Abstract
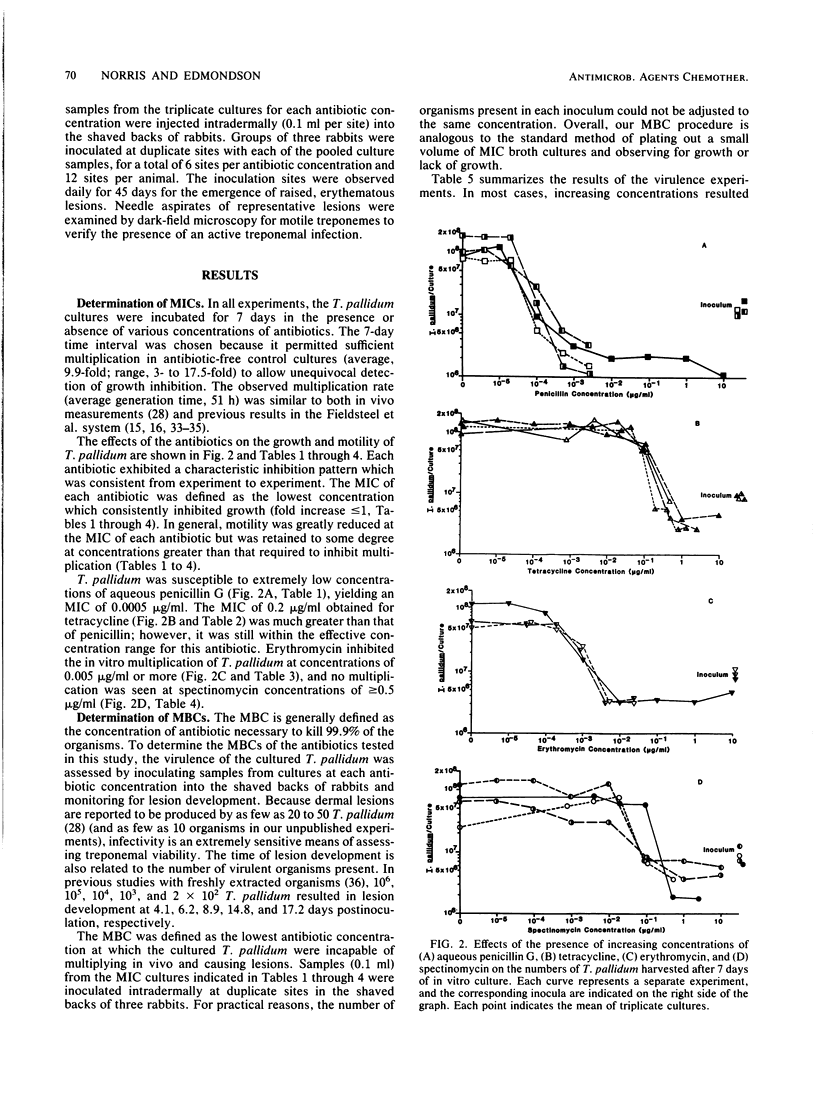
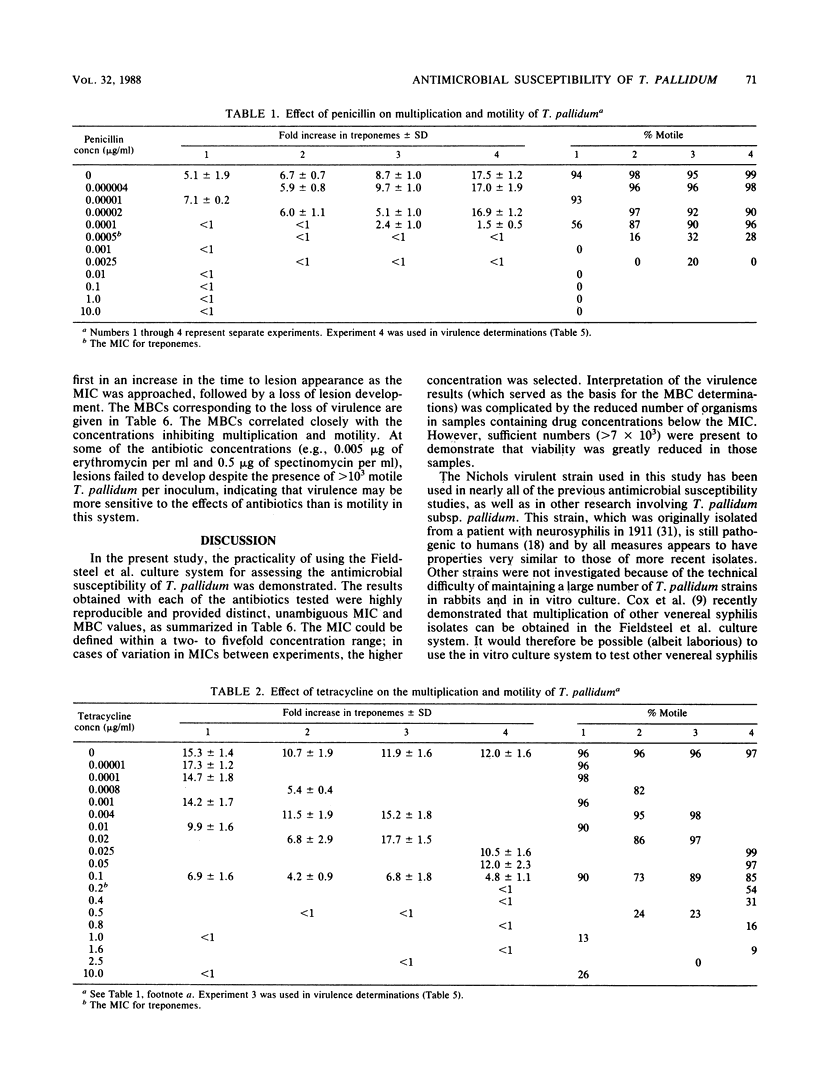
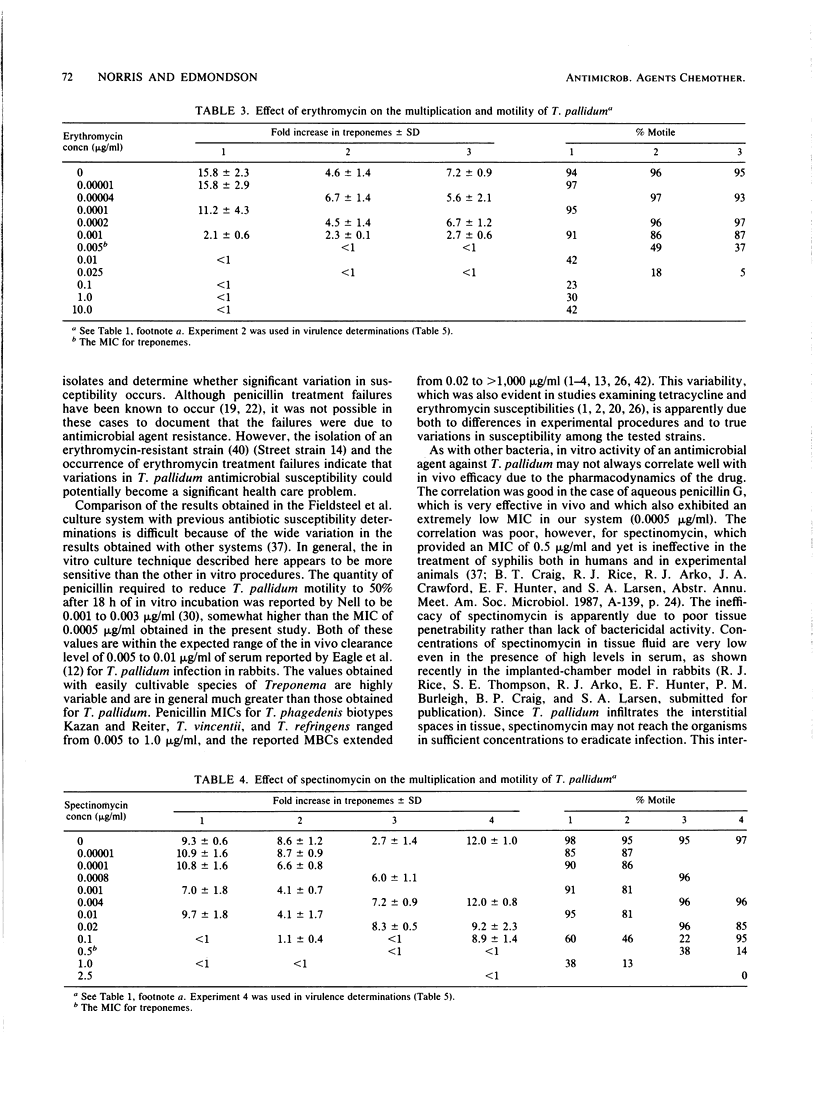
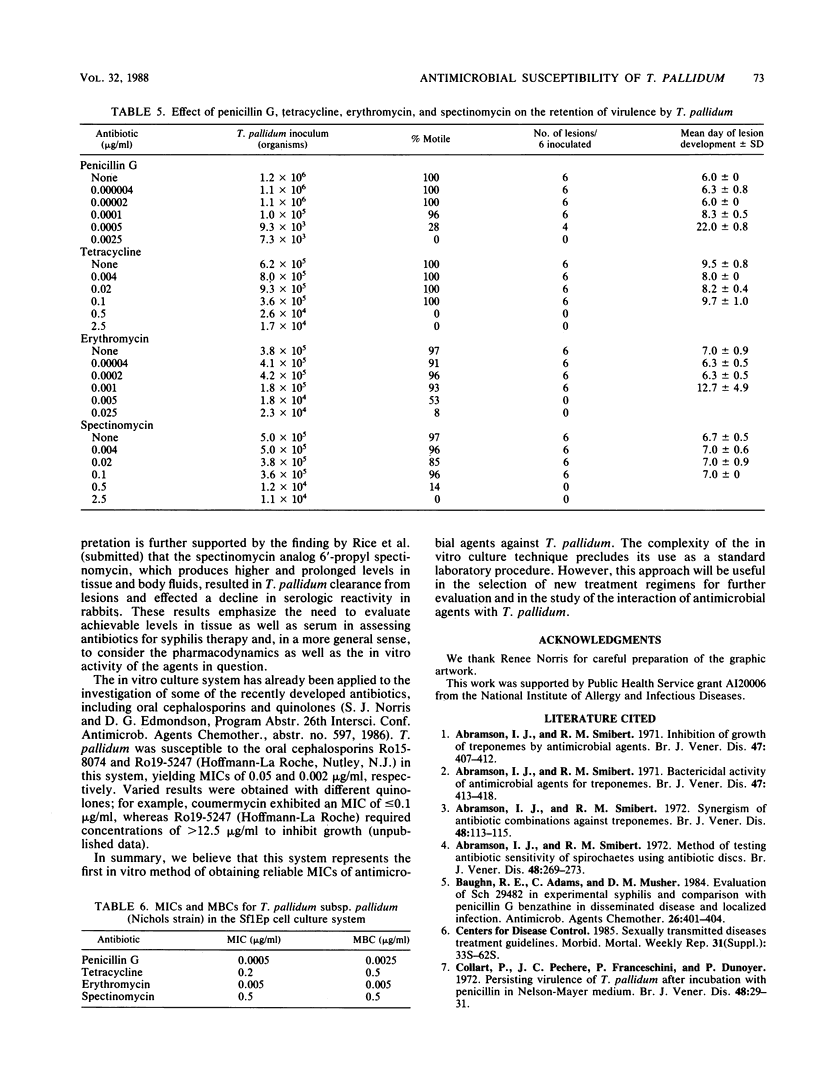
A new procedure for determining the susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum to antimicrobial agents was developed, utilizing a tissue culture system which promotes the in vitro multiplication of this organism. In the absence of antibiotics, T. pallidum (Nichols virulent strain) multiplied an average of 10-fold when incubated for 7 days in the presence of Sf1Ep cottontail rabbit epithelial cell cultures. Varied concentrations of penicillin G, tetracycline, erythromycin, and spectinomycin were added to triplicate cultures to determine their effects on treponemal multiplication, motility, and virulence. The MIC of each antibiotic was defined as the lowest concentration which prevented treponemal multiplication, whereas the MBC was defined as the lowest concentration which abrogated the ability of the cultured treponemes to multiply and cause lesions in rabbits. The in vitro culture technique provided highly reproducible MICs and (in parentheses) MBCs of each of the antibiotics tested: aqueous penicillin G, 0.0005 (0.0025) microgram/ml; tetracycline, 0.2 (0.5) microgram/ml; erythromycin, 0.005 (0.005) microgram/ml; and spectinomycin, 0.5 (0.5) microgram/ml. The significance of these results in light of the in vivo activities and the previous in vitro evaluations of these antibiotics is discussed. The T. pallidum in vitro cultivation system shows promise as a method for studying the interaction between T. pallidum and antimicrobial agents and for screening new antibiotics for syphilis therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents for treponemes. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):413–418. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Inhibition of growth of treponemes by antimicrobial agents. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):407–412. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Method of testing antibiotic sensitivity of spirochaetes, using antibiotic discs. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Aug;48(4):269–273. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Synergism of antibiotic combinations against treponemes. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):113–115. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Adams C., Musher D. M. Evaluation of Sch 29482 in experimental syphilis and comparison with penicillin G benzathine in disseminated disease and localized infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):401–404. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart P., Pechere J. C., Franceschini P., Dunoyer P. Persisting virulence of T. pallidum after incubation with penicillin in Nelson-Mayer medium. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Feb;48(1):29–31. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A., Fieldsteel A. H. Cultivation of pathogenic treponema in tissue cultures of SflEp cells. In Vitro. 1984 Nov;20(11):879–883. doi: 10.1007/BF02619635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., MUSSELMAN A. D. The effective concentrations of penicillin in vitro and in vivo for streptococci, pneumococci, and Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1950 May;59(5):625–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.5.625-643.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., HAMPP E. G. Inhibition of oral spirochetes by antibiotic agents in vitro. J Dent Res. 1952 Feb;31(1):20–24. doi: 10.1177/00220345520310011501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton L. J., Light I. J. Congenital syphilis after maternal treatment with erythromycin. Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Apr;47(4):492–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Cultivation of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):908–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.908-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Further studies on replication of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue cultures of Sf1Ep cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.449-455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. J., Johnson R. C., Smith M. Accidental laboratory infection with Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976 Dec;3(2 Pt 1):76–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. J., Lawrence A. G. Treatment failure with penicillin in early syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Feb;55(1):62–64. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMPP E. G., FITZGERALD R. J. The in vitro effects of antibiotics on oral spirochetes. J Dent Res. 1959 Sep-Oct;38:947–950. doi: 10.1177/00220345590380052501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H. Problems in the treatment of bacterial sexually transmitted diseases. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jul-Sep;13(3 Suppl):179–184. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198607000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. B., Hardy P. H., Oppenheimer E. H., Ryan S. J., Jr, Sheff R. N. Failure of penicillin in a newborn with congenital syphilis. JAMA. 1970 May 25;212(8):1345–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashisaki P., Wertzberger G. G., Conrad G. L., Nichols C. R. Erythromycin failure in the treatment of syphilis in a pregnant woman. Sex Transm Dis. 1983 Jan-Mar;10(1):36–38. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198301000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Baker-Zander S. A., Moskovitz B. L., Lukehart S. A., Handsfield H. H. Ceftriaxone therapy for asymptomatic neurosyphilis. Case report and Western blot analysis of serum and cerebrospinal fluid IgG response to therapy. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jul-Sep;13(3 Suppl):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bey R. F., Wolgamot S. J. Comparison of the activities of ceftriaxone and penicillin G against experimentally induced syphilis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):984–989. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER R., MORTON H. E. Susceptibilities of Kazan, Nichols, and Reiter strains of Treponema and pleuropneumonia-like organisms to the antibiotic erythromycin (ilotycin). Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1953 Jul;37(4):379–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Holmes K. K. Efficacy of aztreonam in treatment of experimental syphilis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):390–391. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELL E. E. Comparative sensitivity of treponemes of syphilis, yaws, and bejel to penicillin in vitro, with observations on factors affecting its treponemicidal action. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Mar;38(2):92–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Plasmid DNA in Treponema pallidum (Nichols): potential for antibiotic resistance by syphilis bacteria. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):553–555. doi: 10.1126/science.6264606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Edmondson D. G. Factors affecting the multiplication and subculture of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum in a tissue culture system. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):534–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.534-539.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Edmondson D. G. Serum requirement for the multiplication of Treponema pallidum in a tissue-culture system: association of growth-promoting activity with the protein fraction. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):207–213. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J. In vitro cultivation of Treponema pallidum: independent confirmation. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.437-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A., Fitzgerald T. J. Influence of oxygen tension, sulfhydryl compounds, and serum on the motility and virulence of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in a cell-free system. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):689–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.689-697.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein M. F. Biopharmacology of syphilotherapy. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976 Dec;3(2 Pt 2):109–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOUTH M. A., SHORT D. H., KNOX J. M. FAILURE OF ERYTHROMYCIN ESTOLATE THERAPY IN IN UTERO SYPHILIS. JAMA. 1964 Oct 5;190:70–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070140076020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton J. T., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Potential for development of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic treponemes. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7 (Suppl 2):S314–S317. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7-supplement_2.s314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöckli H. R. Neurosyphilis heute. Dermatologica. 1982 Oct;165(4):232–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


