Abstract
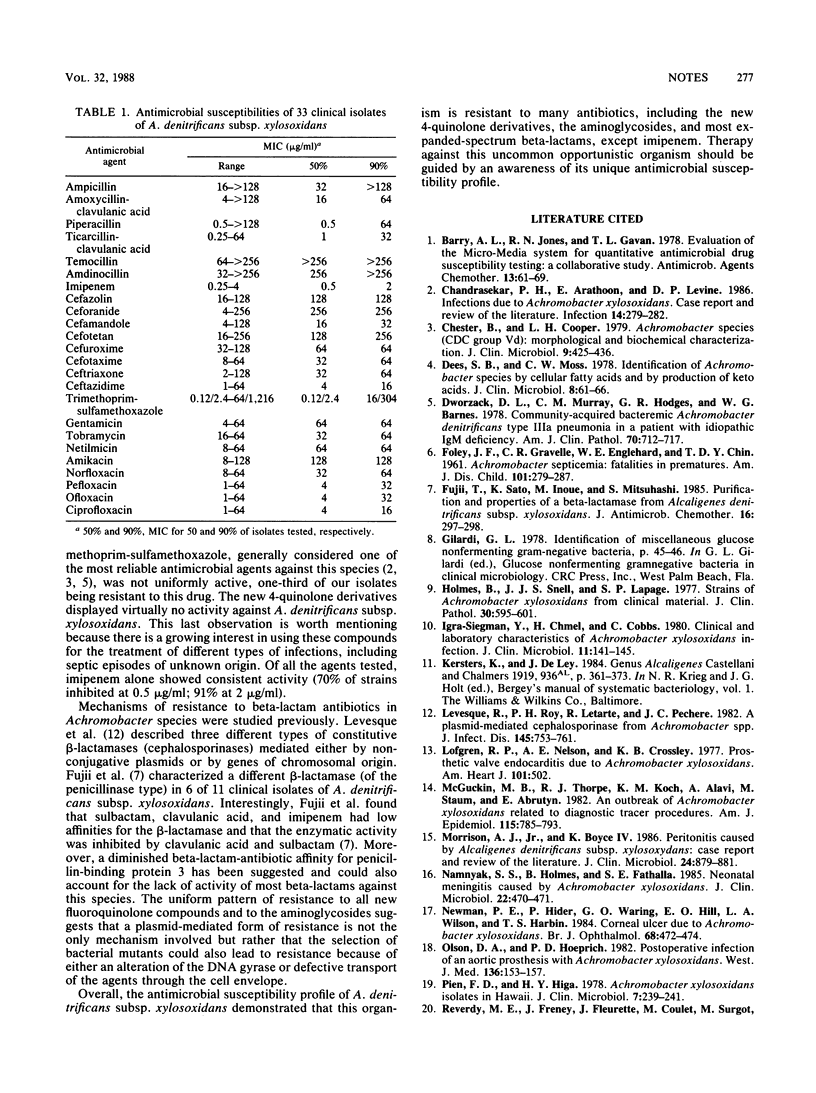
The in vitro susceptibilities of 37 clinical isolates of Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxidans to 24 antimicrobial agents were determined. Imipenem was the only drug with consistent activity (MIC for 90% of isolates, 2 micrograms/ml). Piperacillin, ticarcillin-clavulanic acid, ceftazidime, and co-trimoxazole were active against most strains. All the isolates were resistant to ampicillin, cefazolin, cefuroxime, cefamandole, cefotetan, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, aztreonam, amdinocillin, and temocillin. Most isolates were resistant to the aminoglycosides tested, including amikacin. Lack of activity was also observed for all new 4-quinolone antimicrobial agents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the micro-media system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar P. H., Arathoon E., Levine D. P. Infections due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Case report and review of the literature. Infection. 1986 Nov-Dec;14(6):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01643962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester B., Cooper L. H. Achromobacter species (CDC group Vd): morphological and biochemical characterization. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):425–436. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.425-436.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees S. B., Moss C. W. Identification of Achromobacter species by cellular fatty acids and by production of keto acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):61–66. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.61-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworzack D. L., Murray C. M., Hodges G. R., Barnes W. G. Community-acquired bacteremic Achromobacter xylosoxidans type IIIa pneumonia in a patient with idiopathic IgM deficiency. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Oct;70(4):712–717. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY J. F., GRAVELLE C. R., ENGLEHARD W. E., CHIN T. D. Achromobacter septicemia-fatalities in prematures. I. Clinical and epidemiological study. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Mar;101:279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Sato K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a beta-lactamase from Alcaligenes dentrificans subsp. xylosoxydans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Sep;16(3):297–304. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Snell J. J., Lapage S. P. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;30(7):595–601. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.7.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igra-Siegman Y., Chmel H., Cobbs C. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of Achromobacter xylosoxidans infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):141–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.141-145.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R., Roy P. H., Letarte R., Pechère J. C. A plasmid-mediated cephalosporinase from Achromobacter species. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):753–761. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren R. P., Nelson A. E., Crossley K. B. Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Am Heart J. 1981 Apr;101(4):502–502. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuckin M. B., Thorpe R. J., Koch K. M., Alavi A., Staum M., Abrutyn E. An outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans related to diagnostic tracer procedures. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 May;115(5):785–793. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. J., Jr, Boyce K., 4th Peritonitis caused by Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxydans: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):879–881. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.879-881.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namnyak S. S., Holmes B., Fathalla S. E. Neonatal meningitis caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):470–471. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.470-471.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. E., Hider P., Waring G. O., 3rd, Hill E. O., Wilson L. A., Harbin T. S. Corneal ulcer due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984 Jul;68(7):472–474. doi: 10.1136/bjo.68.7.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. A., Hoeprich P. D. Postoperative infection of an aortic prosthesis with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. West J Med. 1982 Feb;136(2):153–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Higa H. Y. Achromobacter xylosoxidans isolates in Hawaii. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):239–241. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.239-241.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reverdy M. E., Freney J., Fleurette J., Coulet M., Surgot M., Marmet D., Ploton C. Nosocomial colonization and infection by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.140-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeta S., Yasunaga Y., Honzumi K., Okamura H., Kumata R., Endo S. Cerebral ventriculitis associated with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;31(2):156–161. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welk S. W. Achromobacter pneumonia. West J Med. 1982 Apr;136(4):349–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



