Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. T., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Simultaneous antibiotic levels in "breakthrough" gram-negative rod bacteremia. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barriere S. L., Ely E., Kapusnik J. E., Gambertoglio J. G. Analysis of a new method for assessing activity of combinations of antimicrobials: area under the bactericidal activity curve. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16(1):49–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
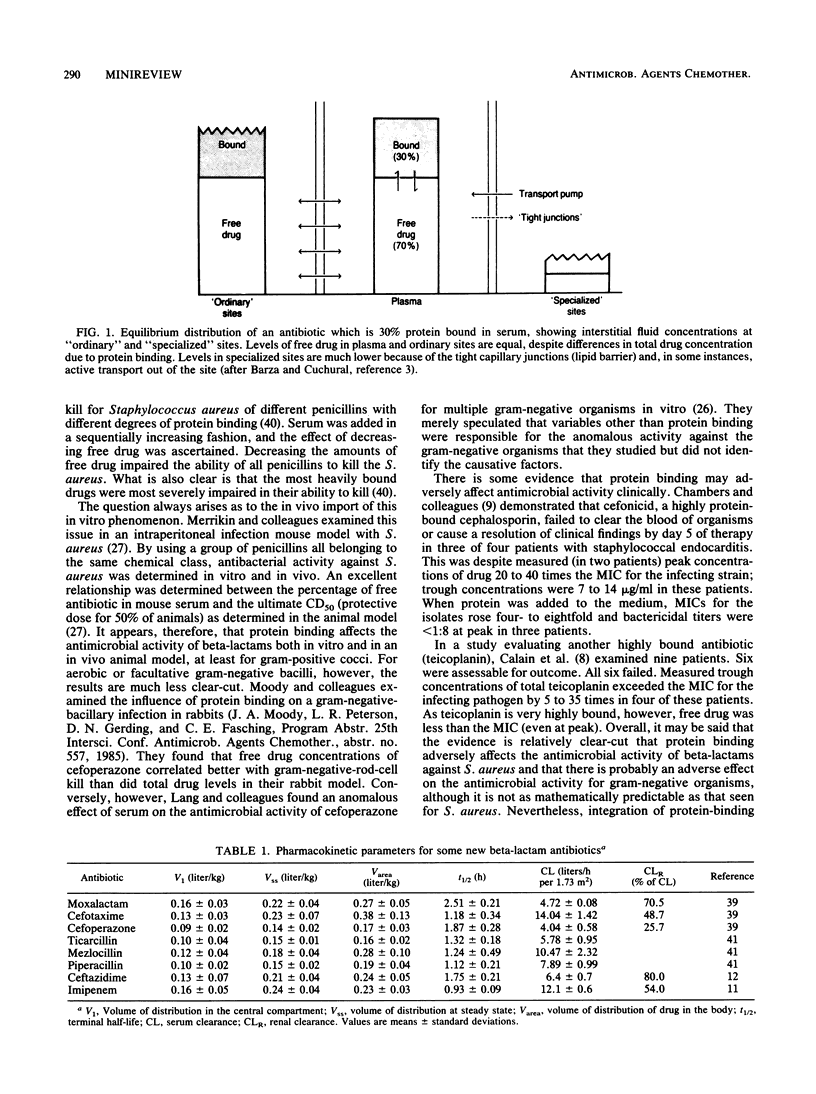
- Barza M., Cuchural G. General principles of antibiotic tissue penetration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):59–75. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser J. In-vitro model for simultaneous simulation of the serum kinetics of two drugs with different half-lives. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):125–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Ketchel S. J., Rodriguez V. A randomized study of carbenicillin plus cefamandole or tobramycin in the treatment of febrile episodes in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1979 Oct;67(4):608–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundtzen R. W., Gerber A. U., Cohn D. L., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):28–37. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C. I., Drusano G. L., Tatem B. A., Standiford H. C. Postantibiotic effect of imipenem on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):678–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Krause K. H., Vaudaux P., Auckenthaler R., Lew D., Waldvogel F., Hirschel B. Early termination of a prospective, randomized trial comparing teicoplanin and flucloxacillin for treating severe staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):187–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Mills J., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Failure of a once-daily regimen of cefonicid for treatment of endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Nov-Dec;6 (Suppl 4):S870–S874. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_4.s870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
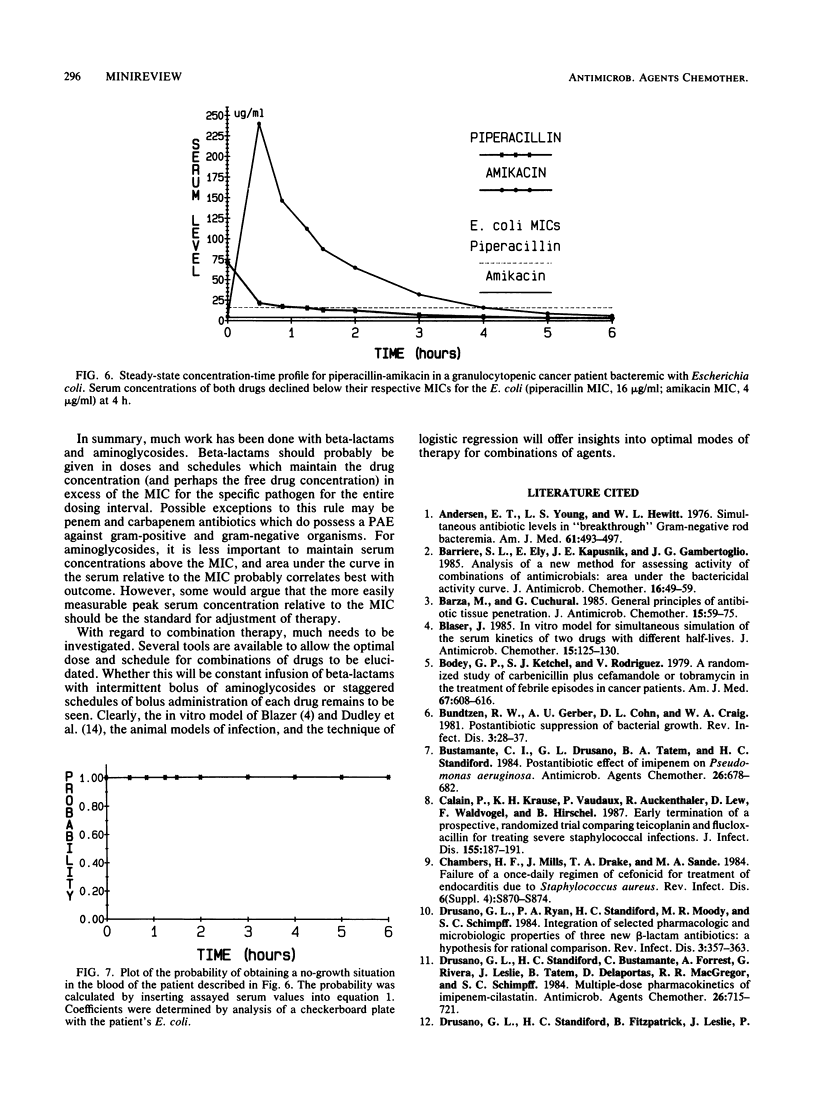
- Drusano G. L., Ryan P. A., Standiford H. C., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C. Integration of selected pharmacologic and microbiologic properties of three new beta-lactam antibiotics: a hypothesis for rational comparison. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):357–363. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Standiford H. C., Bustamante C., Forrest A., Rivera G., Leslie J., Tatem B., Delaportas D., MacGregor R. R., Schimpff S. C. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of imipenem-cilastatin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):715–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Standiford H. C., Fitzpatrick B., Leslie J., Tangtatsawasdi P., Ryan P., Tatem B., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime and moxalactam and their microbiological correlates in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):388–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G., Standiford H., Ryan P., McNamee W., Tatem B., Schimpff S. Correlation of predicted serum bactericidal activities and values measured in volunteers. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;5(1):88–92. doi: 10.1007/BF02013475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
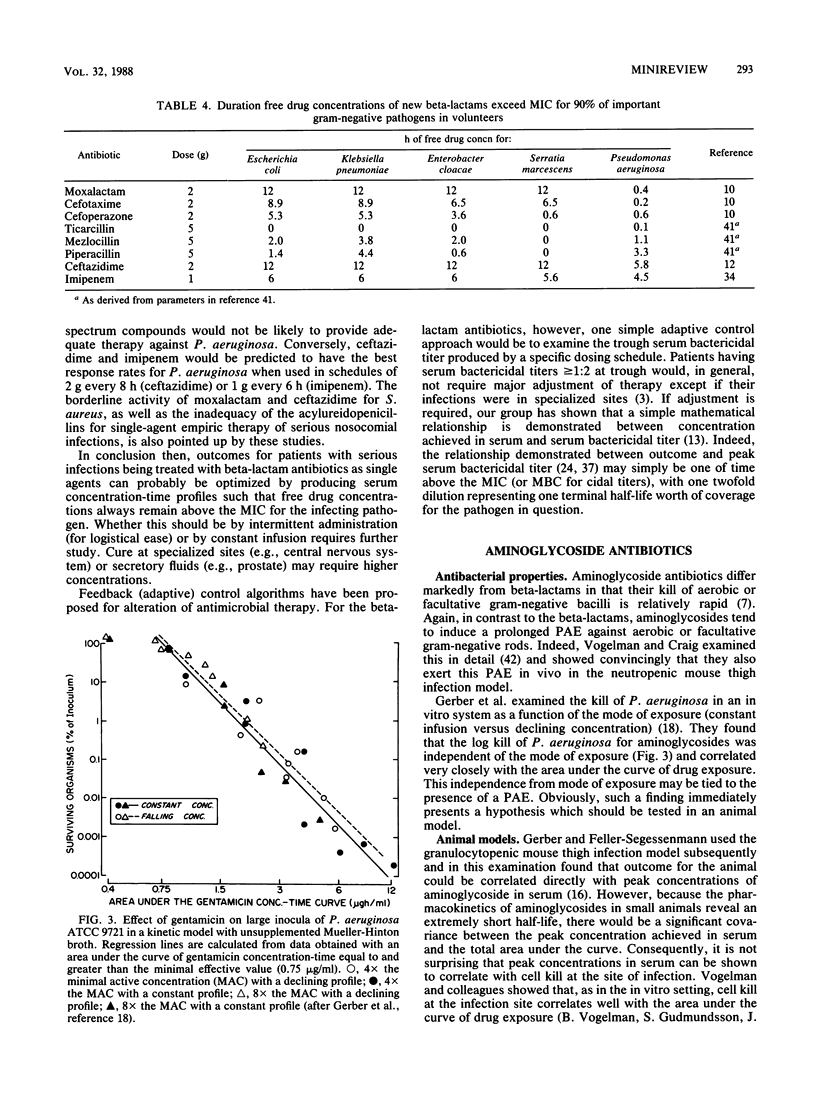
- Dudley M. N., Mandler H. D., Gilbert D., Ericson J., Mayer K. H., Zinner S. H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intravenous ciprofloxacin. Studies in vivo and in an in vitro dynamic model. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
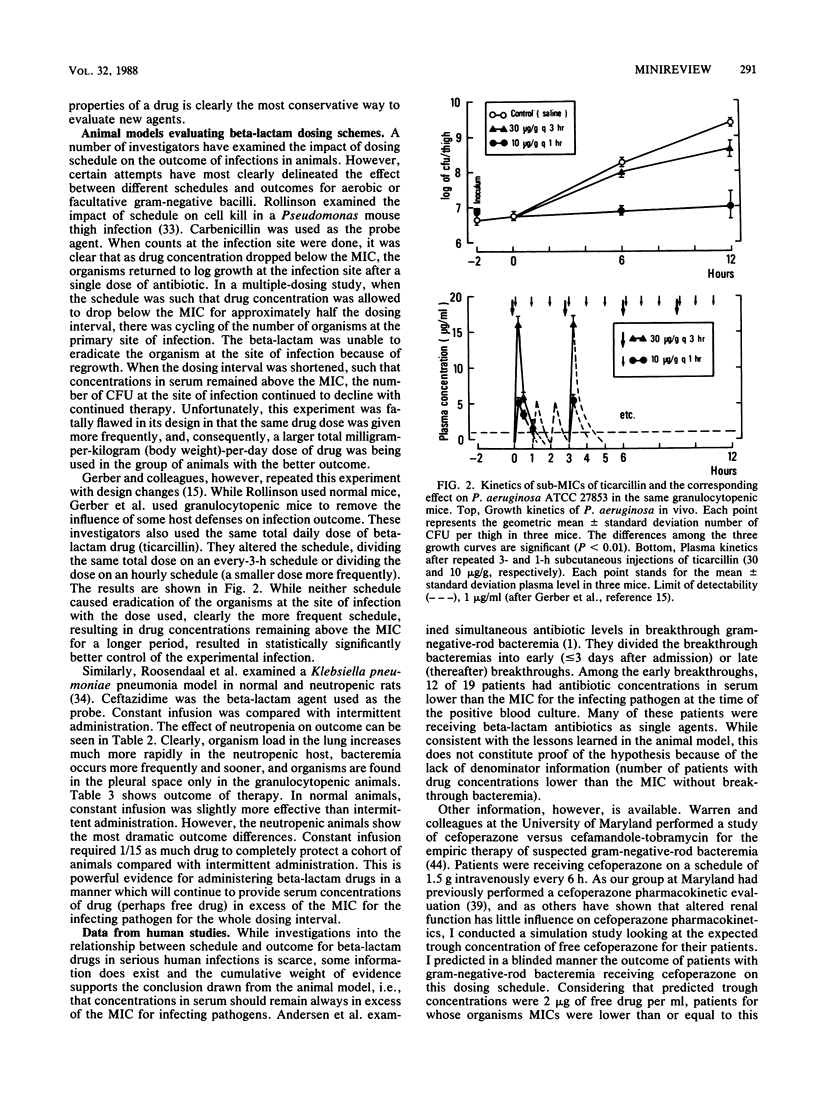
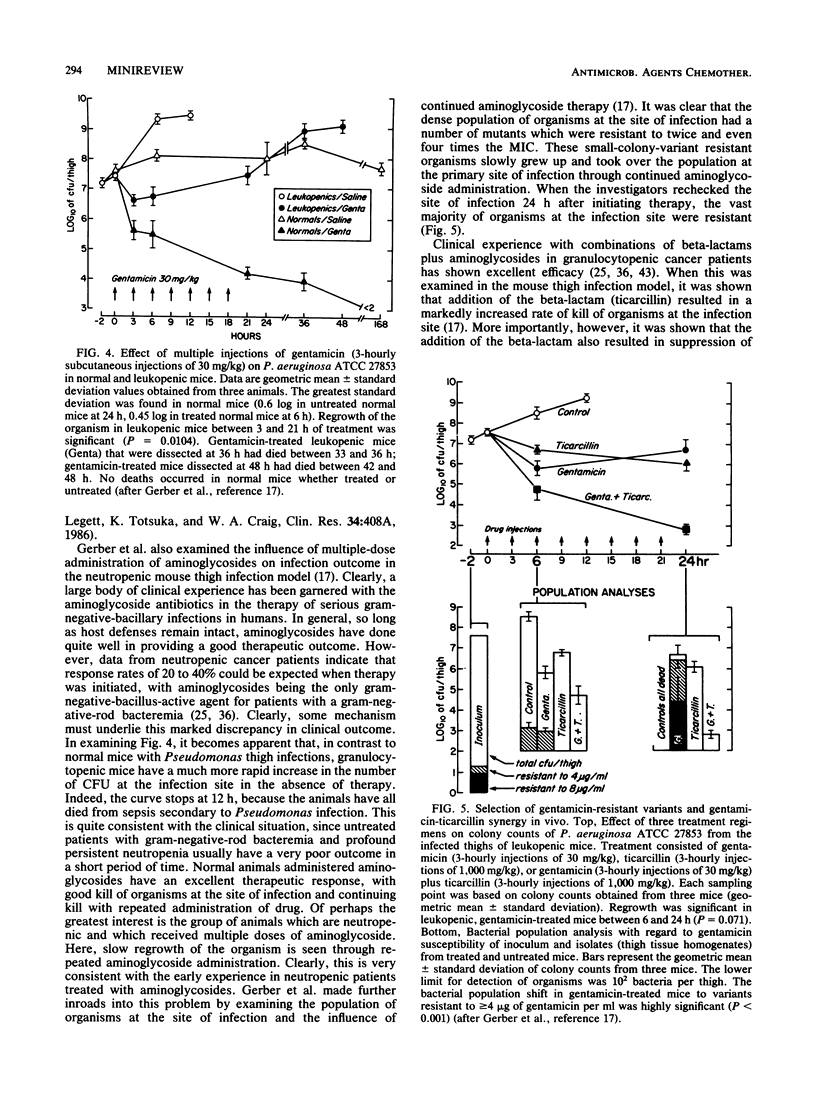
- Gerber A. U., Craig W. A., Brugger H. P., Feller C., Vastola A. P., Brandel J. Impact of dosing intervals on activity of gentamicin and ticarcillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in granulocytopenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):910–917. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Feller-Segessenmann C. In-vivo assessment of in-vitro killing patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):201–206. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Vastola A. P., Brandel J., Craig W. A. Selection of aminoglycoside-resistant variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vivo model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):691–697. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Wiprächtiger P., Stettler-Spichiger U., Lebek G. Constant infusions vs. intermittent doses of gentamicin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):554–560. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R., Moody J. A., Fasching C. E. Mezlocillin, ceftizoxime, and amikacin alone and in combination against six Enterobacteriaceae in a neutropenic site in rabbits. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):207–219. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstedt B., Walder M. Influence of serum protein binding and mode of administration on penetration of five cephalosporins into subcutaneous tissue fluid in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):783–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Thompson B., Calia F. M. Comparative activities of piperacillin, ceftazidime, and amikacin, alone and in all possible combinations, against experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in neutropenic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):735–739. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Thompson B. Efficacy of single-agent therapy with azlocillin, ticarcillin, and amikacin and beta-lactam/amikacin combinations for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in granulocytopenic rats. Am J Med. 1986 May 30;80(5C):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. J., Bodey G. P., Valdivieso M., Rodriguez V. A randomized comparative trial of three aminoglycosides--comparison of continuous infusions of gentamicin, amikacin and sisomicin combined with carbenicillin in the treatment of infections in neutropenic patients with malignancies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Mar;58(2):159–170. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197903000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Daneau D., Swings G., Weerts D. Antibacterial activity in serum and urine as a therapeutic guide in bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang S. D., Cameron G. L., Mullins P. R. Anomalous effect of serum on the antimicrobial activity of cefoperazone. Drugs. 1981;22 (Suppl 1):52–59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198100221-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrikin D. J., Briant J., Rolinson G. N. Effect of protein binding on antibiotic activity in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Mar;11(3):233–238. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Lietman P. S., Smith C. R. Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):93–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. Association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with therapeutic outcome in gram-negative pneumonia. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90358-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. The association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):443–448. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone P., Parsons T. M., Pattison J. R., Slack R. C., Garfield-Davies D., Hughes K. Experience in monitoring gentamicin therapy during treatment of serious gram-negative sepsis. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 16;1(5906):477–481. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5906.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Stratton C. W. Serum dilution test for bactericidal activity. II. Standardization and correlation with antimicrobial assays and susceptibility tests. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):196–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N. Basis and results of therapy with Beta-lactam antibiotics in experimental infections. Infection. 1980;Suppl 1:30–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01644932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
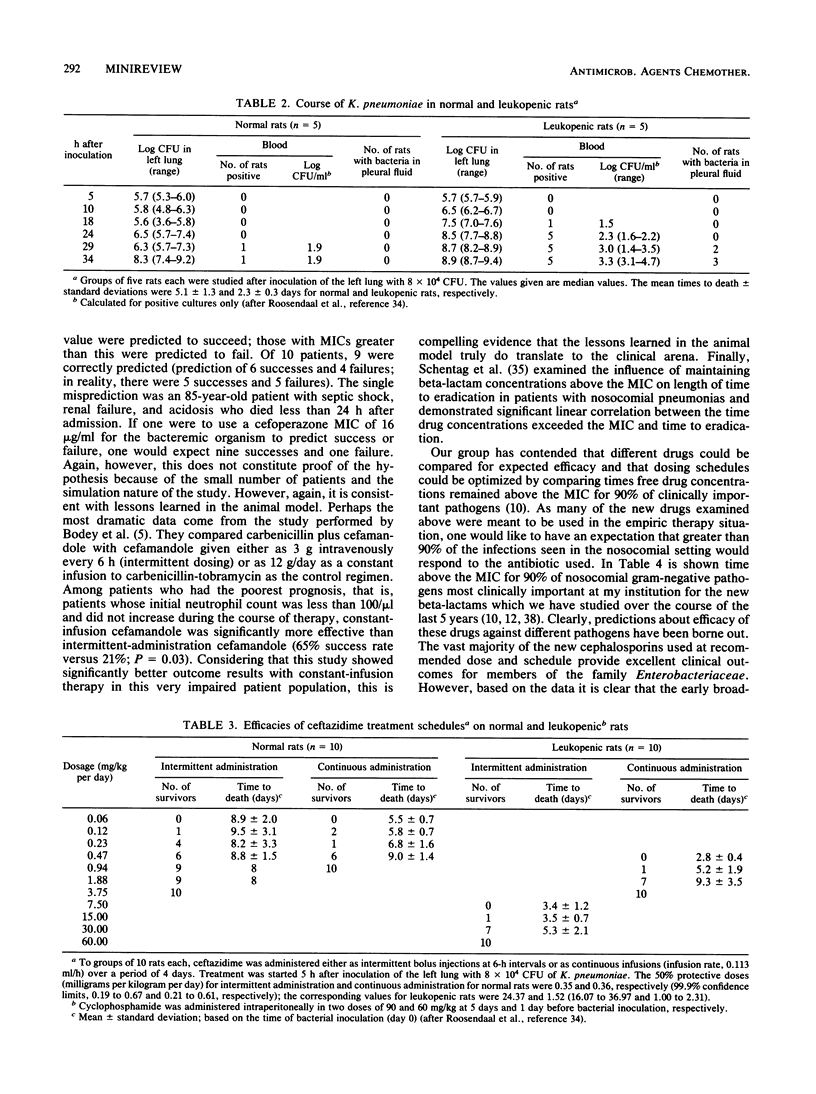
- Roosendaal R., Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berghe-van Raffe M., Michel M. F. Continuous versus intermittent administration of ceftazidime in experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in normal and leukopenic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Smith I. L., Swanson D. J., DeAngelis C., Fracasso J. E., Vari A., Vance J. W. Role for dual individualization with cefmenoxime. Am J Med. 1984 Dec 21;77(6A):43–50. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(84)80074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S., Satterlee W., Young V. M., Serpick A. Empiric therapy with carbenicillin and gentamicin for febrile patients with cancer and granulocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 13;284(19):1061–1065. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105132841904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Klastersky J. Significance of serum bactericidal activity in gram-negative bacillary bacteremia in patients with and without granulocytopenia. Am J Med. 1984 Mar;76(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90662-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. C., Drusano G. L., Bustamante C. I., Rivera G., Forrest A., Tatem B., Leslie J., Moody M. Imipenem coadministered with cilastatin compared with moxalactam: integration of serum pharmacokinetics and microbiologic activity following single-dose administration to normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):412–417. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompsett R., Shultz S., McDermott W. The Relation of Protein Binding to the Pharmacology and Antibacterial Activity of Penicillins X, G, Dihydro F, and K. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):581–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.581-595.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viollier A. F., Standiford H. C., Drusano G. L., Tatem B. A., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C. Comparative pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activity of mezlocillin, ticarcillin and piperacillin, with and without gentamicin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 May;15(5):597–606. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B. S., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic effects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):37–46. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Fortner C. L., Standiford H. C., Wiernik P. H. Piperacillin or ticarcillin plus amikacin. A double-blind prospective comparison of empiric antibiotic therapy for febrile granulocytopenic cancer patients. Am J Med. 1981 Dec;71(6):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. The relevance of pharmacokinetics to in-vitro models: protein binding--does it matter? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):77–83. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]