Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—Paraffin embedded samples have provided an important source of material for retrospective cytofluorimetric studies, useful in establishing the predictive value of DNA content measurements. The aim of this study was to investigate the incidence and type of aneuploidy in choroidal malignant melanomas (CMM) and the significance in the clinical outcome (median follow up 55 months). METHODS—DNA content was quantified by flow cytometry in 61 CMM from archival material. Non-tumour ocular tissue was used as the reference diploid standard. Cases in which the coefficient of variation (CV) of the diploid peak was >8% were excluded. The CMM were classified as spindle A, spindle B, mixed spindle and epithelioid, epithelioid, and necrotic. RESULTS—The frequency of the aneuploid DNA pattern was 38%. Necrotic tumours showed a worse clinical outcome independent of the ploidy pattern. Spindle A tumours were found to be diploid. Spindle B and mixed tumours showed a prevalent diploid and near diploid aneuploid pattern (DI <1.3), yet aneuploidy was not correlated with a worse prognosis. The epithelioid tumours were prevalently diploid. However, 83% of the aneuploid tumours were hypodiploid (DI <0.95), and showed the worst prognosis. CONCLUSION—These results indicate that increasing DNA abnormalities in CMM, especially in the epithelioid histotype, were associated with an increasing mortality. Keywords: ocular melanoma; flow cytometry; DNA
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (112.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
Histogram of spindle B choroidal malignant melanoma (CMM) showing a near diploid aneuploid peak. DI indicates the DNA index.
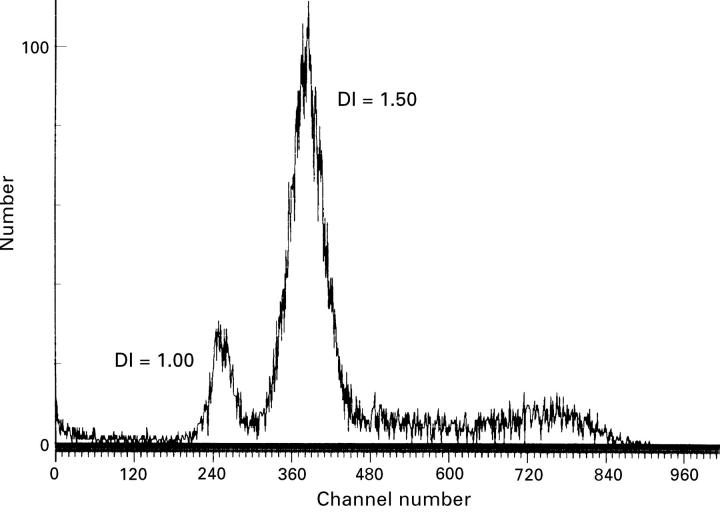
Figure 2 .
Histogram of spindle B choroidal malignant melanoma (CMM) showing a hyperdiploid peak. DI indicates the DNA index.
Figure 3 .
Histogram of epithelioid choroidal malignant melanoma (CMM) showing a hypodiploid peak (A). Diploid peak increased while hypodiploid peak proportionally decreased after the reference diploid standard (non-tumour ocular tissue) was added (B). DI indicates the DNA index.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augsburger J. J., Gamel J. W. Clinical prognostic factors in patients with posterior uveal malignant melanoma. Cancer. 1990 Oct 1;66(7):1596–1600. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901001)66:7<1596::aid-cncr2820660726>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Walker B. F., Solomon A. R., DeRose P. B. DNA ploidy and cell cycle analysis in ear malignant melanoma by flow and image cytometry. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1992 Apr;14(2):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Baak J. P., van Diest P. J., Curran B., Mullaney J., Fenton M., Leader M. DNA ploidy status in 84 ocular melanomas: a study of DNA quantitation in ocular melanomas by flow cytometry and automatic and interactive static image analysis. Hum Pathol. 1995 Jan;26(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson P. B., Thornthwaite J. T., Woolley T. W., Sugarbaker E. V., Seckinger D. Prognostic indicators including DNA histogram type, receptor content, and staging related to human breast cancer patient survival. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4187–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernö M., Baldetorp B., Borg A., Olsson H., Sigurdsson H., Killander D. Flow cytometric DNA index and S-phase fraction in breast cancer in relation to other prognostic variables and to clinical outcome. Acta Oncol. 1992;31(2):157–165. doi: 10.3109/02841869209088897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folberg R., Rummelt V., Parys-Van Ginderdeuren R., Hwang T., Woolson R. F., Pe'er J., Gruman L. M. The prognostic value of tumor blood vessel morphology in primary uveal melanoma. Ophthalmology. 1993 Sep;100(9):1389–1398. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamel J. W., McCurdy J. B., McLean I. W. A comparison of prognostic covariates for uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 May;33(6):1919–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamel J. W., McLean I. W., McCurdy J. B. Biologic distinctions between cure and time to death in 2892 patients with intraocular melanoma. Cancer. 1993 Apr 1;71(7):2299–2305. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930401)71:7<2299::aid-cncr2820710721>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W. Application of DNA flow cytometry to paraffin-embedded archival material for the study of aneuploidy and its clinical significance. Cytometry. 1985 Jul;6(4):327–333. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson M., Boeryd B., Carstensen J., Frånlund B., Gustafsson B., Kågedal B., Sun X. F., Wingren S. Correlations of Ki-67 and PCNA to DNA ploidy, S-phase fraction and survival in uveal melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 1996 Feb;32A(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00562-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kute T. E., Quadri Y., Muss H., Zbieranski N., Cirrincione C., Berry D. A., Barcos M., Thor A. P., Liu E., Koerner F. Flow cytometry in node-positive breast cancer: cancer and leukemia group B protocol 8869. Cytometry. 1995 Dec 15;22(4):297–306. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990220406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzi P., Bruni A., Mangiavacchi P., Cevenini G., Marini D., Tosi P. Ploidy pattern and cell cycle in breast cancer as detected by image analysis and flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1994 Jun 15;18(2):79–87. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Foster W. D., Zimmerman L. E., Gamel J. W. Modifications of Callender's classification of uveal melanoma at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Oct;96(4):502–509. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77914-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Gamel J. W. Prediction of metastasis of uveal melanoma: comparison of morphometric determination of nucleolar size and spectrophotometric determination of DNA. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Apr;29(4):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan J., Char D. H., McLean I. W., Gamel J. W. DNA content analysis of uveal melanoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Sep;107(9):1278–1278. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070020348006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meecham W. J., Char D. H. DNA content abnormalities and prognosis in uveal melanoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Nov;104(11):1626–1629. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050230064033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooy C. M., De Jong P. T. Prognostic parameters in uveal melanoma: a review. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996 Nov-Dec;41(3):215–228. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(96)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooy C., Vissers K., Luyten G., Mulder A., Stijnen T., de Jong P., Bosman F. DNA flow cytometry in uveal melanoma: the effect of pre-enucleation irradiation. Br J Ophthalmol. 1995 Feb;79(2):174–177. doi: 10.1136/bjo.79.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescher G., Bornfeld N., Hirche H., Horsthemke B., Jöckel K. H., Becher R. Prognostic implications of monosomy 3 in uveal melanoma. Lancet. 1996 May 4;347(9010):1222–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90736-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie I. G., Rees R. C., Parsons M. A., Lawry J., Cottam D. Estimation of DNA content in uveal melanomas by flow cytometry. Eye (Lond) 1989;3(Pt 5):611–617. doi: 10.1038/eye.1989.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B., Reynders M. M., Bosman F. T., Blijham G. H. Flow cytometric determination of DNA ploidy level in nuclei isolated from paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytometry. 1985 Jan;6(1):26–30. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Polivogianis L., Hsieh C. C., Albert D. M., Gamel J. W., Gragoudas E. S. Death from uveal melanoma. Number of epithelioid cells and inverse SD of nucleolar area as prognostic factors. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Jun;105(6):801–806. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060060087039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankey T. V., Rabinovitch P. S., Bagwell B., Bauer K. D., Duque R. E., Hedley D. W., Mayall B. H., Wheeless L., Cox C. Guidelines for implementation of clinical DNA cytometry. International Society for Analytical Cytology. Cytometry. 1993;14(5):472–477. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. E., Felberg N. T., Donoso L. A., Augsburger J. J., Shields J. A., Gamel J. Flow cytometry of uveal melanomas. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jul;8(3):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]