Abstract
BACKGROUND—To compare neuroretinal rim area measurements by confocal scanning laser tomography and planimetric evaluation of optic disc photographs. METHODS—For 221 patients with primary and secondary open angle glaucoma, 72 subjects with ocular hypertension, and 139 normal subjects, the optic disc was morphometrically analysed by the confocal scanning laser tomograph HRT (Heidelberg retina tomograph) and by planimetric evaluation of stereo colour optic disc photographs. RESULTS—Absolute rim area and rim to disc area were significantly (p<0.0001) larger with the HRT than with planimetric evaluation of photographs. Differences between the two methods were significantly (p<0.01) larger in normal eyes with small cupping than in normal eyes with large cupping, and differences were significantly (p<0.01) larger in glaucomatous eyes with marked nerve damage than in glaucomatous eyes with moderate nerve damage. Coefficients of correlations between rim measurements of both methods were R2=0.60 for rim to disc area and R2=0.33 for absolute rim area. Planimetric measurements of rim area correlated significantly (p<0.05) better than HRT determinations of rim area with mean visual field defect and retinal nerve fibre layer visibility. CONCLUSIONS—Measurements of absolute rim area and rim to disc area are significantly larger with the HRT compared with planimetry of disc photographs. Differences between both methods depend on disc area, cup size and glaucoma stage. The reason may be that the HRT measures the retinal vessel trunk as part of the neuroretinal rim. The differences between both methods, which should be taken into account if disc measurements performed by both methods are compared with each other, may not influence the main advantage of the HRT—that is, morphological follow up examination of patients with glaucoma. Keywords: glaucoma; neuroretinal rim area; confocal laser scanning tomography; planimetry
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (132.4 KB).
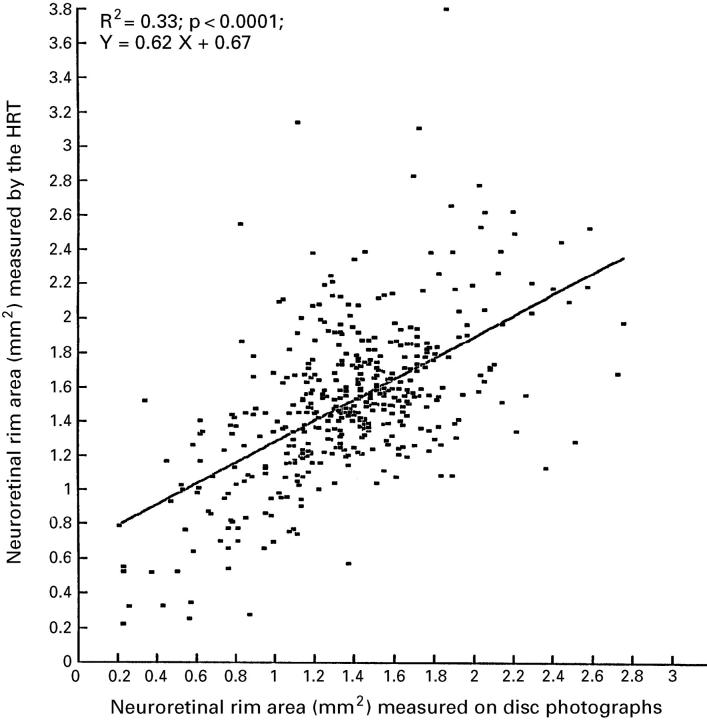
Figure 1 .
Scattergram showing the correlation between measurements of neuroretinal rim area by the HRT and rim area determination by planimetry of optic disc photographs in 221 patients with primary and secondary open angle glaucoma, 72 subjects with ocular hypertension, and 139 normal subjects.
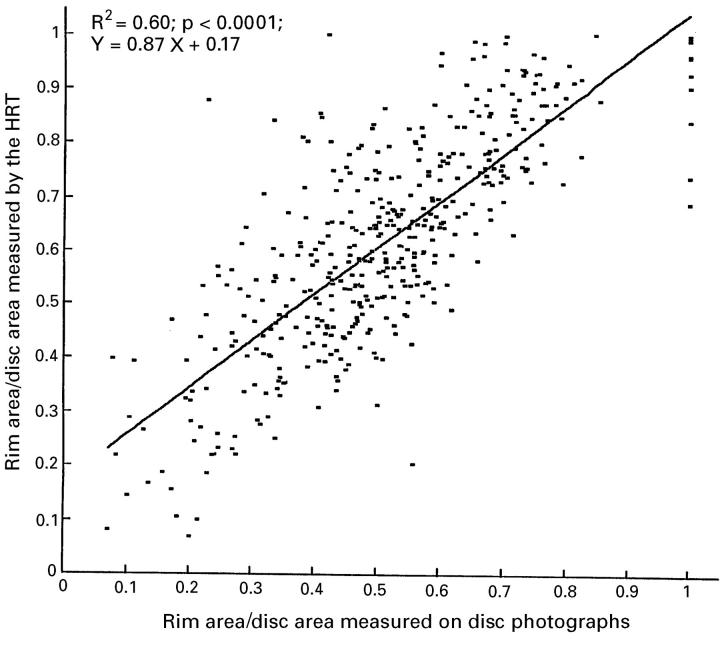
Figure 2 .
Scattergram showing the correlation between measurements of the ratio of neuroretinal rim area to disc area performed by the HRT and by planimetry of optic disc photographs.
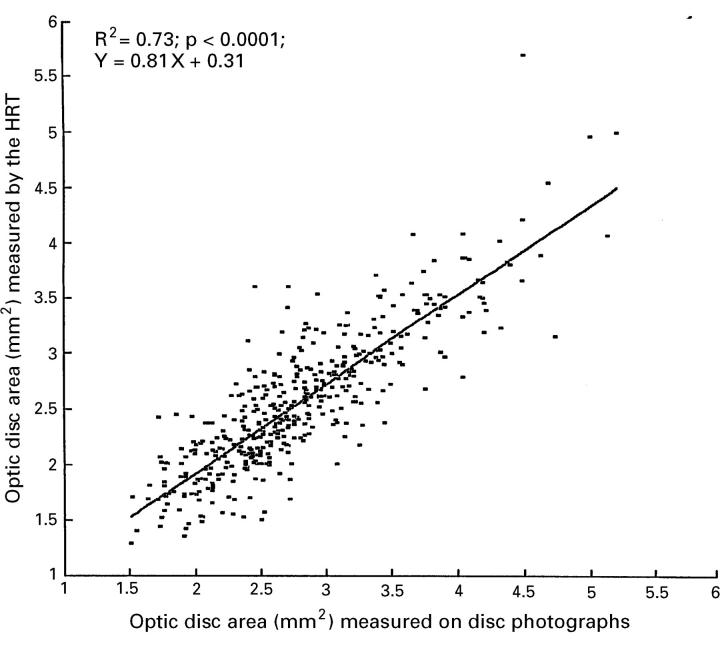
Figure 3 .
Scattergram showing the correlation between measurement of the optic disc area by the HRT and determination of the optic disc area by planimetric evaluation of optic disc photographs.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airaksinen P. J., Drance S. M. Neuroretinal rim area and retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Feb;103(2):203–204. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050020055018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airaksinen P. J., Nieminen H. Retinal nerve fiber layer photography in glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1985 Jul;92(7):877–879. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)33941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartz-Schmidt K. U., Sengersdorf A., Esser P., Walter P., Hilgers R. D., Krieglstein G. K. The cumulative normalised rim/disc area ratio curve. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1996 Apr;234(4):227–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00430414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. The variation and covariation of cup and disc diameters. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1976 Dec;54(6):804–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1976.tb01801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigatti L., Caprioli J. Correlation of visual field with scanning confocal laser optic disc measurements in glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995 Sep;113(9):1191–1194. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1995.01100090117032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. O., Rohrschneider K., Noack H., Völcker H. E. Are large optic nerve heads susceptible to glaucomatous damage at normal intraocular pressure? A three-dimensional study by laser scanning tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992;230(6):552–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00181778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. O., Rohrschneider K., Takamoto T., Völcker H. E., Schwartz B. Laser scanning tomography and stereophotogrammetry in three-dimensional optic disc analysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1993 Apr;231(4):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00918840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli J., Miller J. M. Optic disc rim area is related to disc size in normal subjects. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Dec;105(12):1683–1685. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060120081030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan B. C., LeBlanc R. P., McCormick T. A., Rogers J. B. Test-retest variability of topographic measurements with confocal scanning laser tomography in patients with glaucoma and control subjects. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994 Jul 15;118(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi T., Ritch R., Stickler D., Pitman B., Tsai C., Hsieh F. Y. Racial differences in optic nerve head parameters. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Jun;107(6):836–839. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070010858029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichtl A., Jonas J. B., Mardin C. Y. Comparison between tomographic scanning evaluation and photographic measurement of the neuroretinal rim. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 May;121(5):494–501. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher A. W., Tso P. C., Weinreb R. N. Reproducibility of topographic measurements of the normal and glaucomatous optic nerve head with the laser tomographic scanner. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 Feb 15;111(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht P., Funk J. Optic nerve head analyser and Heidelberg retina tomograph: accuracy and reproducibility of topographic measurements in a model eye and in volunteers. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994 Oct;78(10):760–768. doi: 10.1136/bjo.78.10.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Naumann G. O. Optic disc, cup and neuroretinal rim size, configuration and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jul;29(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Naumann G. O. Optic disk morphometry in high myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226(6):587–590. doi: 10.1007/BF02169209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Nguyen X. N., Naumann G. O. Parapapillary retinal vessel diameter in normal and glaucoma eyes. I. Morphometric data. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Jul;30(7):1599–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Papastathopoulos K. Ophthalmoscopic measurement of the optic disc. Ophthalmology. 1995 Jul;102(7):1102–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(95)30905-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Schiro D. Visibility of the normal retinal nerve fiber layer correlated with rim width and vessel caliber. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1993 Apr;231(4):207–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00918842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littmann H. Zur Bestimmung der wahren Grösse eines Objektes auf dem Hintergrund des lebenden Auges. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1982 Apr;180(4):286–289. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1055068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgül S., Cioffi G. A., Bacon D. R., Van Buskirk E. M. Sources of variability of topometric data with a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996 Feb;114(2):161–164. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1996.01100130155007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider K., Burk R. O., Kruse F. E., Völcker H. E. Reproducibility of the optic nerve head topography with a new laser tomographic scanning device. Ophthalmology. 1994 Jun;101(6):1044–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(94)31220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuulonen A., Airaksinen P. J. Optic disc size in exfoliative, primary open angle, and low-tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992 Feb;110(2):211–213. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1992.01080140067029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida H., Brigatti L., Caprioli J. Detection of structural damage from glaucoma with confocal laser image analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996 Nov;37(12):2393–2401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zangwill L., Shakiba S., Caprioli J., Weinreb R. N. Agreement between clinicians and a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope in estimating cup/disk ratios. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995 Apr;119(4):415–421. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]