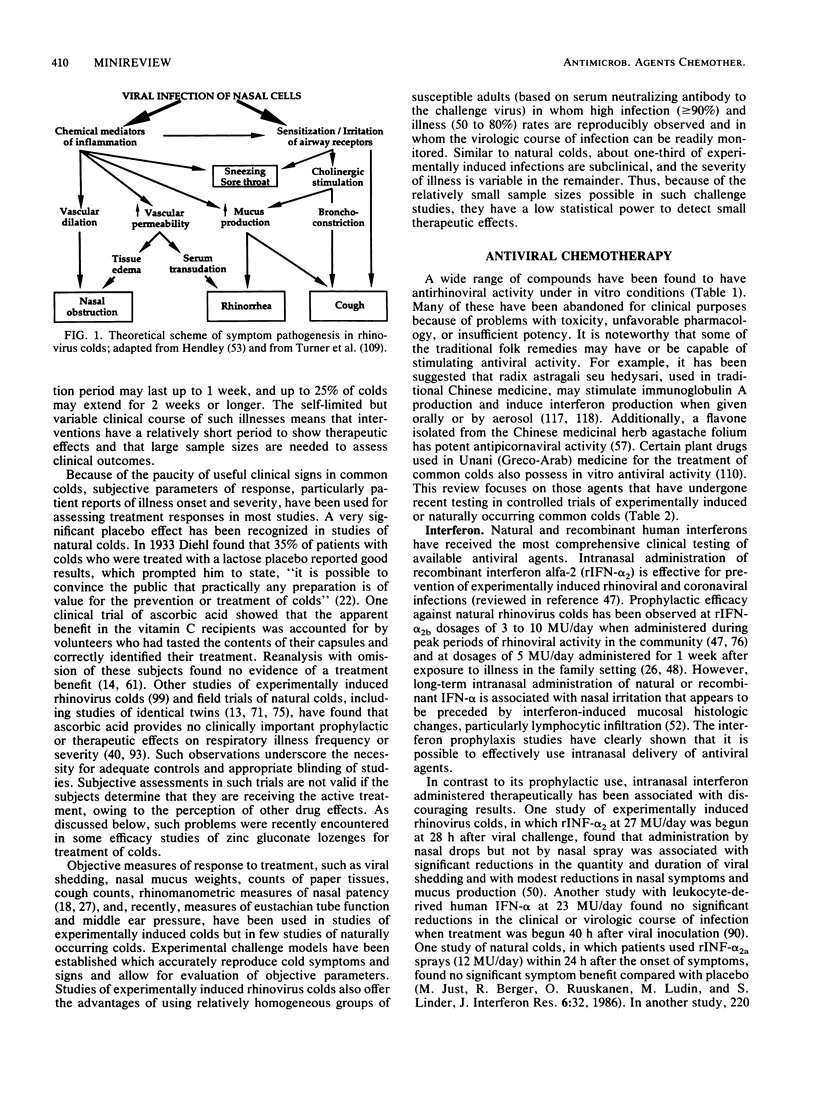
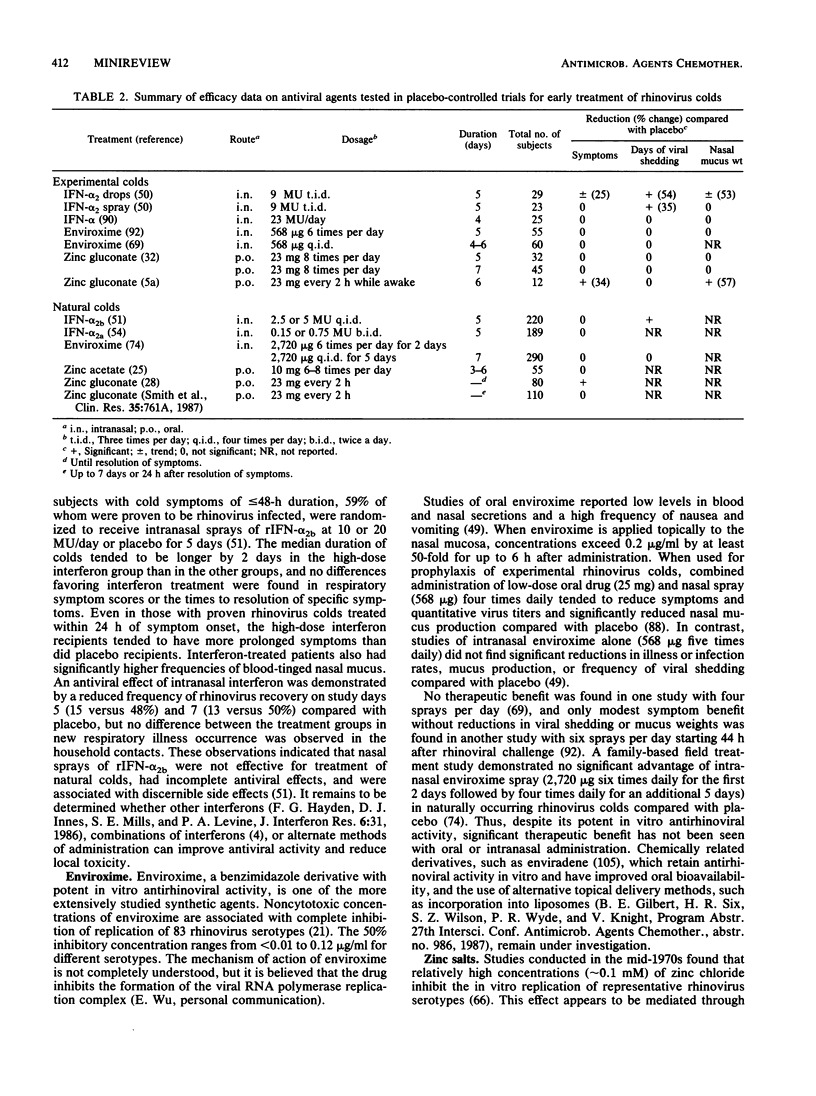
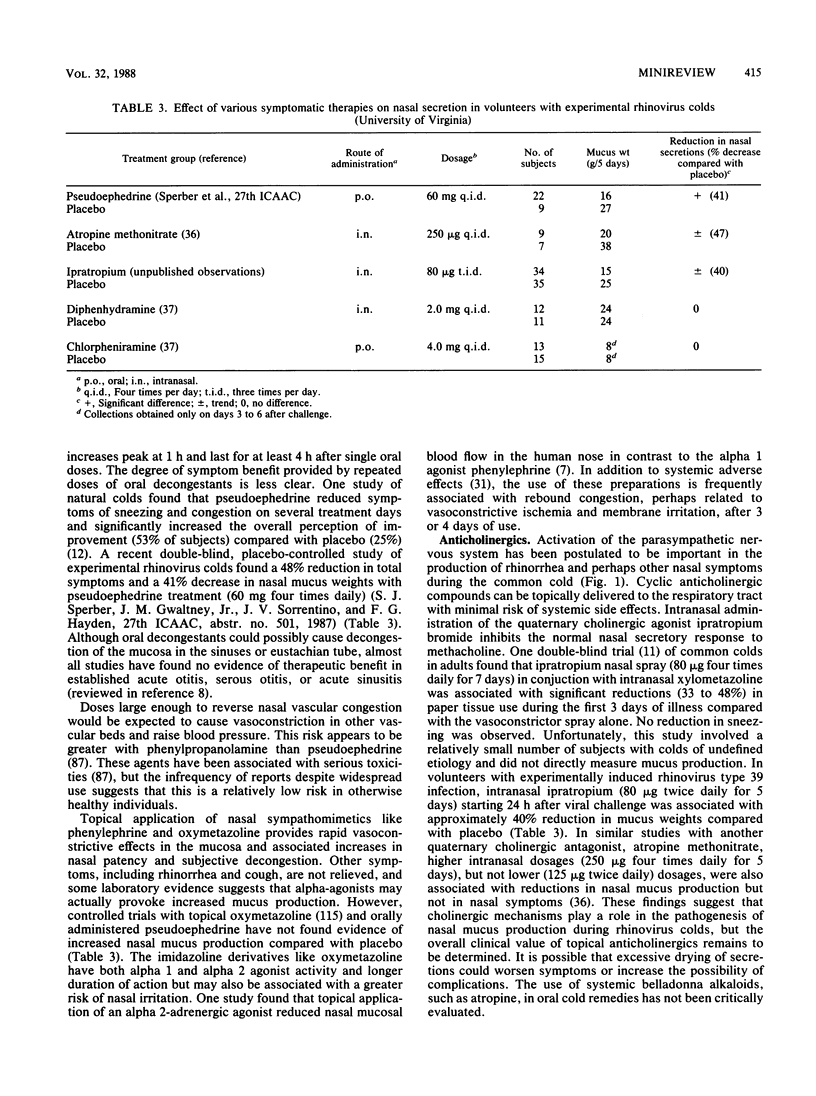
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad A. L., Dowsett A. B., Tyrrell D. A. Studies of rhinovirus resistant to an antiviral chalcone. Antiviral Res. 1987 Aug;8(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad A. L., Tyrrell D. A. Synergism between anti-rhinovirus antivirals: various human interferons and a number of synthetic compounds. Antiviral Res. 1986 Jul;6(4):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nakib W., Higgins P. G., Barrow I., Batstone G., Tyrrell D. A. Prophylaxis and treatment of rhinovirus colds with zinc gluconate lozenges. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):893–901. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nakib W., Higgins P. G., Barrow I., Tyrrell D. A., Lenox-Smith I., Ishitsuka H. Intranasal chalcone, Ro 09-0410, as prophylaxis against rhinovirus infection in human volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):887–892. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nakib W., Tyrrell D. A. A 'new' generation of more potent synthetic antirhinovirus compounds: comparison of their MICs and their synergistic interactions. Antiviral Res. 1987 Nov;8(4):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nakib W., Willman J., Higgins P. G., Tyrrell D. A., Shepherd W. M., Freestone D. S. Failure of intranasally administered 4', 6-dichloroflavan to protect against rhinovirus infection in man. Arch Virol. 1987;92(3-4):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01317482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcon B., Zerial A., Dupiol C., Carrasco L. Antirhinovirus compound 44,081 R.P. inhibits virus uncoating. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):31–34. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson K. E., Bende M. Adrenoceptors in the control of human nasal mucosal blood flow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984 Mar-Apr;93(2 Pt 1):179–182. doi: 10.1177/000348948409300216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård A., Malm L. Orally administered decongestant drugs in disorders of the upper respiratory passages: a survey of clinical results. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1984 Feb;9(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1984.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash R. J., Parker R. A., Hagan A. C., Mayer G. D. RMI 15,731 (1-[5-tetradecyloxy-2-furanyl]-ethanone), a new antirhinovirus compound. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):301–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargar T. M., Dulworth J. K., Kenny M. T., Massad R., Daniel J. K., Wilson T., Sargent R. N. 3,4-Dihydro-2-phenyl-2H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyridines with potent antirhinovirus activity. J Med Chem. 1986 Sep;29(9):1590–1595. doi: 10.1021/jm00159a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borum P., Olsen L., Winther B., Mygind N. Ipratropium nasal spray: a new treatment for rhinorrhea in the common cold. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):418–420. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye C. E., Cooper J., Empey D. W., Fowle A. S., Hughes D. T., Letley E., O'Grady J. Effects of pseudoephedrine and triprolidine, alone and in combination, on symptoms of the common cold. Br Med J. 1980 Jul 19;281(6234):189–190. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6234.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. B., Einstein R., Lai L. Y., Martin N. G., Starmer G. A. Vitamin C and the common cold: using identical twins as controls. Med J Aust. 1981 Oct 17;2(8):411–412. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb101032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers T. C. Effects of ascorbic acid on the common cold. An evaluation of the evidence. Am J Med. 1975 Apr;58(4):532–536. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K. Excessive intake of zinc impairs immune responses. JAMA. 1984 Sep 21;252(11):1443–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. H., Nicholson A. N. Performance studies with antihistamines. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;6(1):31–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell J. T. Rhinometry: measurement of nasal patency. Ann Allergy. 1982 Oct;49(4):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutcher J. E., Kantner T. R. The effectiveness of antihistamines in the common cold. J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;21(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1981.tb01725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. E. Economic costs of respiratory tract infections in the United States. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 28;78(6B):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90363-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Jr, Betts R. F. Effect of induced interferon in experimental rhinovirus infections in volunteers. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):506–510. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.506-510.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. M., Miles H. B., Moore B. W., Ryan P., Pinnock C. B. Failure of effervescent zinc acetate lozenges to alter the course of upper respiratory tract infections in Australian adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1263–1265. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. M., Moore B. W., Miles H. B., Davies L. M., Graham N. M., Ryan P., Worswick D. A., Albrecht J. K. Prophylactic efficacy of intranasal alpha 2-interferon against rhinovirus infections in the family setting. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):65–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601093140201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler W. E., Myers T., Rankell A. S., London S. J., Poetsch C. E. A system of rhinomanometry in the clinical evaluation of nasal decongestants. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977 May-Jun;86(3 Pt 1):310–317. doi: 10.1177/000348947708600306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eby G. A., Davis D. R., Halcomb W. W. Reduction in duration of common colds by zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):20–24. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston P. A., Hendley J. O., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Mediators of immediate hypersensitivity in nasal secretions during natural colds and rhinovirus infection. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1984;413:25–35. doi: 10.3109/00016488409128538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Empey D. W., Medder K. T. Nasal decongestants. Drugs. 1981 Jun;21(6):438–443. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198121060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar J. I., Karno M. Chronic hallucinosis from nasal drops. JAMA. 1982 Apr 2;247(13):1859–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLER A. E., BADGER G. F., HODGES R. G., JORDAN W. S., Jr, RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr, DINGLE J. H. The failure of antihistaminic drugs to prevent or cure the common cold and undifferentiated respiratory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1950 May 11;242(19):737–744. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195005112421901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr B. M., Conner E. M., Betts R. F., Oleske J., Minnefor A., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Two randomized controlled trials of zinc gluconate lozenge therapy of experimentally induced rhinovirus colds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1183–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr B. M., Gwaltney J. M., Jr The problems of taste in placebo matching: an evaluation of zinc gluconate for the common cold. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(9):875–879. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. P., Otto M. J., McKinlay M. A. Prevention of rhinovirus and poliovirus uncoating by WIN 51711, a new antiviral drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffey M. J., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Dressler W. E., Sorrentino J. V., Hayden F. G. Intranasally administered atropine methonitrate treatment of experimental rhinovirus colds. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):241–244. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffey M. J., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Sastre A., Dressler W. E., Sorrentino J. V., Hayden F. G. Intranasally and orally administered antihistamine treatment of experimental rhinovirus colds. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):556–560. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatmaitan B. C., Stanley E. D., Jackson G. G. The limited effect of nasal interferon induced by rhinovirus and a topical chemical inducer on the course of infection. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):401–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geist F. C., Bateman J. A., Hayden F. G. In vitro activity of zinc salts against human rhinoviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):622–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity T. R., Cotromanes E., Garrard C. S., Yeates D. B., Lourenço R. V. The effect of aspirin on lung mucociliary clearance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):139–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladych J. M., Hunt J. H., Jack D., Haff R. F., Boyle J. J., Stewart R. C., Ferlauto R. J. Inhibition of rhinovirus by isatin thiosemicarbazone analogues. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):286–287. doi: 10.1038/221286b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg I. Provocation of airflow limitation by viral infection: implication for treatment. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):369–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr Rhinovirus inhibition by 3-substituted triazinoindoles. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1148–1154. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr The spectrum of rhinovirus inhibitor by 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole and D-(-)-2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole HC1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):665–673. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Albrecht J. K., Kaiser D. L., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Prevention of natural colds by contact prophylaxis with intranasal alpha 2-interferon. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):71–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601093140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Intranasal interferon-alpha 2 treatment of experimental rhinoviral colds. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):174–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Prophylactic activity of intranasal enviroxime against experimentally induced rhinovirus type 39 infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):892–897. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Kaiser D. L., Albrecht J. K. Intranasal recombinant alfa-2b interferon treatment of naturally occurring common colds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):224–230. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Winther B., Donowitz G. R., Mills S. E., Innes D. J. Human nasal mucosal responses to topically applied recombinant leukocyte A interferon. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):64–72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O. Rhinovirus colds: immunology and pathogenesis. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):340–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog C., Berger R., Fernex M., Friesecke K., Havas L., Just M., Dubach U. C. Intranasal interferon (rIFN-alpha A, Ro 22-8181) for contact prophylaxis against common cold: a randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled field study. Antiviral Res. 1986 May;6(3):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(86)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Perkins J. C., Worthington M., Van Kirk J. E., Mills J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Evaluation of an interferon inducer in viral respiratory disease. JAMA. 1972 Feb 28;219(9):1179–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. C., Jr, Kantner T. R., Lilienfield L. S., Princiotto J. V., Krum R. E., Crutcher J. E., Belman M. A., Danzig M. R. Effectiveness of antihistamines in the symptomatic management of the common cold. JAMA. 1979 Nov 30;242(22):2414–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Ninomiya Y. T., Ohsawa C., Fujiu M., Suhara Y. Direct and specific inactivation of rhinovirus by chalcone Ro 09-0410. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):617–621. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Ohsawa C., Ohiwa T., Umeda I., Suhara Y. Antipicornavirus flavone Ro 09-0179. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):611–616. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G. A perspective from controlled investigations of chemotherapy for viral respiratory infections. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A83–A92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.Supplement_2.A83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlowski T. R., Chalmers T. C., Frenkel L. D., Kapikian A. Z., Lewis T. L., Lynch J. M. Ascorbic acid for the common cold. A prophylactic and therapeutic trial. JAMA. 1975 Mar 10;231(10):1038–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Dulworth J. K., Bargar T. M., Torney H. L., Graham M. C., Manelli A. M. In vitro antiviral activity of the 6-substituted 2-(3',4'-dichlorophenoxy)-2H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyridines MDL 20,610, MDL 20,646, and MDL 20,957. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):516–518. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Dulworth J. K., Torney H. L. In vitro and in vivo antipicornavirus activity of some phenoxypyridinecarbonitriles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):745–750. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman N. I., Harder H., Lindwall L., Synnerstad B. Longterm treatment with brompheniramine and phenylpropanolamine in recurrent otitis media--a double-blind study. J Otolaryngol. 1978 Jun;7(3):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Butterworth B. E. Inhibition by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: interaction of zinc with capsid polypeptides. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.298-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Kauer J. C., Butterworth B. E. Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses. Nature. 1974 Apr 12;248(449):588–590. doi: 10.1038/248588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulshrestha V. K., Gupta P. P., Turner P., Wadsworth J. Some clinical pharmacological studies with terfenadine, a new antihistamine drug. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;6(1):25–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea P. A double-blind controlled evaluation of the nasal decongestant effect of Day Nurse in the common cold. J Int Med Res. 1984;12(2):124–127. doi: 10.1177/030006058401200211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levandowski R. A., Pachucki C. T., Rubenis M., Jackson G. G. Topical enviroxime against rhinovirus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1004–1007. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein S. R., Parrino T. A. Management of the common cold. Adv Intern Med. 1987;32:207–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. G., Carr A. B., Oakeshott J. G., Clark P. Co-twin control studies: vitamin C and the common cold. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;103(Pt A):365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Beare A. S., Reed S. E. In vitro antiviral activity and preliminary clinical trials of a new adamantane compound. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):421–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. D., Monto A. S., DeLong D. C., Exelby A., Bryan E. R., Srivastava S. Controlled trial of enviroxime against natural rhinovirus infections in a community. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. Z., Nance W. E., Norton J. A., Wolen R. L., Griffith R. S., Rose R. J. Therapeutic effect of vitamin C. A co-twin control study. JAMA. 1977 Jan 17;237(3):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S., Shope T. C., Schwartz S. A., Albrecht J. K. Intranasal interferon-alpha 2b for seasonal prophylaxis of respiratory infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):128–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio R. M., Proud D., Lichtenstein L. M., Kagey-Sobotka A., Hendley J. O., Sorrentino J., Gwaltney J. M. Kinins are generated during experimental rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):133–142. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. N., Smith P. A., Spencer M. B. Antihistamines and visual function: studies on dynamic acuity and the pupillary response to light. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;14(5):683–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. N., Stone B. M. Performance studies with the H1-histamine receptor antagonists, astemizole and terfenadine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;13(2):199–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Aoyama M., Umeda I., Suhara Y., Ishitsuka H. Comparative studies on the modes of action of the antirhinovirus agents Ro 09-0410, Ro 09-0179, RMI-15,731, 4',6-dichloroflavan, and enviroxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Ohsawa C., Aoyama M., Umeda I., Suhara Y., Ishitsuka H. Antivirus agent, Ro 09-0410, binds to rhinovirus specifically and stabilizes the virus conformation. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D. G., Pantic D., Dane D. S., Briggs M. Protective action of benzimidazole derivatives against virus infections in tissue culture and in vivo. Lancet. 1969 Mar 1;1(7592):446–448. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. J., Fox M. P., Fancher M. J., Kuhrt M. F., Diana G. D., McKinlay M. A. In vitro activity of WIN 51711, a new broad-spectrum antipicornavirus drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):883–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panusarn C., Stanley E. D., Dirda V., Rubenis M., Jackson G. G. Prevention of illness from rhinovirus infection by a topical interferon inducer. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 11;291(2):57–61. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407112910201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaioanou H., Naylor B., McLean J. A. Ciliocytophthoria in nasal secretion and its relation to infection and atopic disease. J Allergy. 1969 Sep;44(3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(69)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentel P. Toxicity of over-the-counter stimulants. JAMA. 1984 Oct 12;252(14):1898–1903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts R. J., Higgins P. G., Willman J. S., Tyrrell D. A., Lenox-Smith I. Evaluation of the antirhinovirus chalcone Ro 09-0415 given orally to volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Oct;14(4):403–409. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts R. J., Jones R. W., Delong D. C., Reed S. E., Wallace J., Tyrrell D. A. The activity of enviroxime against rhinovirus infection in man. Lancet. 1981 Jun 20;1(8234):1342–1344. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts R. J., Tyrrell D. A. Rhinovirus colds. Br Med Bull. 1985 Oct;41(4):386–390. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts R. J., Wallace J., Tyrrell D. A., Freestone D. S., Shepherd W. M. Failure of oral 4',6-dichloroflavan to protect against rhinovirus infection in man. Arch Virol. 1983;75(1-2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01314131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts R. J., Wallace J., Tyrrell D. A., Tagart V. B. Therapeutic activity of enviroxime against rhinovirus infection in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):671–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Costrini A. M. Vitamin C prophylaxis in marine recruits. JAMA. 1979 Mar 2;241(9):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. D., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Hayden F. G. Activity of 2-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-5-nitrobenzonitrile (MDL-860) against picornaviruses in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):639–642. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall J. E., Hendley J. O. A decongestant-antihistamine mixture in the prevention of otitis media in children with colds. Pediatrics. 1979 Mar;63(3):483–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. E., Bynoe M. L. The antiviral activity of isoquinoline drugs for rhinoviruses in vitro and in vivo. J Med Microbiol. 1970 May;3(2):346–352. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. E., Craig J. W., Tyrrell D. A. Four compounds active against rhinovirus: comparison in vitro and in volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A128–A135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. P., Cantekin E. I., Bluestone C. D., Welch R. M., Cho Y. W. Nasal decongestant activity of pseudoephedrine. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977 Mar-Apr;86(2 Pt 1):235–242. doi: 10.1177/000348947708600216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. R., Togo Y., Hornick R. B., Tominaga S., Gleckman R. A. Evaluation of the efficacy of ascorbic acid in prophylaxis of induced rhinovirus 44 infection in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):500–505. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selway J. W. Antiviral activity of flavones and flavans. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;213:521–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipkowitz N. L., Bower R. R., Schleicher J. B., Aquino F., Appell R. N., Roderick W. R. Antiviral activity of a bis-benzimidazole against experimental rhinovirus infections in chimpanzees. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):117–122. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.117-122.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Remigio L. K. Histamine in nasal secretions and serum may be elevated during viral respiratory tract infections. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(4):380–383. doi: 10.1159/000233051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Kremer M. J., Luo M., Vriend G., Arnold E., Kamer G., Rossmann M. G., McKinlay M. A., Diana G. D., Otto M. J. The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1286–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3018924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. D., Jackson G. G., Panusarn C., Rubenis M., Dirda V. Increased virus shedding with aspirin treatment of rhinovirus infection. JAMA. 1975 Mar 24;231(12):1248–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. L., Kampfner G. L. The laboratory selection of antiviral agents. Br Med Bull. 1985 Oct;41(4):322–332. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Selway J. W. Effect of dichloroflavan (BW683C) on the stability and uncoating of rhinovirus type 1B. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Aug;14 (Suppl A):97–105. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_a.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togo Y., Schwartz A. R., Hornick R. B. Antiviral effect of 3, 4-dihydro-1-isoquinolineacetamide hydrochloride in experimental human rhinovirus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):612–616. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torney H. L., Dulworth J. K., Steward D. L. Antiviral activity and mechanism of action of 2-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-5-nitrobenzonitrile (MDL-860). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):635–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. B., Hendley J. O., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Shedding of infected ciliated epithelial cells in rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):849–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vohora S. B. Unani Joshandah drugs for common cold, catarrh, cough and associated fevers. J Ethnopharmacol. 1986 Jun;16(2-3):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(86)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R. C., Wong D. T., Middleton E., Jr, Sun M., McCarthy N., Ogra P. L. Role of parainfluenza virus-specific IgE in pathogenesis of croup and wheezing subsequent to infection. J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;101(6):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R. C., Wong D. T., Sun M., Middleton E., Jr, Vaughan R. S., Ogra P. L. The development of respiratory syncytial virus-specific IgE and the release of histamine in nasopharyngeal secretions after infection. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 8;305(15):841–846. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110083051501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S., Brandon B., Stolley P., Rumrill R. A review of antihistamines and the common cold. Pediatrics. 1975 Jul;56(1):100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. B., 3rd, Gwaltney J. M., Jr Allergic rhinitis or virus cold? Nasal smear eosinophilia in differential diagnosis. Ann Allergy. 1972 Apr;30(4):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winther B., Brofeldt S., Borum P., Pedersen M., Mygind N. Lack of effect on nasal discharge from a vasoconstrictor spray in common cold. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 2):447–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winther B., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Mygind N., Turner R. B., Hendley J. O. Sites of rhinovirus recovery after point inoculation of the upper airway. JAMA. 1986 Oct 3;256(13):1763–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial A., Werner G. H., Phillpotts R. J., Willmann J. S., Higgins P. G., Tyrrell D. A. Studies on 44 081 R.P., a new antirhinovirus compound, in cell cultures and in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):846–850. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



