Abstract
AIMS—Retinal nerve fibre layer photography is a well established method to qualitatively document early structural changes which might be induced by primary open angle glaucoma. The aim was to analyse localised retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) defects in a new quantitative way with respect to surface topography, defect width, and surface reflectivity by means of the technique of confocal scanning laser tomography. METHODS—12 eyes of 12 patients with a localised RNFL defect documented in RNFL photographs and a normal appearance of the optic disc were enrolled in the study. Using confocal laser scanning tomography (Heidelberg retina tomograph, HRT) a series of 32 optical section images from different focal planes of the retina at the site of the RNFL defects were obtained. The optical section images, the reflectivity images, and the topographic images were analysed regarding the visibility of the RNFL defects. The mean surface height and the reflectance at the sites of the RNFL damage were measured and compared with the adjacent apparently normal retina. The width of the RNFL defect at 1 mm distance from the disc border was evaluated. RESULTS—RNFL defects could be detected in nine of 12 reflectivity images (75%). Single optical section images displayed the RNFL defects in 12 of 12 eyes. The defect width ranged from 0.11 to 1.0 mm. In six of 12 eyes a surface depression (34 (SD 5) µm; range 21-47 µm) was present. The reflectance ratio ranged from 0.68 to 0.94 at the site of the RNFL defect. In eyes with a glaucomatous scotoma in a 6° grid visual field (VF), the defect width was at least 0.25 mm. Surface depression and low reflectance ratio were found irrespective of the presence of a scotoma in the 6° grid VF. CONCLUSION—The majority of localised RNFL defects can be detected in reflectivity images from laser scanning tomograms. Localised RNFL defects may be differentiated according to surface topography into those with and those without a measurable surface depression. A small but deep RNFL defect is not necessarily associated with a scotoma in routine 6° grid VF static perimetry. Keywords: primary open angle glaucoma; nerve fibre layer defects; laser scanning tomography; Heidelberg retina tomograph
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (136.4 KB).
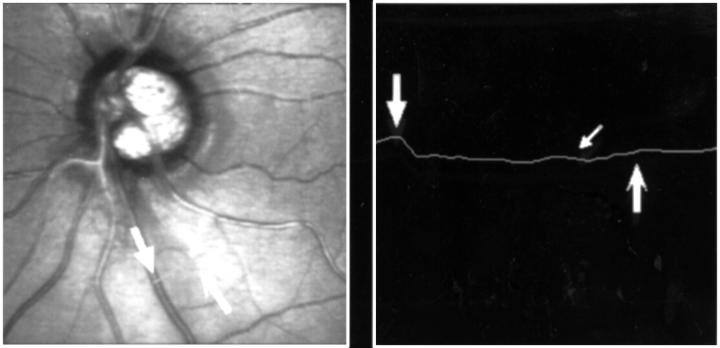
Figure 1 .
(A) A localised nerve fibre layer defect is present at 10'o clock and at 8'o clock in the RNFL photograph. No functional abnormalities were detected (patient no 3; Table 1). (B) 15° Laser scanning optical section image (patient no 3).
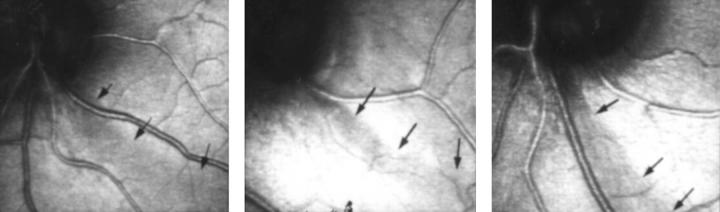
Figure 2 .
Localised RNFL defects in patients 4, 5, and 6 (Table 1) in the temporal inferior sector.
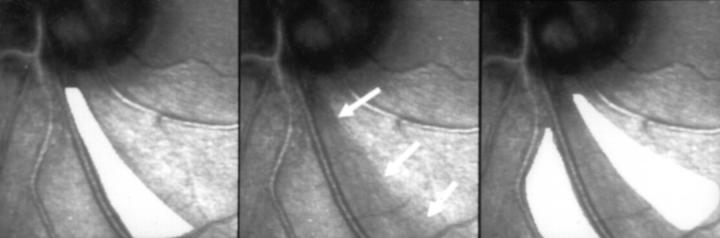
Figure 3 .
Determination of the width of the defect at 1 mm distance from the optic disc border. The profile cut displays the surface topography along the line drawn at the site of the RNFL defect. Arrows indicate the location of large and small vessels, the arrow with the curved head shows the upper border of the RNFL defect.
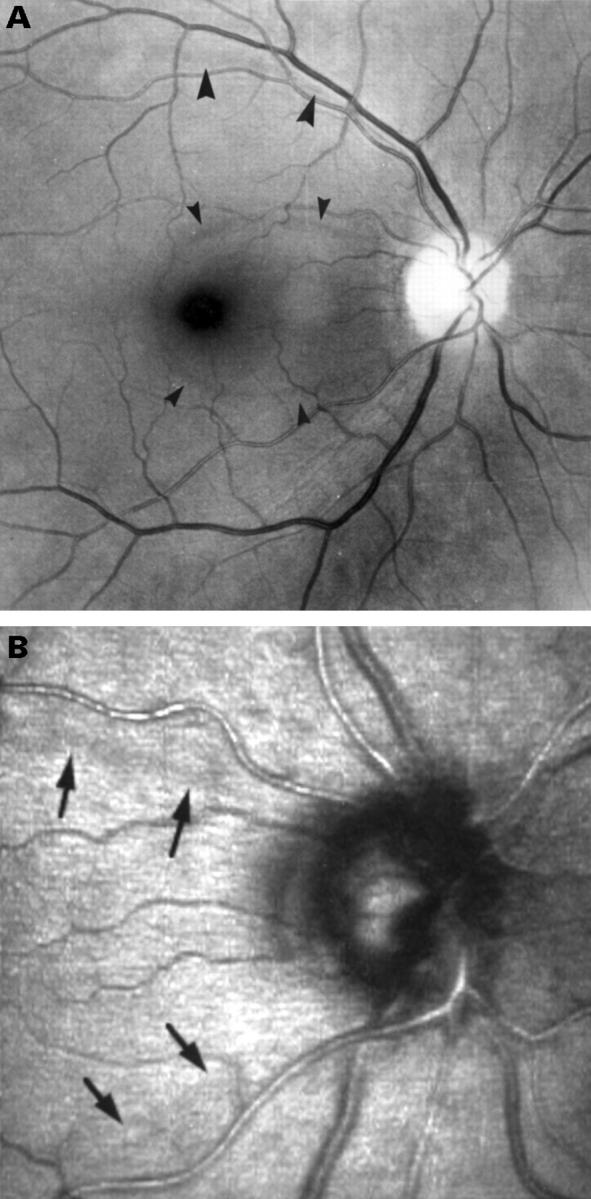
Figure 4 .
10° Optical section image. Outline of the areas from which the average voxel height is calculated. Left: localised RNFL defect, right: adjacent retina with apparently normal reflectance.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airaksinen P. J., Alanko H. I. Effect of retinal nerve fibre loss on the optic nerve head configuration in early glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1983;220(4):193–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02186668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airaksinen P. J., Drance S. M., Douglas G. R., Mawson D. K., Nieminen H. Diffuse and localized nerve fiber loss in glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Nov;98(5):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airaksinen P. J., Nieminen H. Retinal nerve fiber layer photography in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1985 Jul;92(7):877–879. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)33941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings R. A., Spaeth G. L. The optic disc in glaucoma. I: Classification. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;60(11):778–785. doi: 10.1136/bjo.60.11.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt W. F., Newman N. M. The earliest observable defect in glaucoma? Lancet. 1972 Mar 25;1(7752):692–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Nguyen N. X., Naumann G. O. The retinal nerve fiber layer in normal eyes. Ophthalmology. 1989 May;96(5):627–632. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32838-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minckler D. S. The organization of nerve fiber bundles in the primate optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980 Sep;98(9):1630–1636. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020040482019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Katz J., Derick R. J., Gilbert D., Sommer A. An evaluation of optic disc and nerve fiber layer examinations in monitoring progression of early glaucoma damage. Ophthalmology. 1992 Jan;99(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(92)32018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Reacher M., Katz J., Strahlman E., Gilbert D., Scott R. Quantitative grading of nerve fiber layer photographs. Ophthalmology. 1993 Dec;100(12):1800–1807. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31395-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider K., Burk R. O., Kruse F. E., Völcker H. E. Reproducibility of the optic nerve head topography with a new laser tomographic scanning device. Ophthalmology. 1994 Jun;101(6):1044–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(94)31220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulzer M. Intraocular pressure reduction in normal-tension glaucoma patients. The Normal Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Ophthalmology. 1992 Sep;99(9):1468–1470. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(92)31782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Katz J., Quigley H. A., Miller N. R., Robin A. L., Richter R. C., Witt K. A. Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Jan;109(1):77–83. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080010079037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Quigley H. A., Robin A. L., Miller N. R., Katz J., Arkell S. Evaluation of nerve fiber layer assessment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Dec;102(12):1766–1771. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040031430017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuulonen A., Airaksinen P. J. Initial glaucomatous optic disk and retinal nerve fiber layer abnormalities and their progression. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 Apr 15;111(4):485–490. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuulonen A., Lehtola J., Airaksinen P. J. Nerve fiber layer defects with normal visual fields. Do normal optic disc and normal visual field indicate absence of glaucomatous abnormality? Ophthalmology. 1993 May;100(5):587–598. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31598-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Lusky M., Bartsch D. U., Morsman D. Effect of repetitive imaging on topographic measurements of the optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993 May;111(5):636–638. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090050070031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]