Abstract
Background: Childhood leukaemias express novel, clonotypic fusion genes that may already be present at birth before the clinical manifestation of leukaemia. Exposure of the fetus to diagnostic x rays is reported to increase the risk of childhood leukaemia, and may do so by generating leukaemic fusion genes. Advances in neonatal medicine in the past decade that have extended the limits of viability of preterm babies down to 23 weeks of gestation have resulted in the increased use of diagnostic x rays to monitor neonatal progress.
Aim: To investigate whether exposure of very preterm infants to diagnostic x rays in the neonatal period leads to the development of leukaemic fusion genes.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples were collected at birth from very preterm infants (23–30 weeks gestation) and following exposure to diagnostic x rays at intervals of two weeks, until discharge. Cord blood samples from normal full term infants served as controls. Total RNA was extracted from the blood and the expression of the fusion genes TEL-AML1, MLL-AF4, and BCR-ABL, characteristic of three subtypes of childhood leukaemia, was investigated in the preterm and full term infant samples using a nested reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction method. Serial pre- and post-x ray samples from 42 preterm babies, pre-x ray samples from an additional 46 preterm infants, and cord blood samples from 100 normal full term infants were screened for fusion gene transcripts.
Results: No leukaemic fusion gene transcripts were detected in preterm infants following exposure to diagnostic x rays. A BCR-ABL transcript was identified in a single preterm infant prior to x ray exposure. TEL-AML1 transcripts were detected in cord blood samples from two full term infants. MLL-AF4 transcripts were not detected in any of the pre- or full term infants tested.
Conclusions: Exposure of the preterm infants to x rays in this small series and at the doses used for diagnostic purposes did not induce leukaemic fusion gene expression, but we cannot exclude the possibility that a small proportion of preterm infants may be unusually sensitive to x rays.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (190.5 KB).
Figure 1 .
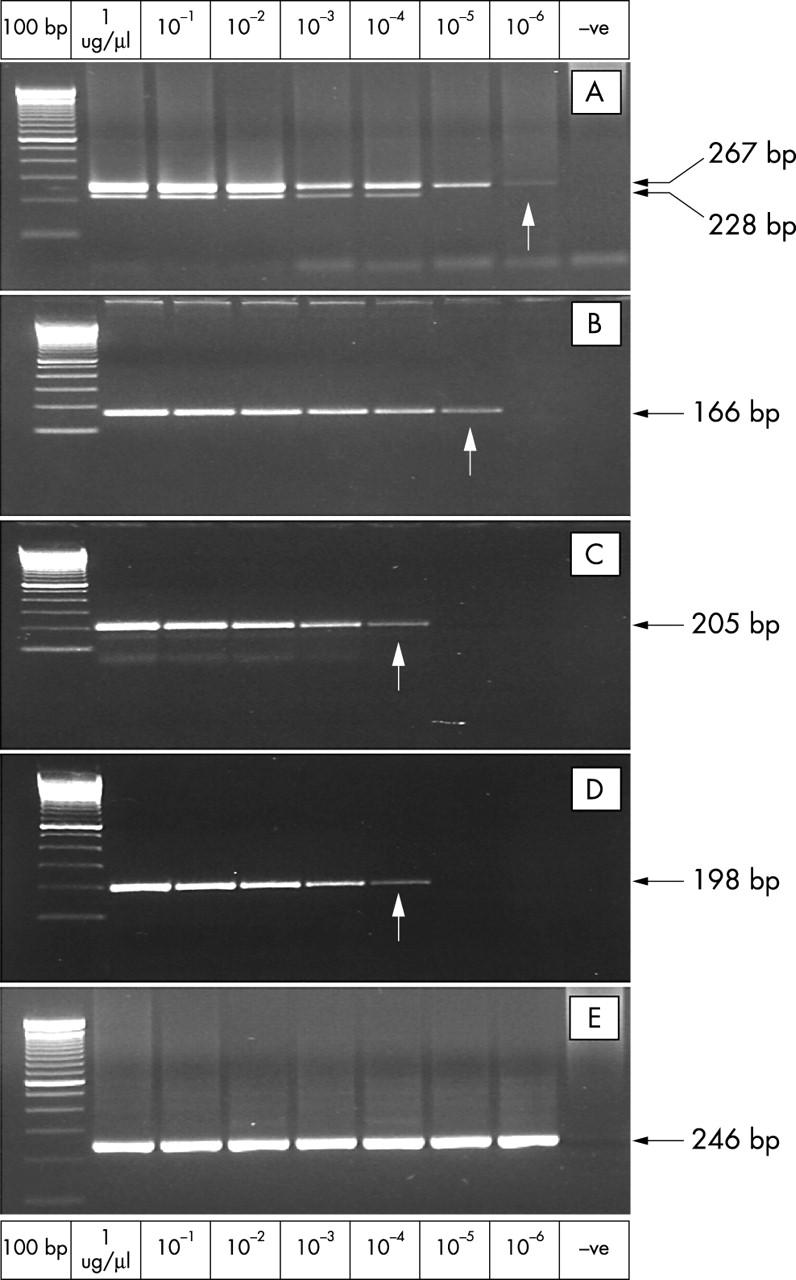
RT-PCR sensitivity experiments. (A) TEL-AML1 (REH). (B) MLL-AF4 (MV4;11). (C) BCR-ABL minor breakpoint junction (BV173). (D) BCR-ABL major breakpoint junction (BV173). (E) ß actin positive control (REH). Arrows indicate sensitivity threshold.
Figure 2 .
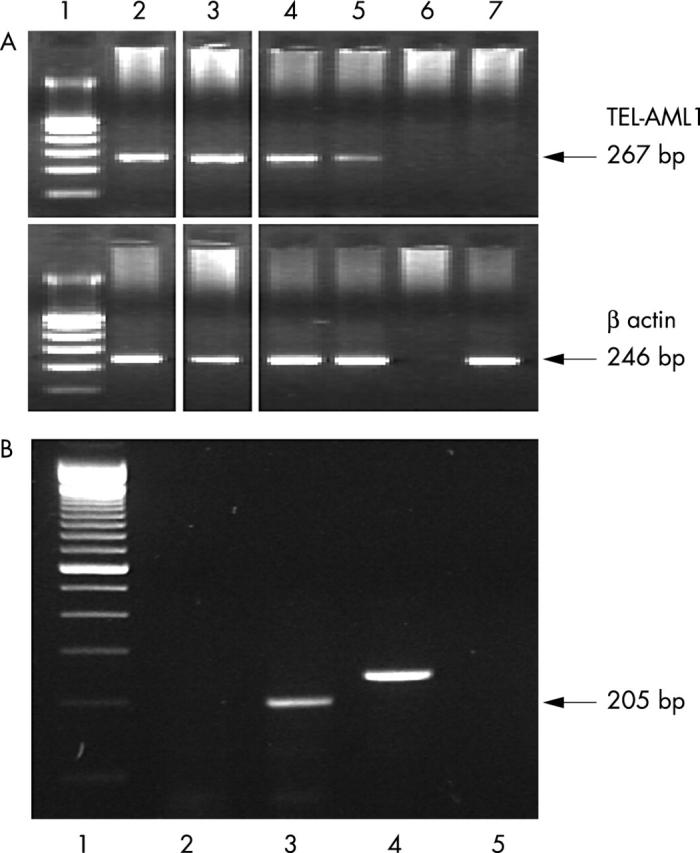
(A) Second round TEL-AML1 transcript showing positive full term infant cord blood samples. Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; 2, positive cord blood (a); 3, positive cord blood (b); 4, 10-4 REH (TEL-AML1+) cells diluted in SV18 (normal lymphoid) cells; 5, as 4, but REH diluted 10-5 with SV18; 6, water (negative) control; 7, normal lymphoid cell line SV18. (B) Second round BCR-ABL transcript from single preterm infant sample (for details, see text). Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; 2, b2a2/b3a2 (p210) transcript; 3, E1a2 (p190) transcript; 4, ß actin positive control; 5, water (negative) control.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrøe M. The risk of X-ray examinations of the lungs in neonates. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1991 May;80(5):489–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1991.tb11891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernaux C., Loos M., Sels A., Huez G., Stryckmans P. Detection of major bcr-abl gene expression at a very low level in blood cells of some healthy individuals. Blood. 1995 Oct 15;86(8):3118–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S., Deininger M., Gora-Tybor J., Goldman J. M., Melo J. V. The presence of typical and atypical BCR-ABL fusion genes in leukocytes of normal individuals: biologic significance and implications for the assessment of minimal residual disease. Blood. 1998 Nov 1;92(9):3362–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayuela J. M., Baruchel A., Orange C., Madani A., Auclerc M. F., Daniel M. T., Schaison G., Sigaux F. TEL-AML1 fusion RNA as a new target to detect minimal residual disease in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1996 Jul 1;88(1):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapple C. L., Faulkner K., Hunter E. W. Energy imparted to neonates during X-ray examinations in a special care baby unit. Br J Radiol. 1994 Apr;67(796):366–370. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-67-796-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenak F. A., McCullough L. B. The limits of viability. J Perinat Med. 1997;25(5):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral J., Forster A., Thompson S., Lampert F., Kaneko Y., Slater R., Kroes W. G., van der Schoot C. E., Ludwig W. D., Karpas A. Acute leukemias of different lineages have similar MLL gene fusions encoding related chimeric proteins resulting from chromosomal translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8538–8542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger M. W., Bose S., Gora-Tybor J., Yan X. H., Goldman J. M., Melo J. V. Selective induction of leukemia-associated fusion genes by high-dose ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1998 Feb 1;58(3):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Wakeford R. Risk of childhood cancer from fetal irradiation. Br J Radiol. 1997 Feb;70:130–139. doi: 10.1259/bjr.70.830.9135438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper E. S., Manktelow B., Field D. J., James D. Prediction of survival for preterm births by weight and gestational age: retrospective population based study. BMJ. 1999 Oct 23;319(7217):1093–1097. doi: 10.1136/bmj.319.7217.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi-Ishimae M., Eguchi M., Ishii E., Miyazaki S., Ueda K., Kamada N., Mizutani S. Breakage and fusion of the TEL (ETV6) gene in immature B lymphocytes induced by apoptogenic signals. Blood. 2001 Feb 1;97(3):737–743. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.3.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner K., Barry J. L., Smalley P. Radiation dose to neonates on a Special Care Baby Unit. Br J Radiol. 1989 Mar;62(735):230–233. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-62-735-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher E. W., Baum J. D., Draper G. The risk of diagnostic radiation of the newborn. Br J Radiol. 1986 Feb;59(698):165–170. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-698-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. M., Bennett C. A., Price C. M., Bruin M. C., Van Wering E. R., Greaves M. Fetal origins of the TEL-AML1 fusion gene in identical twins with leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4584–4588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES D., HEWITT D., STEWART A., WEBB J. Malignant disease in childhood and diagnostic irradiation in utero. Lancet. 1956 Sep 1;271(6940):447–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91923-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K. B., Ford A. M., Repp R., Borkhardt A., Keller C., Eden O. B., Greaves M. F. Backtracking leukemia to birth: identification of clonotypic gene fusion sequences in neonatal blood spots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 9;94(25):13950–13954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhead D. T. Initial events in the cellular effects of ionizing radiations: clustered damage in DNA. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Jan;65(1):7–17. doi: 10.1080/09553009414550021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huda W., Chamberlain C. C., Rosenbaum A. E., Garrisi W. Radiation doses to infants and adults undergoing head CT examinations. Med Phys. 2001 Mar;28(3):393–399. doi: 10.1118/1.1350435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadhim M. A., Marsden S. J., Goodhead D. T., Malcolmson A. M., Folkard M., Prise K. M., Michael B. D. Long-term genomic instability in human lymphocytes induced by single-particle irradiation. Radiat Res. 2001 Jan;155(1 Pt 1):122–126. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2001)155[0122:ltgiih]2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim-Rouille M. H., MacGregor A., Wiedemann L. M., Greaves M. F., Navarrete C. MLL-AF4 gene fusions in normal newborns. Blood. 1999 Feb 1;93(3):1107–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozubek S., Lukásová E., Rýznar L., Kozubek M., Lisková A., Govorun R. D., Krasavin E. A., Horneck G. Distribution of ABL and BCR genes in cell nuclei of normal and irradiated lymphocytes. Blood. 1997 Jun 15;89(12):4537–4545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhart Y., Bashiri A., Maymon E., Shoham-Vardi I., Furman B., Vardi H., Mazor M. Congenital anomalies are an independent risk factor for neonatal morbidity and perinatal mortality in preterm birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2000 May;90(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(99)00196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B. Radiation-induced genomic instability. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998 Dec;74(6):663–671. doi: 10.1080/095530098140925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACMAHON B. Prenatal x-ray exposure and childhood cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 May;28:1173–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. R., Dodd H. E., Draper G. J., Waterhouse J. A., Birch J. M., Cartwright R. A., Hartley A. L., McKinney P. A., Stiller C. A. Congenital abnormalities in children with cancer and their relatives: results from a case-control study (IRESCC). Br J Cancer. 1993 Aug;68(2):357–363. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. V. The diversity of BCR-ABL fusion proteins and their relationship to leukemia phenotype. Blood. 1996 Oct 1;88(7):2375–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforova M. N., Stringer J. R., Blough R., Medvedovic M., Fagin J. A., Nikiforov Y. E. Proximity of chromosomal loci that participate in radiation-induced rearrangements in human cells. Science. 2000 Oct 6;290(5489):138–141. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5489.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro L., Matera L., Ritz J., Levis A., Palumbo A., Biagini G. Establishment of a Ph1-positive human cell line (BV173). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Mar;70(3):447–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Behm F. G., Crist W. M. Clinical and biologic relevance of immunologic marker studies in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1993 Jul 15;82(2):343–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Kane J. R., Crist W. M. Biology and treatment of infant leukemias. Leukemia. 1995 May;9(5):762–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie J. M. Perinatal management at the lower margin of viability. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996 May;74(3):F214–F218. doi: 10.1136/fn.74.3.f214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Jasin M. Frequent chromosomal translocations induced by DNA double-strand breaks. Nature. 2000 Jun 8;405(6787):697–700. doi: 10.1038/35015097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romana S. P., Mauchauffé M., Le Coniat M., Chumakov I., Le Paslier D., Berger R., Bernard O. A. The t(12;21) of acute lymphoblastic leukemia results in a tel-AML1 gene fusion. Blood. 1995 Jun 15;85(12):3662–3670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglio G., Pane F., Gottardi E., Frigeri F., Buonaiuto M. R., Guerrasio A., de Micheli D., Parziale A., Fornaci M. N., Martinelli G. Consistent amounts of acute leukemia-associated P190BCR/ABL transcripts are expressed by chronic myelogenous leukemia patients at diagnosis. Blood. 1996 Feb 1;87(3):1075–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittger S., Wörmann B., Hiddemann W., Griesinger F. Partial tandem duplications of the MLL gene are detectable in peripheral blood and bone marrow of nearly all healthy donors. Blood. 1998 Sep 1;92(5):1728–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer A., Granter N. Leukemia patient-derived lymphoblastoid cell lines exhibit increased induction of leukemia-associated transcripts following high-dose irradiation. Exp Hematol. 1999 Sep;27(9):1397–1401. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A., Kneale G. W. Radiation dose effects in relation to obstetric x-rays and childhood cancers. Lancet. 1970 Jun 6;1(7658):1185–1188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller C. A., Allen M. B., Eatock E. M. Childhood cancer in Britain: the National Registry of Childhood Tumours and incidence rates 1978-1987. Eur J Cancer. 1995 Nov;31A(12):2028–2034. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton P. M., Arthur R. J., Taylor C., Stringer M. D. Ionising radiation from diagnostic x rays in very low birthweight babies. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1998 May;78(3):F227–F229. doi: 10.1136/fn.78.3.f227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trka J., Zuna J., Hrusák O., Michalová K., Muziková K., Kalinová M., Horák J., Starý J. No evidence for MLL/AF4 expression in normal cord blood samples. Blood. 1999 Feb 1;93(3):1106–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Herman-Hatten K., Crotty M. L., Sensel M. G., Sather H. N., Tuel-Ahlgren L., Sarquis M. B., Bostrom B., Nachman J. B., Steinherz P. G. Clinical significance of MLL-AF4 fusion transcript expression in the absence of a cytogenetically detectable t(4;11)(q21;q23) chromosomal translocation. Blood. 1998 Aug 1;92(3):810–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uphoff C. C., MacLeod R. A., Denkmann S. A., Golub T. R., Borkhardt A., Janssen J. W., Drexler H. G. Occurrence of TEL-AML1 fusion resulting from (12;21) translocation in human early B-lineage leukemia cell lines. Leukemia. 1997 Mar;11(3):441–447. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall B. F., Hart D. Revised radiation doses for typical X-ray examinations. Report on a recent review of doses to patients from medical X-ray examinations in the UK by NRPB. National Radiological Protection Board. Br J Radiol. 1997 May;70(833):437–439. doi: 10.1259/bjr.70.833.9227222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh A. P., Beare D. M., Arlett C. F., Green M. H., Cole J. Comparative human cellular radiosensitivity: IV. The increased sensitivity of human neonatal cord blood lymphocytes to gamma-irradiation compared with lymphocytes from children and adults. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Mar;59(3):767–776. doi: 10.1080/09553009114550671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemels J. L., Cazzaniga G., Daniotti M., Eden O. B., Addison G. M., Masera G., Saha V., Biondi A., Greaves M. F. Prenatal origin of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children. Lancet. 1999 Oct 30;354(9189):1499–1503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)09403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemels J. L., Ford A. M., Van Wering E. R., Postma A., Greaves M. Protracted and variable latency of acute lymphoblastic leukemia after TEL-AML1 gene fusion in utero. Blood. 1999 Aug 1;94(3):1057–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotnda P., Garcia F., Peuchmaur M., Grandchamp B., Duval M., Lemonnier F., Vilmer E., Langlade-Demoyen P. Cytotoxic T cell response against the chimeric ETV6-AML1 protein in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1998 Jul 15;102(2):455–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun C., Senju S., Fujita H., Tsuji Y., Irie A., Matsushita S., Nishimura Y. Augmentation of immune response by altered peptide ligands of the antigenic peptide in a human CD4+ T-cell clone reacting to TEL/AML1 fusion protein. Tissue Antigens. 1999 Aug;54(2):153–161. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.1999.540206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


