Abstract
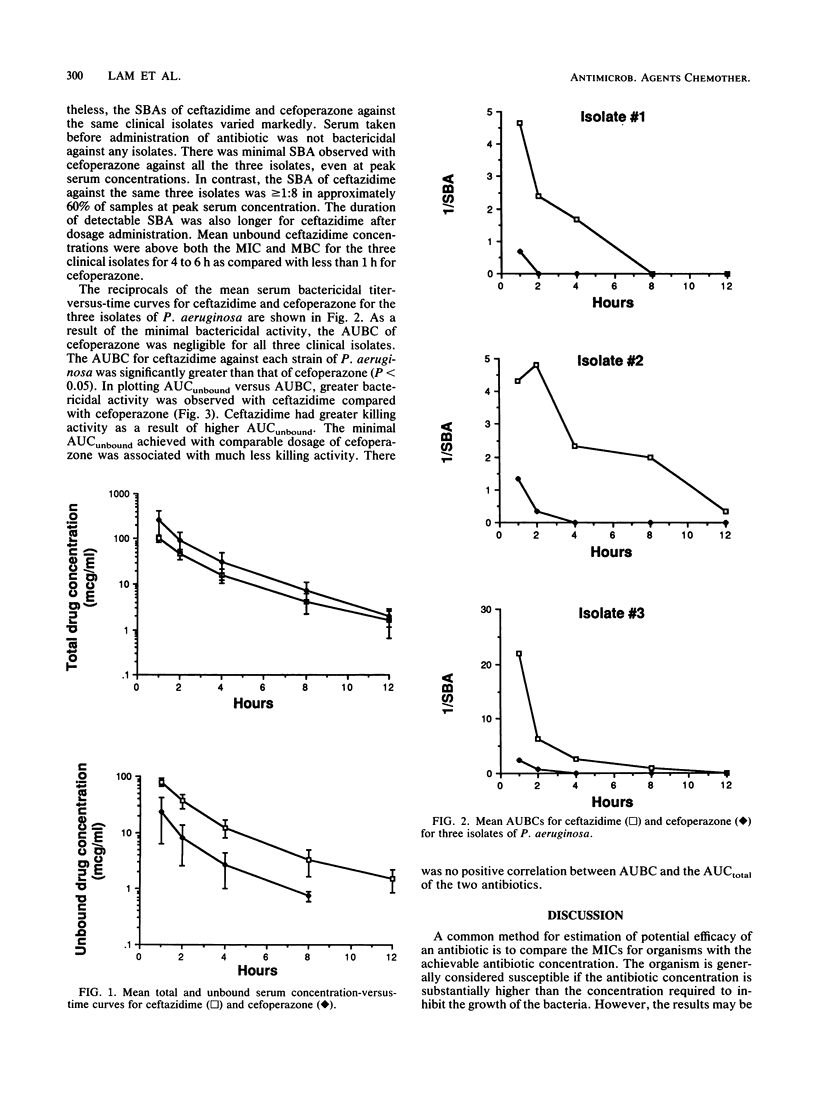
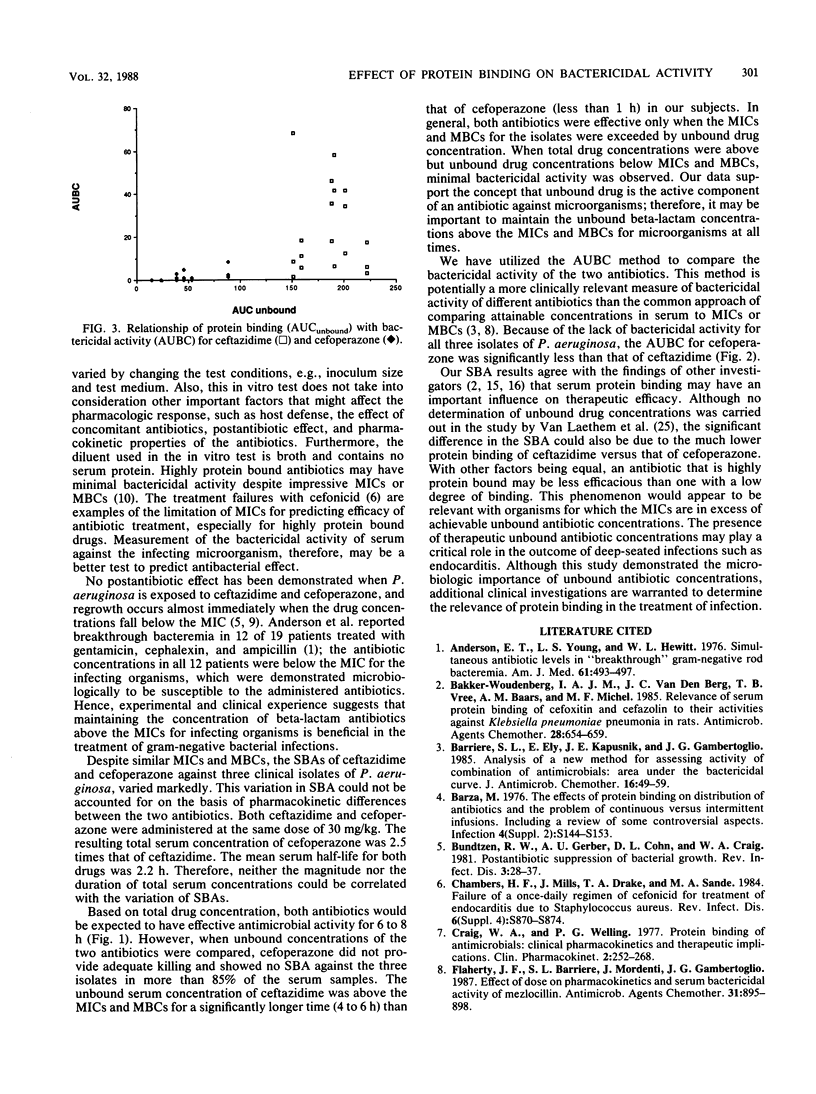
The effect of protein binding on antibiotic efficacy is controversial. The pharmacologic effect of an antibiotic is believed to be related to its unbound concentration at the site of infection. It is unknown whether antibiotics with a low degree of serum protein binding are clinically superior to antibiotics that are highly protein bound. In a randomized, crossover investigation, the serum bactericidal activities of a single dose of ceftazidime (30 mg/kg) and cefoperazone (30 mg/kg) were studied in six healthy volunteers against three clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for which both antibiotics had similar MICs and MBCs. Serum samples were collected over 12 h. The total and unbound antibiotic concentrations were determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Mean peak total concentrations of ceftazidime and cefoperazone in serum were 101.7 +/- 18.6 and 264.1 +/- 149.6 micrograms/ml, respectively. Due to its lower protein binding (21 +/- 6%), ceftazidime had significantly higher unbound concentrations in serum than did the highly bound cefoperazone (91.5 +/- 2%). Mean peak unbound concentrations were 78.5 +/- 12.5 and 24.2 +/- 17.8 micrograms/ml for ceftazidime and cefoperazone, respectively. The unbound concentration of ceftazidime at each sampling time was higher than that of cefoperazone. Although total concentrations were consistently higher than the MICs, serum containing cefoperazone showed minimal bactericidal activity against the isolates. In contrast, despite lower total concentrations, ceftazidime had greater antibacterial activity than cefoperazone. Serum bactericidal activity was more closely related to unbound rather than total antibiotic concentrations. Our data support the concept that only the unbound drug is microbiologically active.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. T., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Simultaneous antibiotic levels in "breakthrough" gram-negative rod bacteremia. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berg J. C., Vree T. B., Baars A. M., Michel M. F. Relevance of serum protein binding of cefoxitin and cefazolin to their activities against Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):654–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barriere S. L., Ely E., Kapusnik J. E., Gambertoglio J. G. Analysis of a new method for assessing activity of combinations of antimicrobials: area under the bactericidal activity curve. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16(1):49–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundtzen R. W., Gerber A. U., Cohn D. L., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):28–37. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Mills J., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Failure of a once-daily regimen of cefonicid for treatment of endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Nov-Dec;6 (Suppl 4):S870–S874. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_4.s870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Welling P. G. Protein binding of antimicrobials: clinical pharmacokinetic and therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 Jul-Aug;2(4):252–268. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty J. F., Barriere S. L., Mordenti J., Gambertoglio J. G. Effect of dose on pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activity of mezlocillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):895–898. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso S., Meinardi G., de Carneri I., Tamassia V. New in vitro model to study the effect of antibiotic concentration and rate of elimination on antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):570–576. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. In vitro veritas? Antimicrobial susceptibility tests and their clinical relevance. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):380–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell A., Sutherland R., Rolinson G. N. Effect of protein binding on levels of ampicillin and cloxacillin in synovial fluid. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Sep-Oct;13(5):724–732. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972135part1724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Craig W. A., Kornguth M., Monson R. Influence of binding on the pharmacologic activity of antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Nov 26;226:214–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb20483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang S. D., Cameron G. L., Mullins P. R. Anomalous effect of serum on the antimicrobial activity of cefoperazone. Drugs. 1981;22 (Suppl 1):52–59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198100221-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H., Goslings W. R., Noach E. L. Cloxacillin and nafcillin: serum binding and its relationship to antibacterial effect in mice. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):170–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrikin D. J., Briant J., Rolinson G. N. Effect of protein binding on antibiotic activity in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Mar;11(3):233–238. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mückter H., Sous H., Poszich G., Arend P. Comparative studies of the activity of ciclacillin and dicloxacillin. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(3-4):183–189. doi: 10.1159/000221925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Prediction of cefazolin penetration in high- and low-protein-containing extravascular fluid: new method for performing simultaneous studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):533–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Sherertz R. J., Zak O., Strausbaugh L. J. Cephalosporin antibiotics in therapy of experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S161–S168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. S., Trott A., Phair J. P., Watanakunakorn C. A method for measurement of antibiotics in human interstitial fluid. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):492–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompsett R., Shultz S., McDermott W. The Relation of Protein Binding to the Pharmacology and Antibacterial Activity of Penicillins X, G, Dihydro F, and K. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):581–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.581-595.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etta L. L., Kravitz G. R., Russ T. E., Fasching C. E., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Effect of method of administration on extravascular penetration of four antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Laethem Y., Lagast H., Husson M., Klastersky J. Serum bactericidal activity of cefoperazone and ceftazidime at increasing dosages against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Nov;12(5):475–480. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Protein binding of beta-lactams: the effects on activity and pharmacology particularly tissue penetration. I. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jul;12(1):1–18. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Protein binding of beta-lactams: the effects on activity and pharmacology particularly tissue penetration. II. Studies in man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):105–118. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


