pressure. J Pediatr. 1989 May;114(5):735–741. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]