Abstract
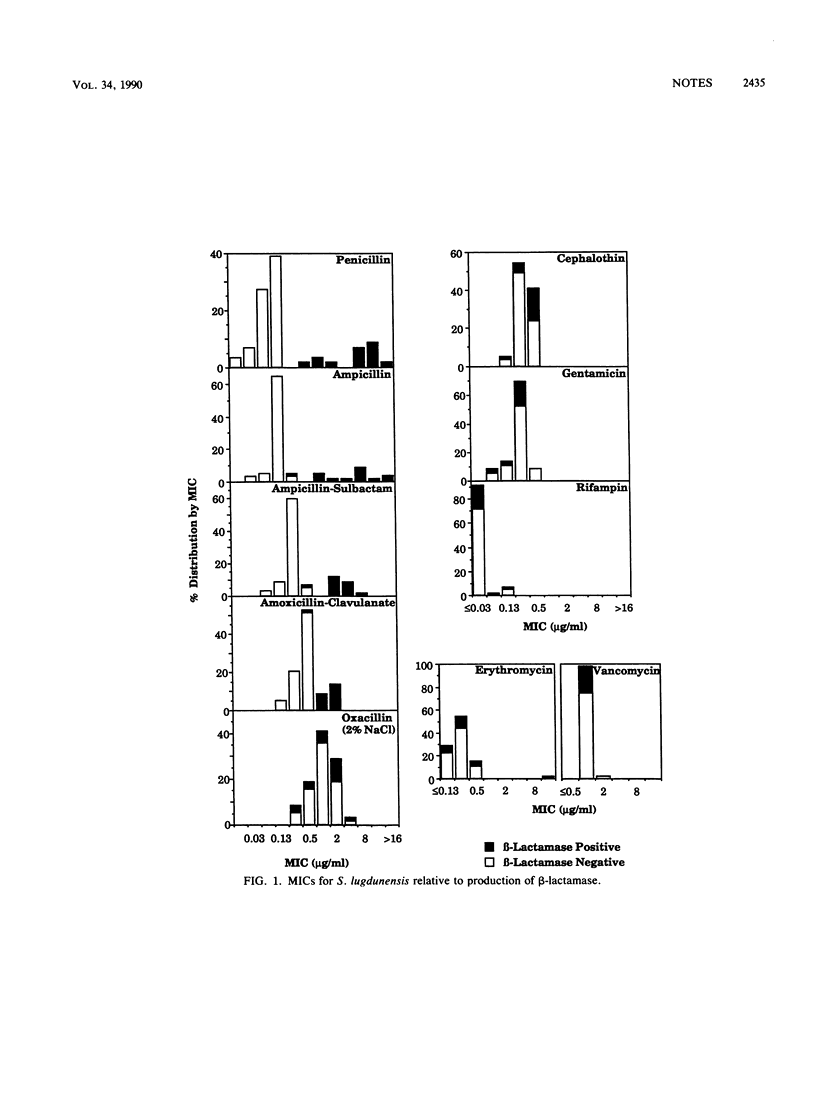
Of 59 clinical isolates of Staphylococcus lugdunensis, 76% were beta-lactamase negative, with penicillin G MICs of less than or equal to 0.13 microgram/ml, and 24% were beta-lactamase positive, with penicillin MICs of greater than or equal to 0.5 microgram/ml. Bimodal distributions were observed also with ampicillin, ampicillin-sulbactam, and amoxicillin-clavulanate. All strains were susceptible to oxacillin, cephalothin, gentamicin, rifampin, and vancomycin; 98% were erythromycin susceptible.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fass R. J., Helsel V. L., Barnishan J., Ayers L. W. In vitro susceptibilities of four species of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):545–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleurette J., Bès M., Brun Y., Freney J., Forey F., Coulet M., Reverdy M. E., Etienne J. Clinical isolates of Staphylococcus lugdunensis and S. schleiferi: bacteriological characteristics and susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. Res Microbiol. 1989 Feb;140(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


