Abstract
Background: Although it is a well known phenomenon, limited normative data on neonatal weight loss and subsequent gain are available, making it hard to assess individual children with prolonged weight loss.
Objective: To establish, using data from a large prospective population based cohort study, norms and limits for postnatal weight loss and its impact on current growth reference charts.
Method: A cohort of 961 term infants were recruited at birth and followed using parental questionnaires and community nursing returns. Routine weights were collected for half the cohort at 5 days and for all at 12 days and 6 weeks.
Results: Less weight loss was seen than the 3–6% suggested by previous studies, but one in five infants had not regained their birth weight by 12 days. Those lightest at birth showed least weight loss. Twenty six (3%) children had more than 10% weight loss, but none showed evidence of major organic disease. Actual weights in the first fortnight are half to one centile space lower than growth charts suggest, while birthweight centiles for children born at 37 weeks were two centile spaces lower.
Conclusions: Neonatal weight loss is brief, with few children remaining more than 10% below birth weight after 5 days. Growth charts are misleading in the first 2 weeks, because they make no allowance for neonatal weight loss.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (149.9 KB).
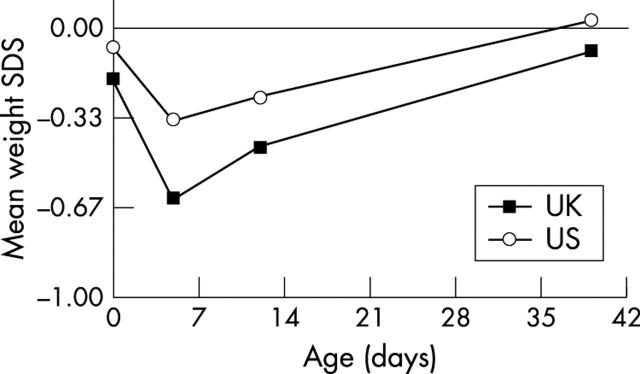
Figure 1 .
Neonatal weight standard deviation scores (SDS), UK and US standards compared. 0 = 50th centile; –0.67SDS = 25th centile.
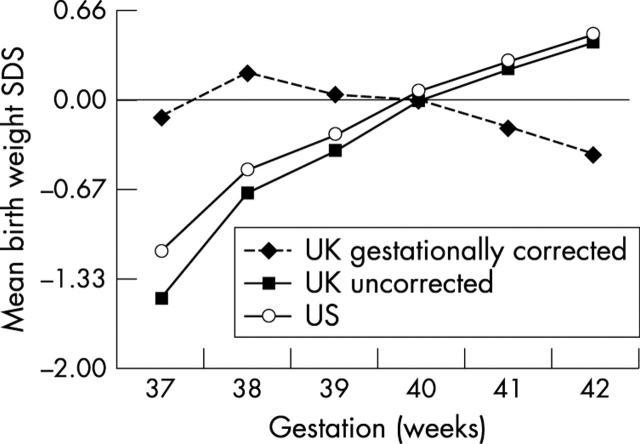
Figure 2 .
Birth weight standard deviation scores (SDS) by gestation, US references compared with UK, with and without gestational correction. 0 = 50th centile; –2 SDS = 2nd centile.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avoa A., Fischer P. R. The influence of perinatal instruction about breast-feeding on neonatal weight loss. Pediatrics. 1990 Aug;86(2):313–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. J., King F. J., Lucas A. Linear growth in the early neonatal period. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jul;65(7 Spec No):707–708. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.7_spec_no.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzunga A., Fischer P. R. Neonatal weight loss in rural Zaire. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1990;10(2):159–163. doi: 10.1080/02724936.1990.11747424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. V., Cole T. J., Chinn S., Jones P. R., White E. M., Preece M. A. Cross sectional stature and weight reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jul;73(1):17–24. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzawa C. W. Adipose tissue in human infancy and childhood: an evolutionary perspective. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1998;Suppl 27:177–209. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8644(1998)107:27+<177::aid-ajpa7>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisels M. J., Gifford K., Antle C. E., Leib G. R. Jaundice in the healthy newborn infant: a new approach to an old problem. Pediatrics. 1988 Apr;81(4):505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchini G., Stock S. Thirst and vasopressin secretion counteract dehydration in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1997 May;130(5):736–739. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(97)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. E., Rogers R. R., Ziegler E. E., Fomon S. J. Gain in weight and length during early infancy. Early Hum Dev. 1989 Jul;19(4):223–239. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(89)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd R. W., Oxborough D. B., Holt T. L., Thomas B. J., Thong Y. H. Longitudinal study of the body composition of weight gain in exclusively breast-fed and intake-measured whey-based formula-fed infants to age 3 months. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Sep-Oct;7(5):732–739. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198809000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M., Booth I. W., Buckler J. M. H., Cameron N., Cole T. J., Healy M. J. R., Hulse J. A., Preece M. A., Reilly J. J., Williams A. F. Growth reference charts for use in the United Kingdom. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Jan;86(1):11–14. doi: 10.1136/adc.86.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M., Matthews J. N., Waterston A., Aynsley-Green A. What is a normal rate of weight gain in infancy? Acta Paediatr. 1994 Apr;83(4):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb18118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M. Who comes to be weighed: an exception to the inverse care law. Lancet. 1997 Aug 30;350(9078):642–642. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)63332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]