Abstract
Objective: To study the effect of minimal enteral feeding (MEF) on intestinal permeability and feeding tolerance in preterm infants with intrauterine growth retardation (gestational age < 37 weeks, birth weight for gestational age p < 10). Furthermore, to determine whether fetal blood flow pulsatility or intestinal permeability predict feeding tolerance in these infants.
Design: Randomised controlled trial.
Methods: Within 48 hours of birth, infants were randomised to MEF or no enteral feeding (NEF) for five days in addition to parenteral feeding. Intestinal permeability was measured by the sugar absorption test before (SAT1) and after (SAT2) the study. The sugar absorption test measured the urinary lactulose/mannitol (LM) ratio after oral ingestion of a solution (375 mosm) containing mannitol and lactulose. Charts of all infants were assessed for measures of feeding tolerance. Fetal blood flow pulsatility index (U/C ratio) was measured within the seven days before birth.
Results: Of the 56 infants enrolled, 42 completed the study: 20 received MEF and 22 NEF. The decrease in LM ratio (LM ratio 1 – LM ratio 2) was not significantly different between the two groups (0.25 v 0.11; p = 0.14). Feeding tolerance, growth, and incidence of necrotising enterocolitis were not significantly different between the two groups. Neither the U/C nor the LM ratio 1 predicted feeding tolerance.
Conclusions: The results suggest that MEF of preterm infants with intrauterine growth retardation has no effect on the decrease in intestinal permeability after birth. Neither fetal blood flow pulsatility nor intestinal permeability predicts feeding tolerance.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (91.4 KB).
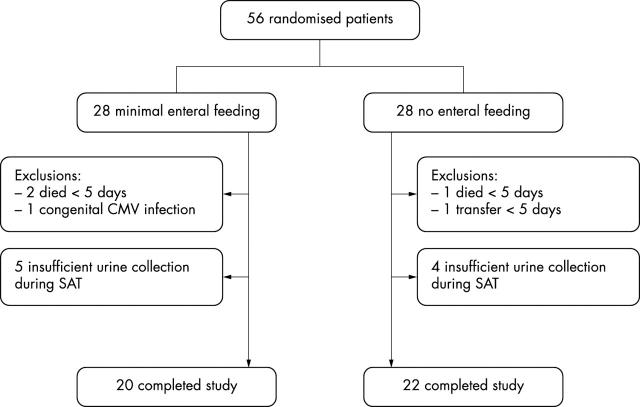
Figure 1.
Trial profile. CMV, Cytomegalovirus; SAT, sugar absorption test.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beach R. C., Menzies I. S., Clayden G. S., Scopes J. W. Gastrointestinal permeability changes in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Feb;57(2):141–145. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berseth C. L. Effect of early feeding on maturation of the preterm infant's small intestine. J Pediatr. 1992 Jun;120(6):947–953. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81969-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L., Hulman S., Weiner J., Kliegman R. Beneficial effects of early hypocaloric enteral feeding on neonatal gastrointestinal function: preliminary report of a randomized trial. J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;112(4):622–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett G. A., Campbell S., Gamsu H., Cohen-Overbeek T., Pearce J. M. Doppler studies in the growth retarded fetus and prediction of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis, haemorrhage, and neonatal morbidity. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jan 3;294(6563):13–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6563.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsdorp V. H., van Vugt J. M., van Geijn H. P., Kostense P. J., Arduini D., Montenegro N., Todros T. Clinical significance of absent or reversed end diastolic velocity waveforms in umbilical artery. Lancet. 1994 Dec 17;344(8938):1664–1668. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90457-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellmer I., Karlsson K., Olsson T., Rosén K. G. Cerebral reactions during intrauterine asphyxia in the sheep. I. Circulation and oxygen consumption in the fetal brain. Pediatr Res. 1974 Jan;8(1):50–57. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197401000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Bloom S. R., Aynsley-Green A. Gut hormones and 'minimal enteral feeding'. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Sep;75(5):719–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhseed M., Jirous J., Ahmed M. A., Viswanathan D. L. Middle cerebral artery to umbilical artery resistance index ratio in the prediction of neonatal outcome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2000 Nov;71(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7292(00)00262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm G., Ellwood D., Devonald K., Beilby R., Henderson-Smart D. Absent or reversed end diastolic flow velocity in the umbilical artery and necrotising enterocolitis. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jul;66(7 Spec No):805–807. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.7_spec_no.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure R. J., Newell S. J. Randomised controlled study of clinical outcome following trophic feeding. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000 Jan;82(1):F29–F33. doi: 10.1136/fn.82.1.F29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meetze W. H., Valentine C., McGuigan J. E., Conlon M., Sacks N., Neu J. Gastrointestinal priming prior to full enteral nutrition in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992 Aug;15(2):163–170. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199208000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihatsch Walter Alexander, Pohlandt Frank, Franz Axel Rainer, Flock Felix. Early feeding advancement in very low-birth-weight infants with intrauterine growth retardation and increased umbilical artery resistance. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002 Aug;35(2):144–148. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200208000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag S. G., LaGamma E. F., Reisen C. E., Ferrentino F. L. Early enteral feeding does not affect the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics. 1986 Mar;77(3):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters L. L., Sheldon R. E., Jones M. D., Jr, Makowski E. L., Meschia G. Blood flow to fetal organs as a function of arterial oxygen content. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Nov 1;135(5):637–646. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32989-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piena M., Albers M. J., Van Haard P. M., Gischler S., Tibboel D. Introduction of enteral feeding in neonates on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation after evaluation of intestinal permeability changes. J Pediatr Surg. 1998 Jan;33(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(98)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robel-Tillig E., Vogtmann C., Bennek J. Prenatal hemodynamic disturbances -- pathophysiological background of intestinal motility disturbances in small for gestational age infants. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2002 Jun;12(3):175–179. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-32723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robel-Tillig E., Vogtmann C., Faber R. Postnatal intestinal disturbances in small-for-gestational-age premature infants after prenatal haemodynamic disturbances. Acta Paediatr. 2000 Mar;89(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouwet Ellen V., Heineman Erik, Buurman Wim A., ter Riet Gerben, Ramsay Graham, Blanco Carlos E. Intestinal permeability and carrier-mediated monosaccharide absorption in preterm neonates during the early postnatal period. Pediatr Res. 2002 Jan;51(1):64–70. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200201000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherjon S. A., Kok J. H., Oosting H., Wolf H., Zondervan H. A. Fetal and neonatal cerebral circulation: a pulsed Doppler study. J Perinat Med. 1992;20(1):79–82. doi: 10.1515/jpme.1992.20.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. J., Schanler R. J., Lau C., Heitkemper M., Ou C. N., Smith E. O. Early feeding, feeding tolerance, and lactase activity in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1998 Nov;133(5):645–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slagle T. A., Gross S. J. Effect of early low-volume enteral substrate on subsequent feeding tolerance in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 1988 Sep;113(3):526–531. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80646-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troche B., Harvey-Wilkes K., Engle W. D., Nielsen H. C., Frantz I. D., 3rd, Mitchell M. L., Hermos R. J. Early minimal feedings promote growth in critically ill premature infants. Biol Neonate. 1995;67(3):172–181. doi: 10.1159/000244160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson J. E., Kennedy K. A. Minimal enteral nutrition for promoting feeding tolerance and preventing morbidity in parenterally fed infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD000504–CD000504. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uil J. J., van Elburg R. M., van Overbeek F. M., Mulder C. J., VanBerge-Henegouwen G. P., Heymans H. S. Clinical implications of the sugar absorption test: intestinal permeability test to assess mucosal barrier function. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1997;223:70–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. T., Laker M. F., Nelson R. Intestinal permeability in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Mar;59(3):236–241. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wladimiroff J. W., Tonge H. M., Stewart P. A. Doppler ultrasound assessment of cerebral blood flow in the human fetus. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986 May;93(5):471–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wladimiroff J. W., vd Wijngaard J. A., Degani S., Noordam M. J., van Eyck J., Tonge H. M. Cerebral and umbilical arterial blood flow velocity waveforms in normal and growth-retarded pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 May;69(5):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elburg R. M., Fetter W. P. F., Bunkers C. M., Heymans H. S. A. Intestinal permeability in relation to birth weight and gestational and postnatal age. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003 Jan;88(1):F52–F55. doi: 10.1136/fn.88.1.F52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elburg R. M., Uil J. J., Kokke F. T., Mulder A. M., van de Broek W. G., Mulder C. J., Heymans H. S. Repeatability of the sugar-absorption test, using lactulose and mannitol, for measuring intestinal permeability for sugars. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 Feb;20(2):184–188. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199502000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elburg R. M., Uil J. J., Mulder C. J., Heymans H. S. Intestinal permeability in patients with coeliac disease and relatives of patients with coeliac disease. Gut. 1993 Mar;34(3):354–357. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.3.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elburg R. M., Uil J. J., van Aalderen W. M., Mulder C. J., Heymans H. S. Intestinal permeability in exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to cystic fibrosis or chronic pancreatitis. Pediatr Res. 1996 Jun;39(6):985–991. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199606000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]