Abstract
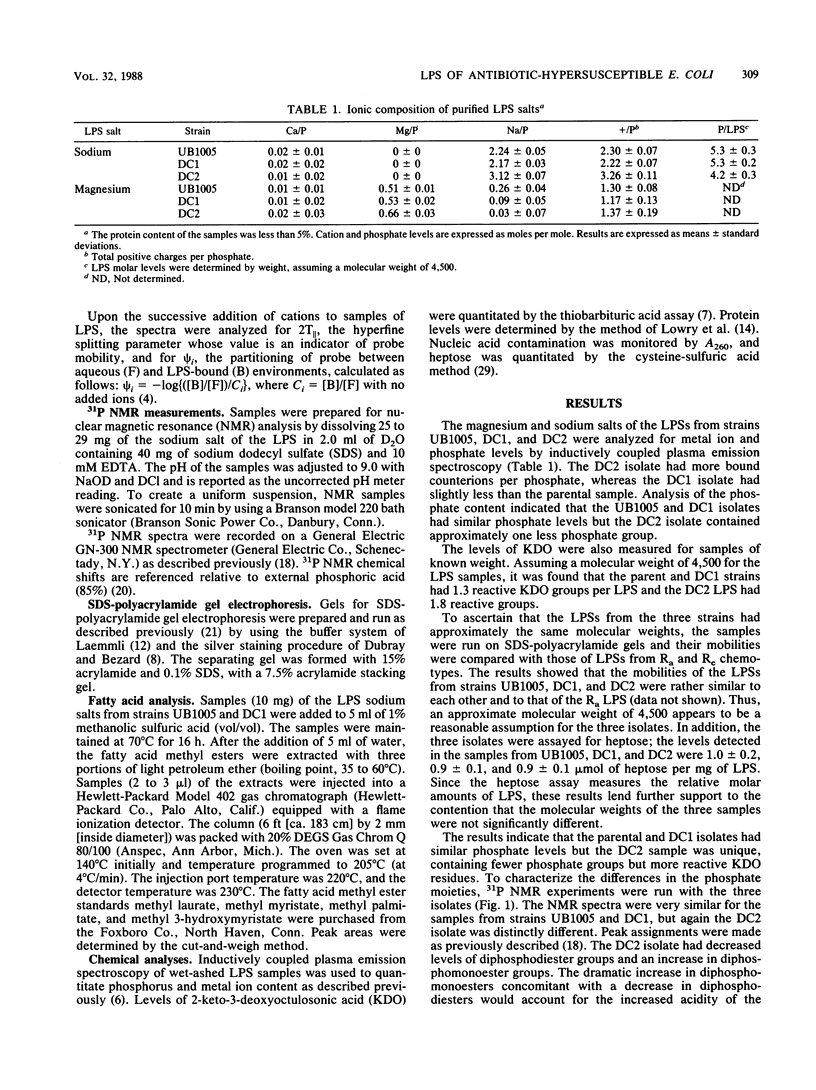
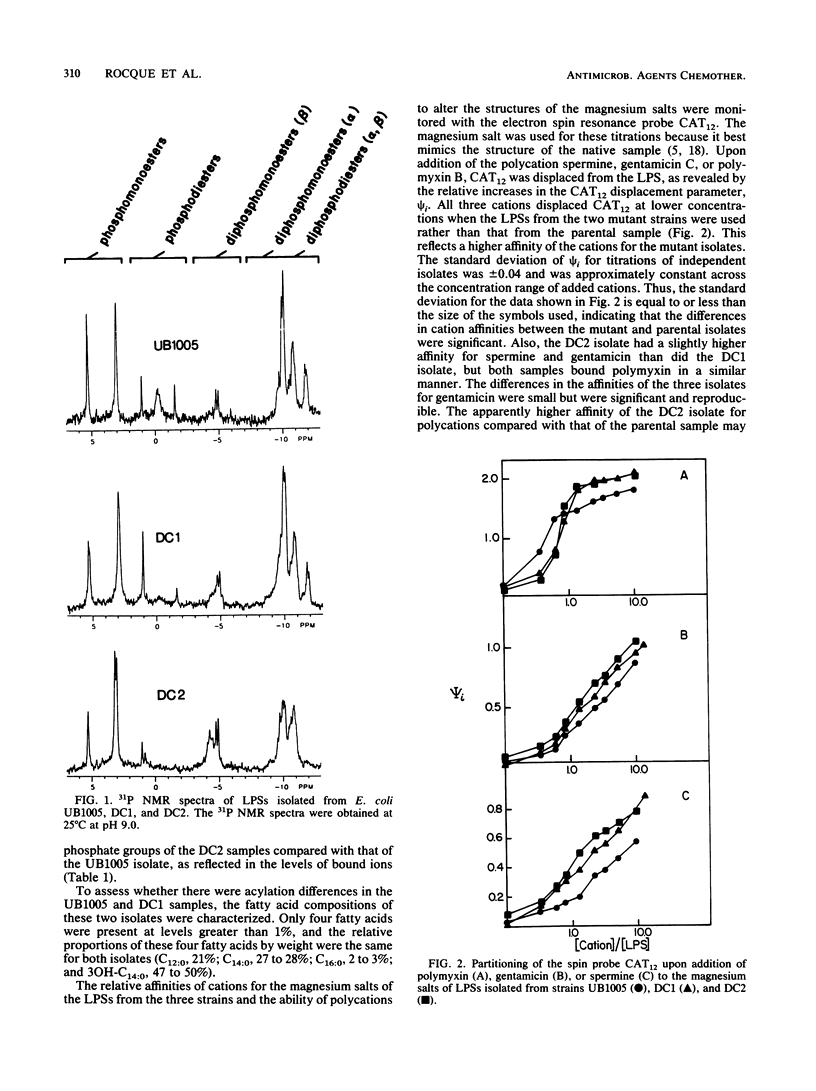
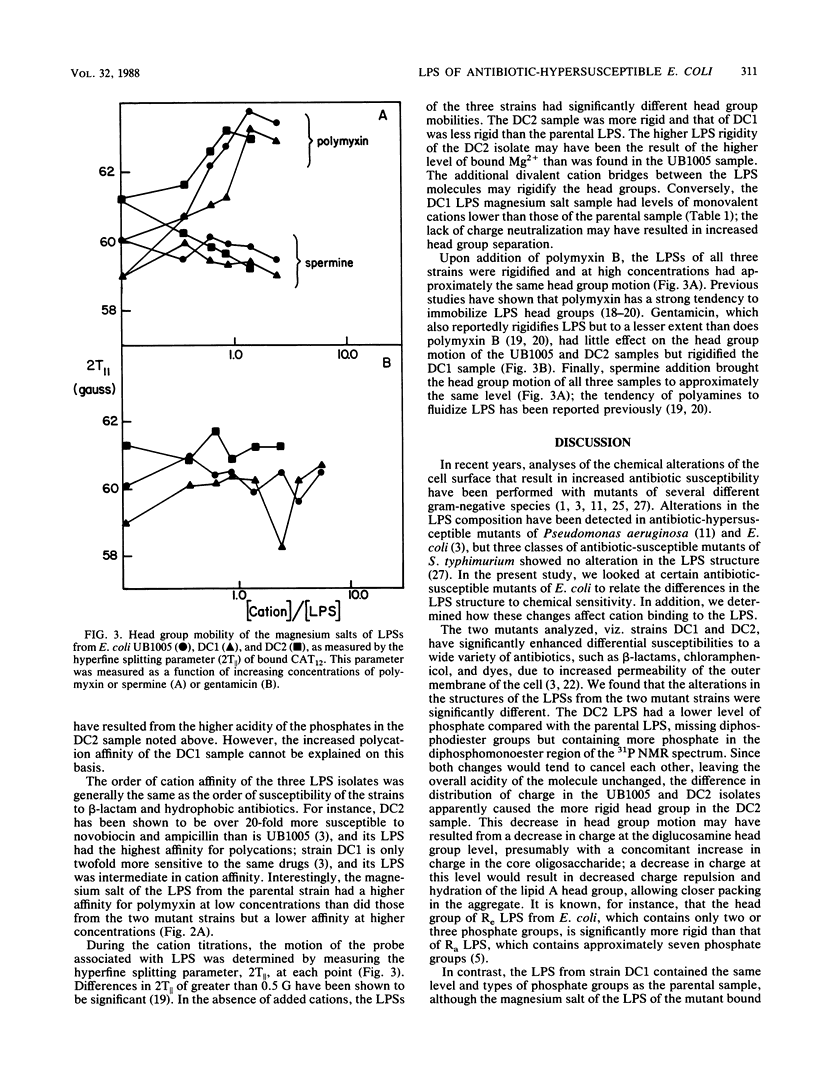
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) samples isolated from a parent and two antibiotic-hypersusceptible mutant strains of Escherichia coli were analyzed for polycation affinity and level of binding. Purified salts of the LPSs from the parent strain, UB1005, and from one of the mutant strains, DC1, bound similar amounts of sodium and magnesium, but the samples from the second mutant strain, DC2, had significantly greater amounts of counterions bound per phosphate than did the other two isolates. The 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectra indicated that, compared with LPS from the parental strain, the sample from strain DC1 was similar but the DC2 sample contained fewer diphosphodiester and more diphosphomonoester groups. Motion within the lipid A head group regions of the magnesium salts of the three isolates was dramatically different, as revealed by an electron spin resonance probe. The binding of the cations to the LPS aggregates was measured by the displacement of this cationic spin probe from the LPS samples. The polycations polymyxin, gentamicin, and spermine displaced more probe from samples of the two mutant strains than from that of the parental strain. The sample from the most antibiotic-susceptible strain, DC2, had the highest affinity for all the polyvalent cations tested. The results indicate that antibiotic hypersusceptibility can result from at least two distinct alterations in LPS structure. The decrease in diphosphodiesters and increase in diphosphomonoesters in the LPS of the DC2 sample resulted in more acidic phosphate moieties and a more antibiotic-susceptible cell. In contrast, the alterations in the LPS of DC1 that resulted in antibiotic hypersusceptibility of the cell were not in the phosphate substituents. In both mutants, however, hypersusceptibility resulted in an alteration in LPS structure that increased the affinity of the molecules for polycations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Caldwell C. R., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. A cationic electron spin resonance probe used to analyze cation interactions with lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Physical properties of defined lipopolysaccharide salts. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2007–2013. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Tonsager S., McGroarty E. J. Quantitation of metal cations bound to membranes and extracted lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson P., Nordström K., Normark S. Outer penetration barrier of Escherichia coli K-12: kinetics of the uptake of gentian violet by wild type and envelope mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.893-900.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. M., Walker J. R. Genetic analysis of acrA and lir mutations of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1301–1302. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1301-1302.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H. Genetic determination of resistance to acriflavine, phenethyl alcohol, and sodium dodecyl sulfate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):987–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.987-996.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S. Genetics of a chain-forming mutant of Escherichia coli. Transduction and dominance of the envA gene mediating increased penetration to some antibacterial agents. Genet Res. 1970 Aug;16(1):63–78. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Fesik S. W., McGroarty E. J. Decreased binding of antibiotics to lipopolysaccharides from polymyxin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Binding of polycationic antibiotics and polyamines to lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1256-1261.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Physical properties of short- and long-O-antigen-containing fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111:B4. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.116-122.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Clark D. C., Wotton S. Indirect method for assessing the penetration of beta-lactamase-nonsusceptible penicillins and cephalosporins in Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):215–218. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Kuo T. T., MacPhee D. G. The effect of defined lipopolysaccharide core defects upon antibiotic resistances of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Markowitz O., Hasin M., Razin S. Outer membrane proteins of smooth and rough strains of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):141–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukupolvi S., Vaara M., Helander I. M., Viljanen P., Mäkelä P. H. New Salmonella typhimurium mutants with altered outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.704-712.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Increased outer membrane resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate and cations in novel lipid A mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.426-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


