Abstract
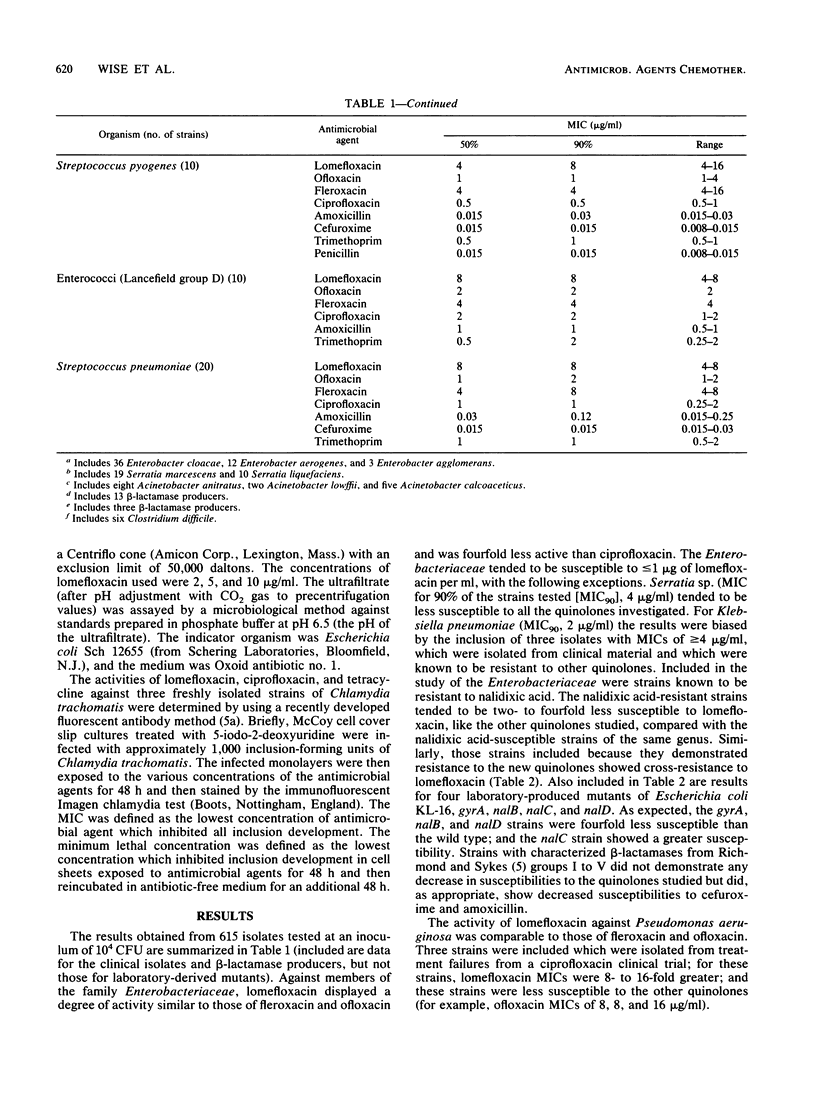
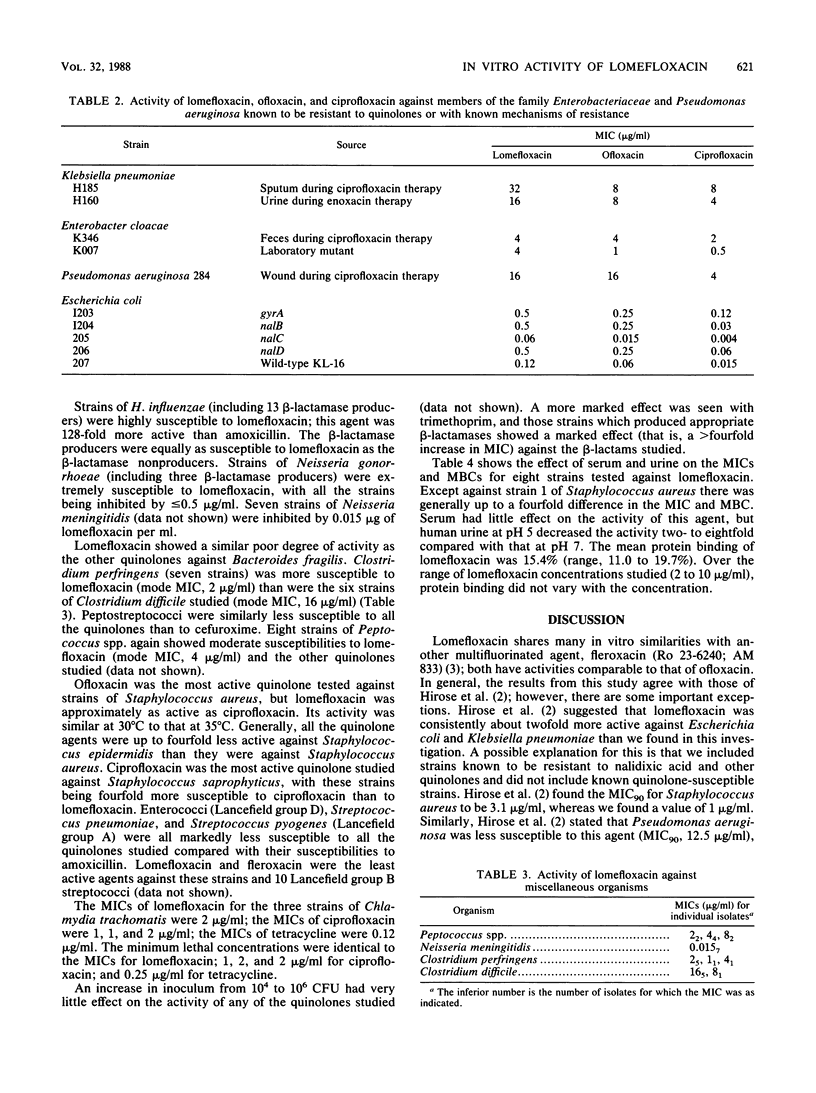
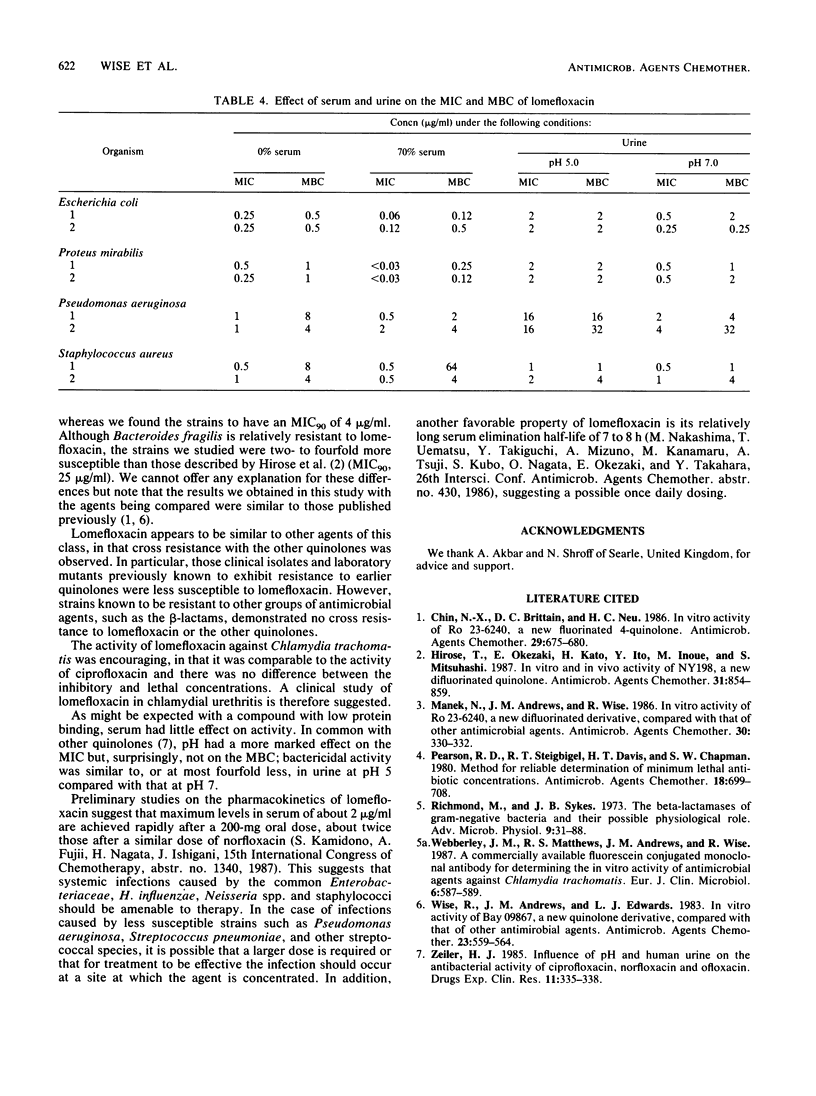
The in vitro activity of lomefloxacin (SC-47111; NY-198), a new difluorinated quinolone, was compared with those of ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, fleroxacin, amoxicillin, cefuroxime, and trimethoprim against 585 recent clinical isolates and other strains with known mechanisms of resistance. The MICs of lomefloxacin against 90% of the members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and staphylococci were between 0.25 and 4 micrograms/ml. Ninety percent of Neisseria sp. and Haemophilus influenzae were susceptible to less than or equal to 0.06 micrograms/ml, and streptococci (including Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and enterococci) and Bacteroides fragilis were susceptible to 8 micrograms/ml. Lomefloxacin was comparable in activity to fleroxacin and ofloxacin, but it was less active than ciprofloxacin. There was cross-resistance between the quinolone group of antimicrobial agents. The protein binding of lomefloxacin was 15.4%, and serum had little effect on the activity of the compound. However, urine at pH 5.0 decreased the activity by two- to eightfold compared with that at pH 7.0
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Okezaki E., Kato H., Ito Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of NY-198, a new difluorinated quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):854–859. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manek N., Andrews J. M., Wise R. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new difluoroquinolone derivative, compared with that of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):330–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webberley J. M., Matthews R. S., Andrews J. M., Wise R. Commercially available fluorescein-conjugated monoclonal antibody for determining the in vitro activity of antimicrobial agents against Chlamydia trachomatis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):587–589. doi: 10.1007/BF02014256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J. Influence of pH and human urine on the antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(5):335–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



