Abstract
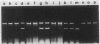
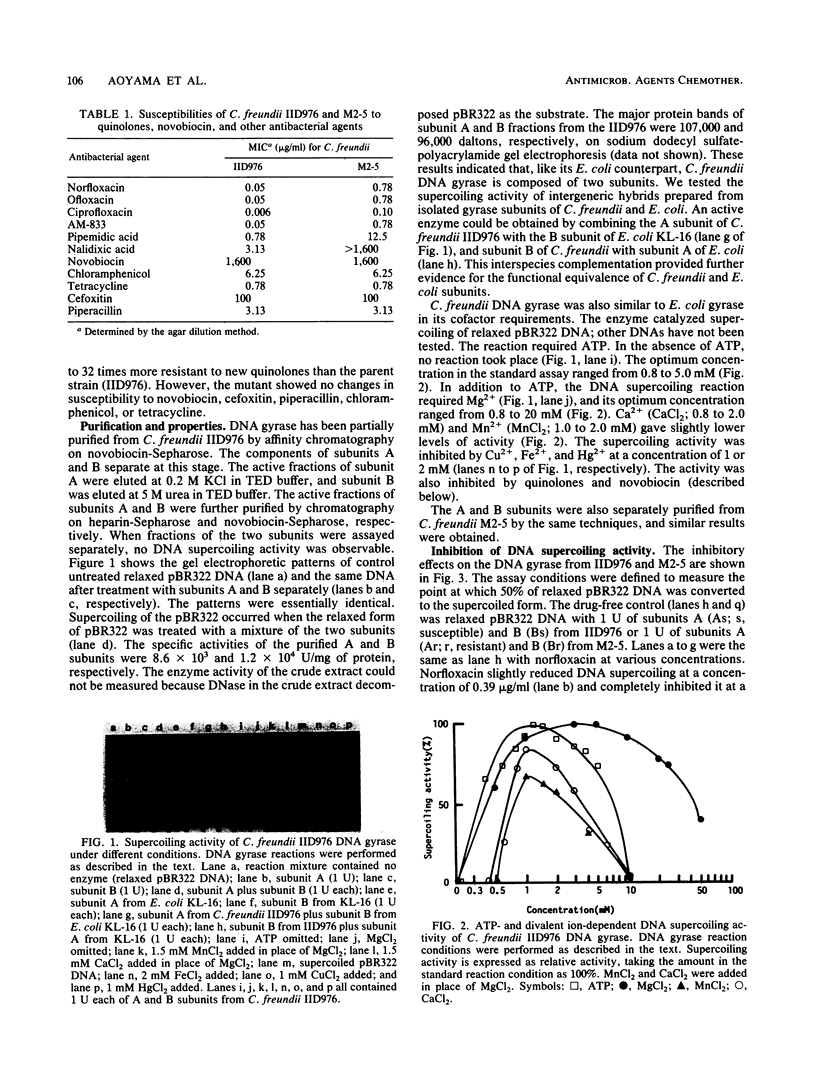
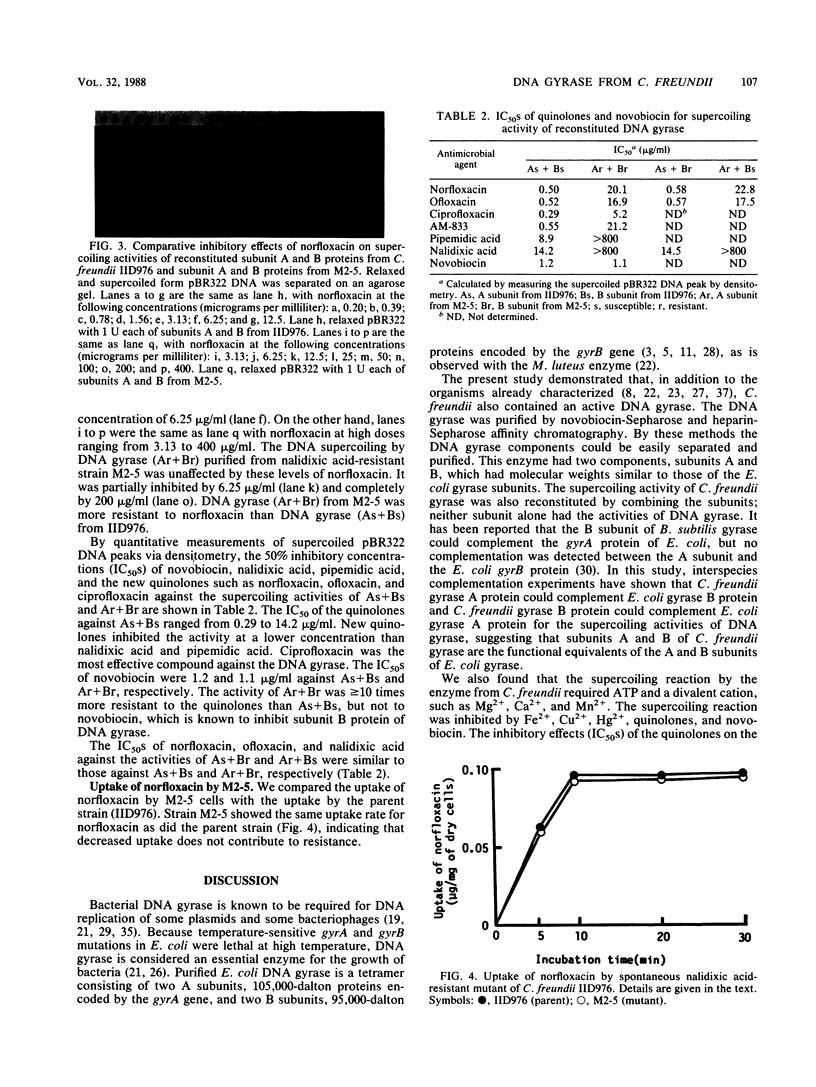
DNA gyrase is a bacterial enzyme which catalyzes the ATP-dependent negative supercoiling of DNA. It is the accepted target of quinolones. The enzyme from Citrobacter freundii IID976 was purified by affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and heparin-Sepharose. It had two subunits, designated A and B, which closely resembled those of the enzyme from Escherichia coli and Micrococcus luteus in enzymatic requirements. The inhibitory effects of the quinolones on the supercoiling activities of the enzyme correlated with their antibacterial activities. New quinolones were better inhibitors of DNA gyrase than nalidixic acid and pipemidic acid. We also purified DNA gyrase from a spontaneous nalidixic acid-resistant mutant (M2-5). The gyrases from IID976 and M2-5 were defined as mixtures of subunits As+Bs (s, susceptible) and Ar+Br (r, resistant), respectively. The supercoiling activities of reconstituted Ar+Br and Ar+Bs were more resistant to quinolones than As+Bs and As+Br. These findings indicate that one mechanism of C. freundii resistance against quinolones is resistance modification of the A subunit protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourguignon G. J., Levitt M., Sternglanz R. Studies on the mechanism of action of nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):479–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G. Apparent absence of transferable resistance to nalidixic acid in pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Sep;3(5):509–516. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagala J. M., Hanna L. D., Heifetz C. L., Hutt M. P., Mich T. F., Sanchez J. P., Solomon M. New structure-activity relationships of the quinolone antibacterials using the target enzyme. The development and application of a DNA gyrase assay. J Med Chem. 1986 Mar;29(3):394–404. doi: 10.1021/jm00153a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Fisher L. M., O'Dea M. H. DNA gyrase: purification and catalytic properties of a fragment of gyrase B protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6289–6293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Hosaka M., Oomori Y., Niwata Y., Suzue S., Irikura T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of AM-833, a new quinolone derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1059–1066. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., McHugh G. L., Winters M. B., Swartz M. N. Effects of novobiocin, coumermycin A1, clorobiocin, and their analogs on Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and bacterial growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):662–671. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrebenda J., Heleszko H., Brzostek K., Bielecki J. Mutation affecting resistance of Escherichia coli K12 to nalidixic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Ohue T., Yamagishi J., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. Mode of incomplete cross-resistance among pipemidic, piromidic, and nalidixic acids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Hirai K., Inoue M., Koga H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–108. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Involvement of DNA gyrase in bacteriophage T7 DNA replication. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):78–80. doi: 10.1038/270078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouno K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of AT-2266. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., McEntee K., Geballe A. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Lambda transducing phages for the nalA gene of Escherichia coli and conditional lethal nalA mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 29;167(2):129–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00266906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Scurlock T. R. DNA gyrase (Topoisomerase II) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):694–700. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase: subunit structure and ATPase activity of the purified enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5960–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J., van Veldhuizen G. Comparative activities of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867), norfloxacin, pipemidic acid, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):302–304. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr E., Fairweather N. F., Holland I. B., Pritchard R. H. Isolation and characterisation of a strain carrying a conditional lethal mutation in the cou gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00267259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr E., Staudenbauer W. L. Bacillus subtilis DNA gyrase: purification of subunits and reconstitution of supercoiling activity. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):524–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.524-527.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Higgins N. P., Kreuzer K. N., Morrison A., Brown P. O., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Structure and activities of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):41–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara Y., Tomizawa J. I. Replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA in cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V., Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue Y., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of DNA gyrase from a fluoroquinolone-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T. Mutational resistance to 4-quinolone antibacterial agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):347–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01977492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Drlica K. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: DNA cleavage induced by oxolinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Bott K. F. Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1331–1339. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1331-1339.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. The intrinsic ATPase of DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6299–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Furutani Y., Inoue S., Ohue T., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. New nalidixic acid resistance mutations related to deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]