Abstract
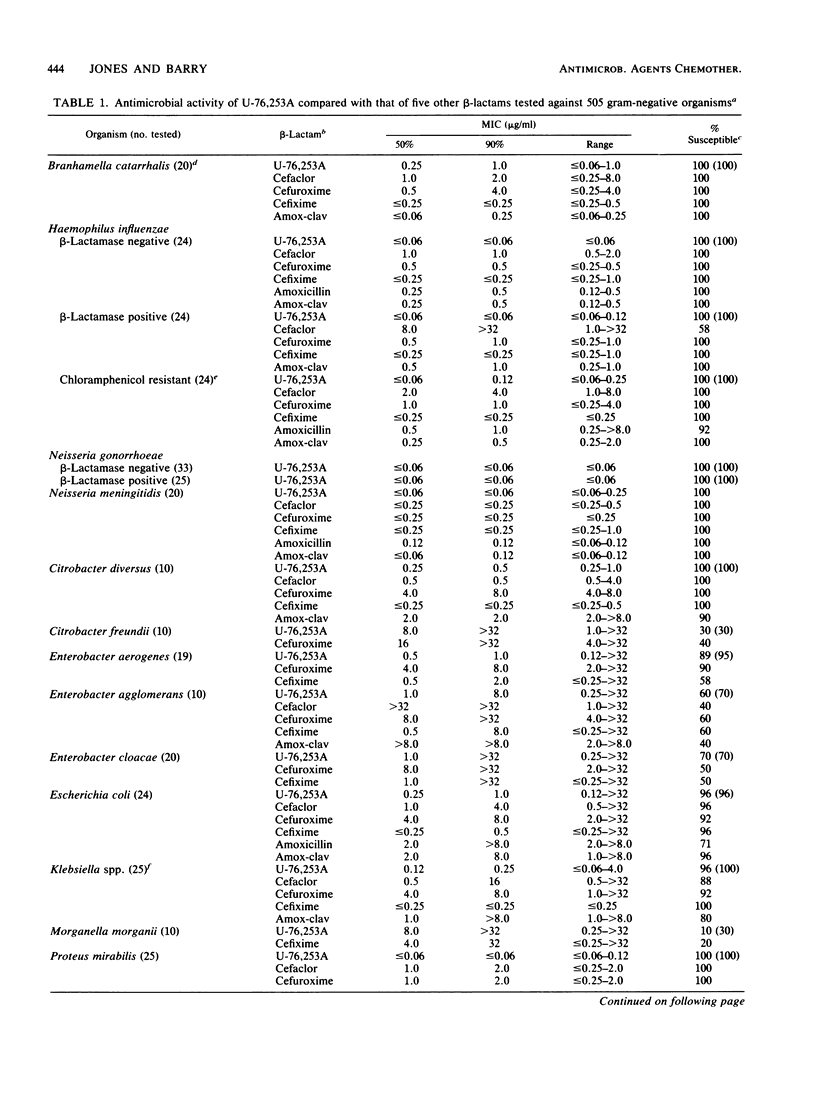
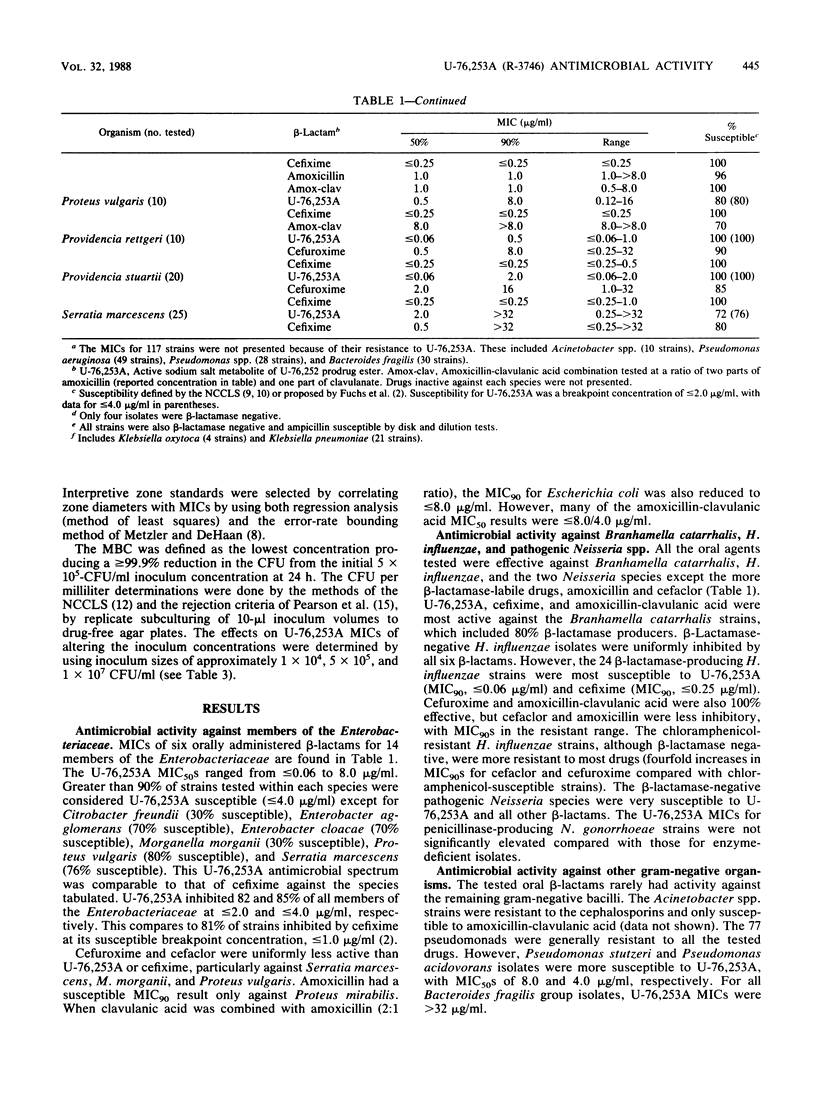
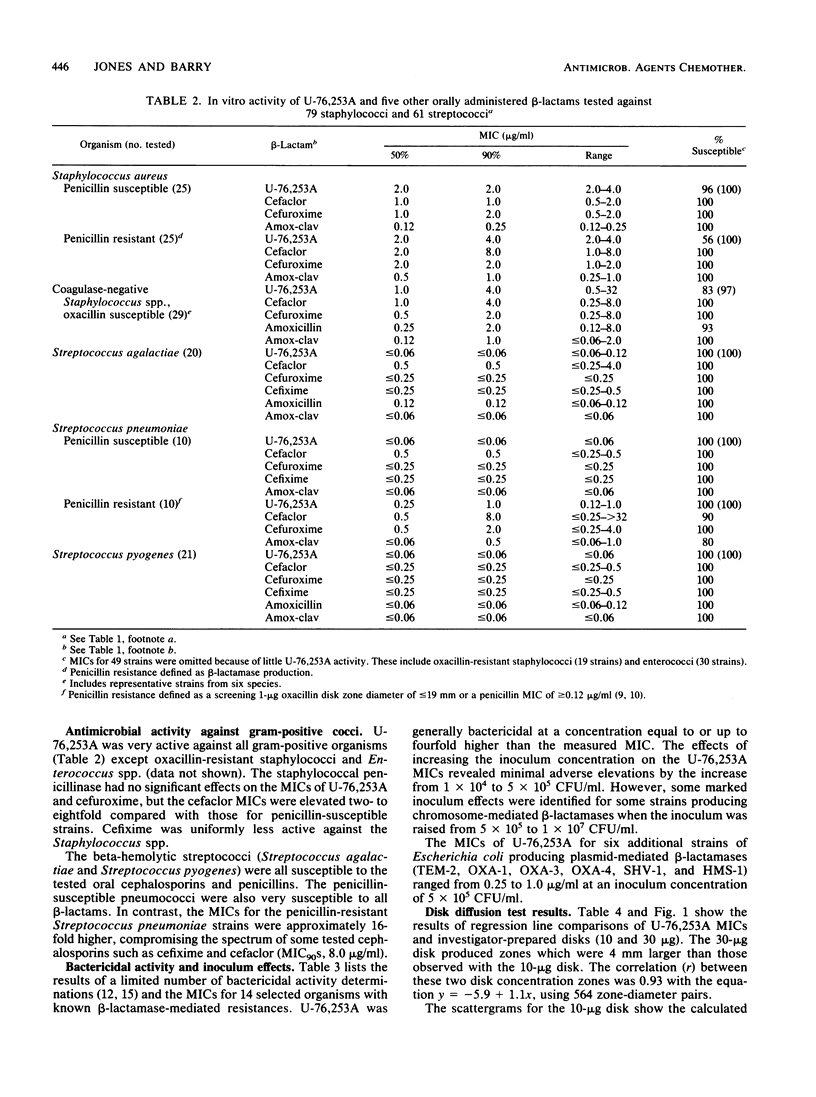
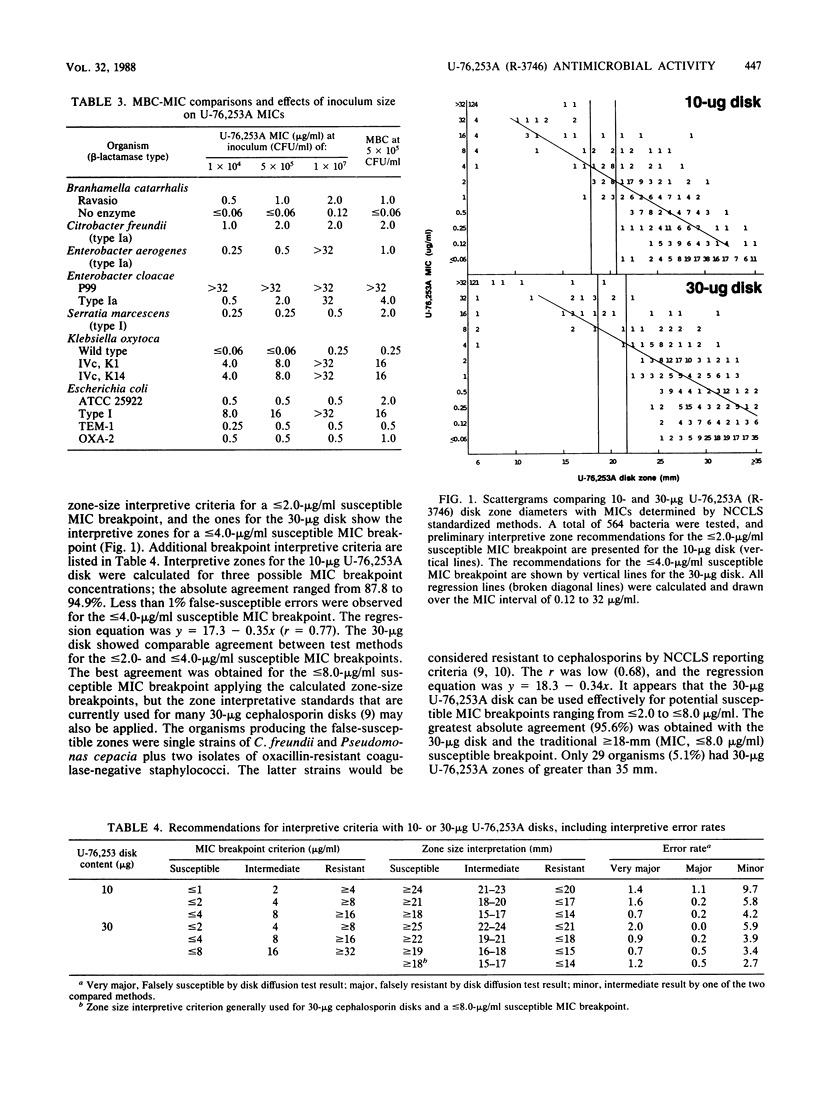
Compound U-76,253A (R-3746), the active metabolite sodium salt of the prodrug ester U-76,252 (CS-807), was demonstrated to be active against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae with 82 and 85% of strains inhibited by less than or equal to 2.0 and less than or equal to 4.0 micrograms/ml, respectively. In addition, U-76,253A inhibited all strains of Branhamella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, pathogenic Neisseria spp., oxacillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, beta-hemolytic streptococci, and pneumococci at less than or equal to 4.0 micrograms/ml. Pseudomonas spp., Acinetobacter spp., enterococci, and oxacillin-resistant staphylococci were resistant to U-76,253A. This U-76,253A antimicrobial activity and spectrum was generally superior to that of comparison orally administered cephems (cefaclor, cefuroxime, and cefixime) and the amoxicillin-clavulanic acid combination. Tests with beta-lactamase-producing isolates indicated that U-76,253A was bactericidal and that its MICs were only influenced by high inoculum concentrations (10(7) CFU/ml) against type Ia and IVc enzyme-producing strains. Preliminary disk diffusion interpretive zone criteria were calculated for 10- and 30-micrograms U-76,253A disks and several possible susceptible MIC breakpoints. The absolute interpretive agreement between MICs and zone diameters ranged from 87.8 to 95.6%. Final selection of interpretive criteria awaits further U-76,252 pharmacokinetic information.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosley G. S., Elliott J. A., Oxtoby M. J., Facklam R. R. Susceptibility of relatively penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae to newer cephalosporin antibiotics. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 May;7(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Barry A. L., Jones R. N. Cefixime disk susceptibility test criteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):647–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.647-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto K., Ishihara S., Yanagisawa H., Ide J., Nakayama E., Nakao H., Sugawara S., Iwata M. Studies on orally active cephalosporin esters. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 Mar;40(3):370–384. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding S. M., Williams P. E., Ayrton J. Pharmacology of Cefuroxime as the 1-acetoxyethyl ester in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L. Preliminary antimicrobial susceptibility interpretive criteria for cefetamet (Ro 15-8074) and cefteram (Ro 19-5247) disk tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1796–1799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1796-1799.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura T., Kojo H., Matsumoto Y., Mine Y., Goto S., Kuwahara S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial properties of FK 027, a new orally active cephem antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F., Pursiano T. A., Buck R. E., Tsai Y. H., Chisholm D. R., Misiek M., Desiderio J. V., Kessler R. E. BMY 28100, a new oral cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):238–243. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. M., DeHaan R. M. Susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria: statistical and clinical considerations. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):588–594. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Hamana Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of T-2588, a new oral cephalosporin, compared with those of other oral beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. A., Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. Comparison of the antibacterial spectra of cephalexin and cefaclor with those of cephalothin and newer cephalosporins: reevaluation of the class representative concept of susceptibility testing. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1156–1158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1156-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of CS-807, a new oral cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Piddock L. J. In vitro activity of Ro 15-8074 and Ro 19-5247, two orally administered cephalosporin metabolites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zighelboim S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of multiply antibiotic-resistant South African strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):434–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



