Abstract
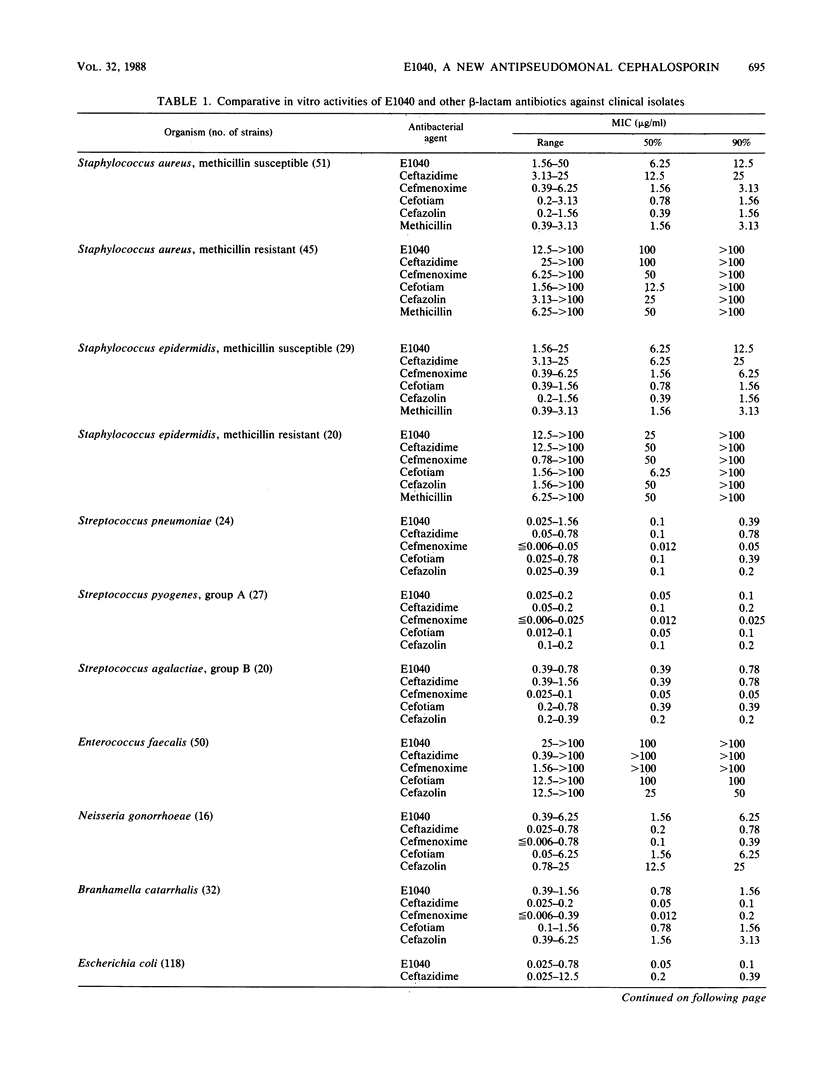
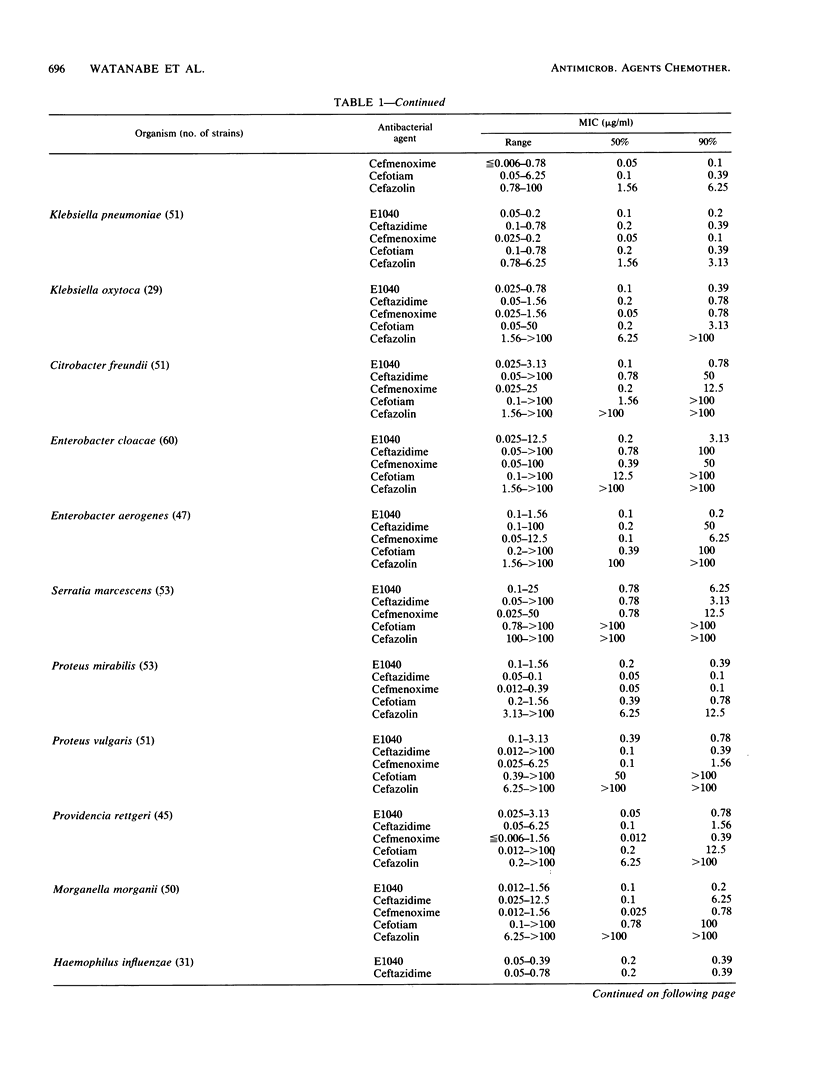
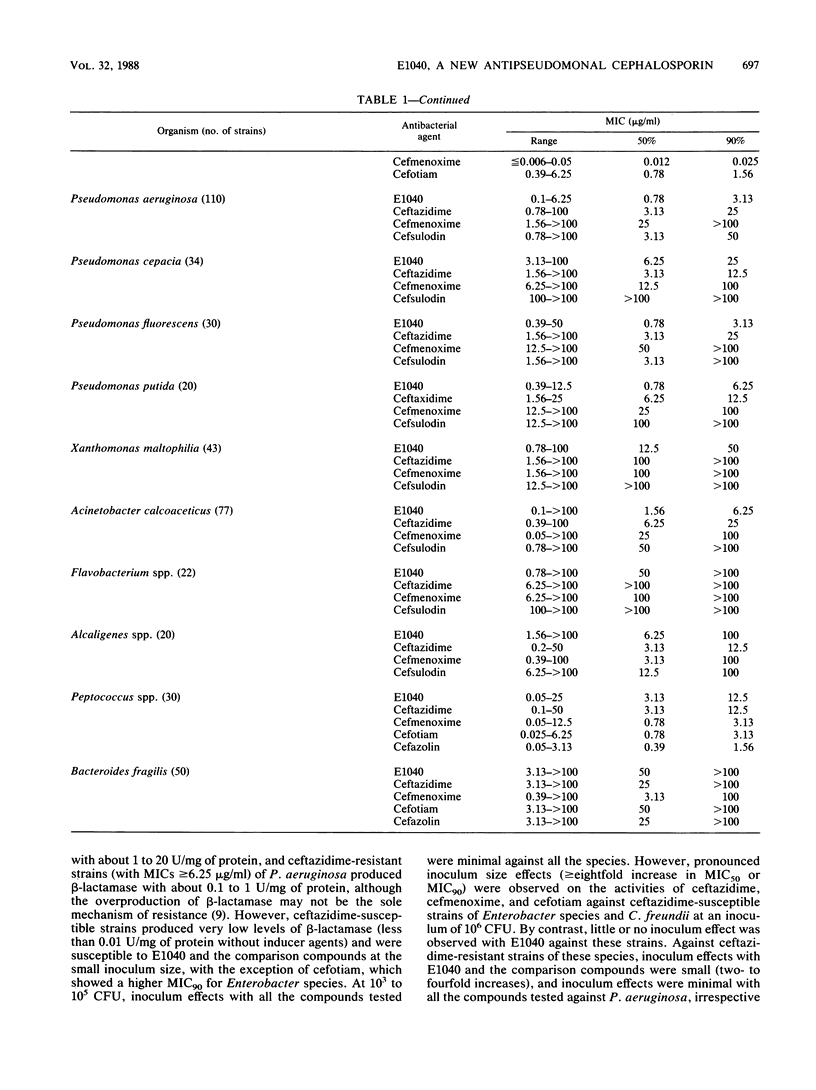
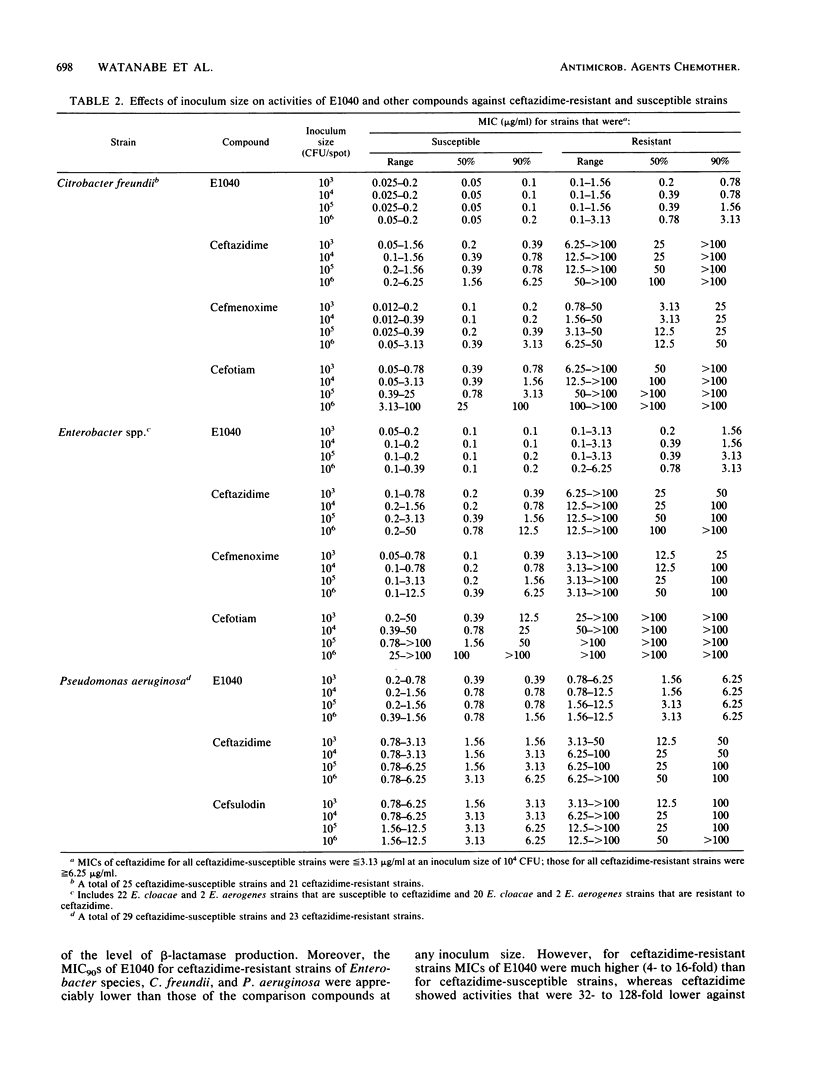
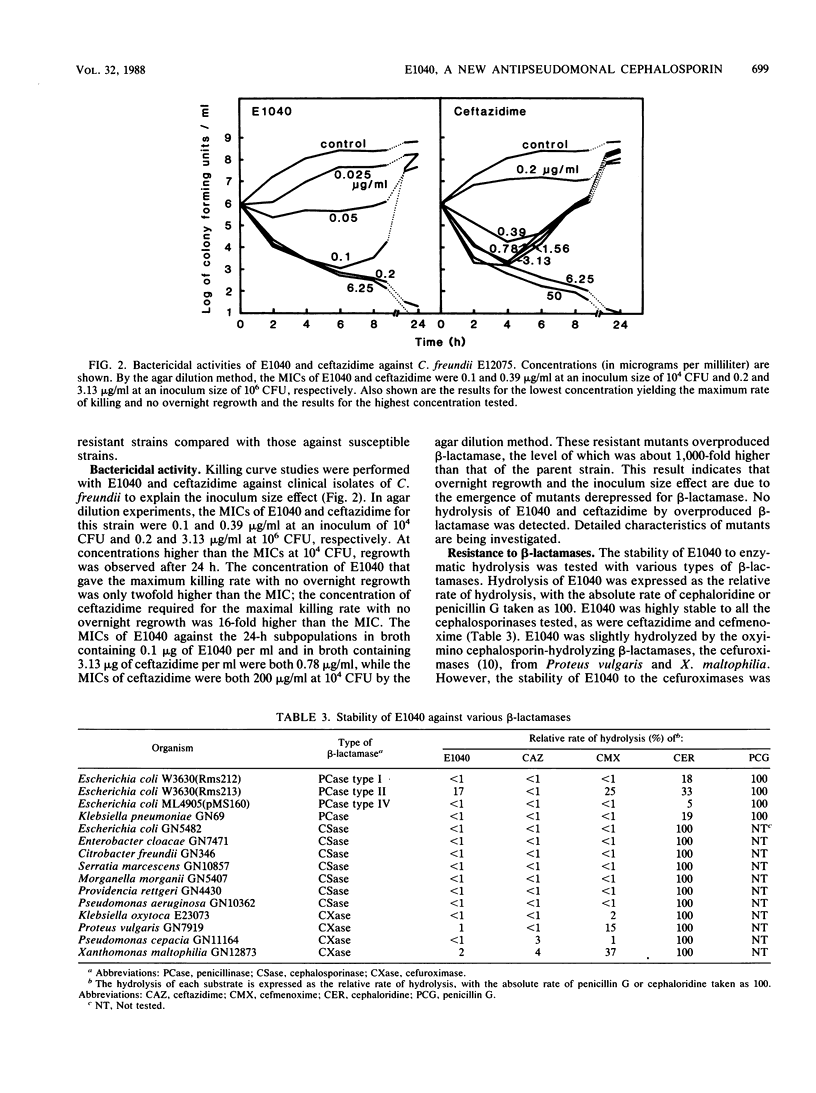
E1040 is a new parenteral cephalosporin with a broad antibacterial spectrum and potent antipseudomonal activity. The compound was four- to eightfold more active than ceftazidime and cefsulodin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MIC of E1040 for 90% of strains tested [MIC90], 3.13 micrograms/ml). E1040 also showed a potent activity against other glucose-nonfermentative rods, including Acinetobacter species. The activities of E1040 against most species of the family Enterobacteriaceae were roughly comparable to the activities of ceftazidime and cefmenoxime and exceeded that of cefotiam. Against Citrobacter freundii (MIC90, 0.78 micrograms/ml), Enterobacter cloacae (MIC90, 3.13 micrograms/ml), and Enterobacter aerogenes (MIC90, 0.2 micrograms/ml), E1040 was 16- to 256-fold more active than ceftazidime and cefmenoxime. The activities of E1040 against gram-positive cocci and anaerobes were comparable to those of ceftazidime, but the compound was less active than cefmenoxime. E1040 was at least as resistant as ceftazidime and cefmenoxime to hydrolysis by various beta-lactamases and showed high affinities for penicillin-binding protein 3 of both Escherichia coli and P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby J., Kirkpatrick B., Piddock L. J., Wise R. The effect of imipenem on strains of Enterobacteriaceae expressing Richmond & Sykes class I beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jul;20(1):15–22. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Dick W. Cefpirome (HR 810): lack of selection of beta-lactamase overproducing variants. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Jul;38(7):912–919. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. V., Orr D. C. Mode of action of ceftazidime: affinity for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):119–126. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J. M., Towner K. J., Slack R. C., Harper P. B., Simpson I. N. Selection of enhanced cefotaxime resistance in Enterobacter spp. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Oct;20(4):489–496. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsu K., Kitoh K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of E-0702, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):181–185. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Arai S., Hayashi S., Fujimoto K. Beta-lactamase stability of cefpirome (HR 810), a new cephalosporin with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):713–718. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Murakami K., Nishikawa T. Penetration of moxalactam into its target proteins in Escherichia coli K-12: comparison of a highly moxalactam resistant mutant with its parent strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):613–619. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfmann G., Kliebe C., Wiedemann B. Beta-lactam antibiotics and selection of resistance: speculation on the evolution of R-plasmids. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18 (Suppl 100):113–121. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_c.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchou B., Bellido F., Charnas R., Lucain C., Pechère J. C. Contribution of beta-lactamase hydrolysis and outer membrane permeability to ceftriaxone resistance in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Matsubara T., Murakawa T., Mine Y., Yokota Y., Kuwahara S., Goto S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin C derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative studies of penicillin-binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. J., Carlton D. D., Farrell C. A., Kessler R. E. Affinity of cephalosporins for beta-lactamases as a factor in antibacterial efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):845–848. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A. A direct spectrophotometric assay and determination of Michaelis constants for the beta-lactamase reaction. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Chromosomal cephalosporinases responsible for multiple resistance to newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:573–593. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Wiedemann B. Application of in-vitro models: development of resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):241–249. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H. Azthreonam (SQ 26,776), a synthetic monobactam specifically active against aerobic gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kida M., Kondo M., Ono H., Takeuchi M., Nishi T. SCE-963, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):557–568. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kondo M., Kida M., Nakao M., Iwahi T., Nishi T., Noji Y., Takeuchi M., Nozaki Y. Cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):56–65. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kondo M., Nagatomo H. SCE-129, antipseudomonal cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):137–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N. A., Nagasu T., Katsu K., Kitoh K. E-0702, a new cephalosporin, is incorporated into Escherichia coli cells via the tonB-dependent iron transport system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):497–504. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. Comparison of in vitro activity of GR 20263, a novel cephalosporin derivative, with activities of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):884–889. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]