Abstract
AIM—To determine the staining pattern of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) at different stages of diabetic retinopathy (including post-laser photocoagulation) and to compare staining in excised fibrovascular and fibrocellular (non-diabetic) preretinal membranes. METHODS—Immunohistochemical localisation of VEGF, using antibodies raised against VEGF165 and VEGF121,165,189, was carried out on specimens of normal human retina (n=15), diabetic retinas ((a) with no overt retinopathy (n=19), (b) with intraretinal vascular abnormalities but no proliferative retinopathy (n=6), (c) with active proliferative retinopathy (n=6), (d) with no residual proliferative retinopathy after photocoagulation therapy (n=15)), excised diabetic fibrovascular membranes (n=19), and non-diabetic fibrocellular membranes (n=7). The degree and pattern of immunostaining was recorded. RESULTS—In general, VEGF was absent from the majority of normal retinas. VEGF staining was apparent in most diabetic tissues but the staining pattern was dependent on both the specificity of the antibody used and the category of tissue. Staining with the VEGF165 antibody was generally confined to endothelial cells and perivascular regions while the VEGF121,165,189 antibody was also associated with extravascular components of the inner retina. Intensity of immunostaining of diabetic eyes was dependent on the severity of retinopathy being least in diabetics with no overt retinopathy and greatest in retinas with proliferative retinopathy. Interestingly, the intensity of immunostaining in diabetic retinas which had undergone laser surgery for proliferative retinopathy was reduced to basal levels. Moderate to intense immunostaining was observed in all fibrovascular and fibrocellular membranes examined. CONCLUSIONS—This study supports a circumstantial role for VEGF in the pathogenesis of both the preclinical and proliferative stages of diabetic retinopathy. Keywords: vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGF; diabetes; diabetic retinopathy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (199.6 KB).
Figure 1 .
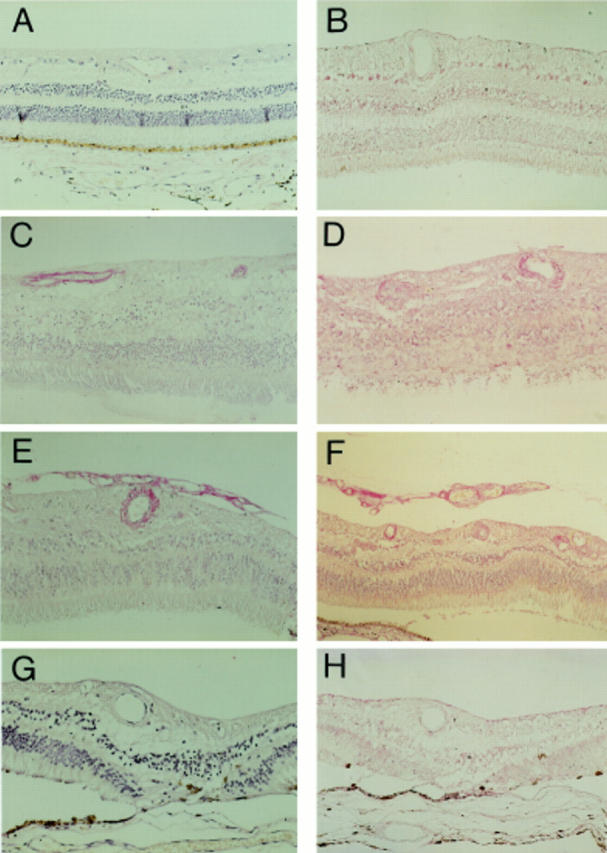
Photomicrographs demonstrating VEGF immunostaining of normal retina (A), diabetic retina with no obvious retinopathy (B), diabetic retina with obvious intraretinal vascular changes but no evidence of PDR (C, D), diabetic retina with PDR (E, F), and diabetic retina after laser treatment for PDR (G, H). Sections were immunostained with either an antibody raised against VEGF165 (A, C, E, G) or VEGF121,165,189 (B, D, F, H). Immunostaining was greatest in diabetic retinas with PDR for both antibodies tested, minimal in normal retinas, and intermediate in diabetic retinas without PDR. It was interesting to note that immunostaining in lasered diabetic retinas with no current evidence of PDR was greatly reduced compared with the staining intensity in retinas with PDR. Magnification, A-E, G ×90; F, H ×70.
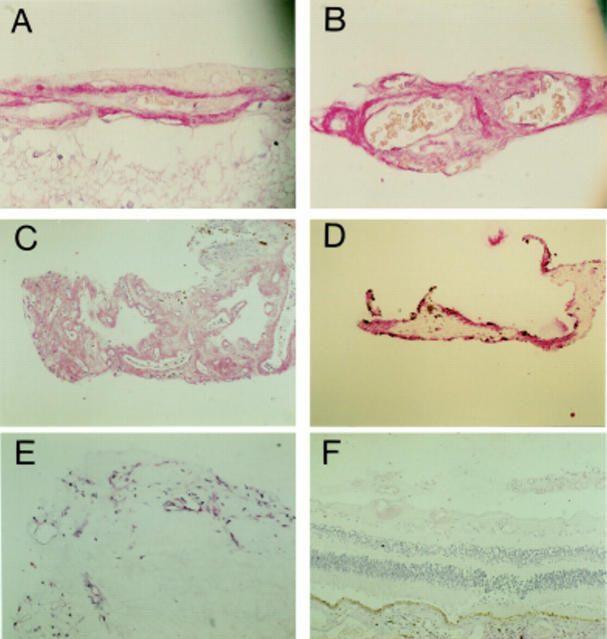
Figure 2 .
Photomicrographs demonstrating VEGF immunostaining of PDR retina and excised membranes. Intense immunostaining for VEGF165 is localised to the vasculature (A) while VEGF121,165,189 immunostaining is observed in both vascular and extravascular tissue (B). Moderate to intense staining can be observed in all specimens of excised fibrovascular (C) and fibrocellular (D) epiretinal membranes. Immunoreactivity for VEGF was abolished in control sections of PDR retina and membranes processed with omission of the primary antibody (E) or prior incubation of the antibody with VEGF. Magnification, A, B ×200; C-F ×70.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamis A. P., Miller J. W., Bernal M. T., D'Amico D. J., Folkman J., Yeo T. K., Yeo K. T. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994 Oct 15;118(4):445–450. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiello L. P., Avery R. L., Arrigg P. G., Keyt B. A., Jampel H. D., Shah S. T., Pasquale L. R., Thieme H., Iwamoto M. A., Park J. E. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994 Dec 1;331(22):1480–1487. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199412013312203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin R. H., Frank R. N., Kennedy A., Eliott D., Puklin J. E., Abrams G. W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is present in glial cells of the retina and optic nerve of human subjects with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997 Jan;38(1):36–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton M. E., Foreman D., McLeod D. Vascularised vitreoretinopathy: the role of growth factors. Eye (Lond) 1996;10(Pt 6):691–696. doi: 10.1038/eye.1996.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hackett S. F., Schoenfeld C. L., Vinores M. A., Vinores S. A., Campochiaro P. A. Localisation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors to cells of vascular and avascular epiretinal membranes. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Oct;81(10):919–926. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.10.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Olander J. V., Heuvelman D., Nelson R., Monsell R., Siegel N., Haymore B. L., Leimgruber R., Feder J. Human vascular permeability factor. Isolation from U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20017–20024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills D. G., Moss S. E., Klein R., Klein B. E. Association of elevated IGF-I levels with increased retinopathy in late-onset diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Dec;40(12):1725–1730. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.12.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1650–1659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez V. H., Hu L. K., Theodossiadis P. G., Flotte T. J., Gragoudas E. S., Young L. H. Photodynamic therapy of pigmented choroidal melanomas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 Apr;36(5):871–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez V. H., Hu L. K., Theodossiadis P. G., Flotte T. J., Gragoudas E. S., Young L. H. Photodynamic therapy of pigmented choroidal melanomas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 Apr;36(5):871–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrin M., Moukadiri H., Chollet P., Moro F., Dutt K., Malecaze F., Plouët J. Vasculotropin/vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor for human retinal pigment epithelial cells cultured in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1995 Aug;164(2):385–394. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041640219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanneken A., de Juan E., Jr, Lutty G. A., Fox G. M., Schiffer S., Hjelmeland L. M. Altered distribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Jul;109(7):1005–1011. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080070117048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck K. A., Ferrara N., Winer J., Cachianes G., Li B., Leung D. W. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1806–1814. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutty G. A., McLeod D. S., Merges C., Diggs A., Plouét J. Localization of vascular endothelial growth factor in human retina and choroid. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996 Aug;114(8):971–977. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1996.01100140179011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malecaze F., Clamens S., Simorre-Pinatel V., Mathis A., Chollet P., Favard C., Bayard F., Plouet J. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor messenger RNA and vascular endothelial growth factor-like activity in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994 Nov;112(11):1476–1482. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1994.01090230090028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. W., Adamis A. P., Shima D. T., D'Amore P. A., Moulton R. S., O'Reilly M. S., Folkman J., Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F., Berse B. Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is temporally and spatially correlated with ocular angiogenesis in a primate model. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):574–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchenko A., Bauer T., Salceda S., Caro J. Hypoxic stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest. 1994 Sep;71(3):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Ishibashi T., Khalil A., Hata Y., Yoshikawa H., Inomata H. Vascular endothelial growth factor plays a role in hyperpermeability of diabetic retinal vessels. Ophthalmic Res. 1995;27(1):48–52. doi: 10.1159/000267567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Nakagawa K., Khalil A., Ishibashi T., Inomata H., Sueishi K. The relation between expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic rat retinas. Lab Invest. 1996 Apr;74(4):819–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pe'er J., Folberg R., Itin A., Gnessin H., Hemo I., Keshet E. Upregulated expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996 Mar;80(3):241–245. doi: 10.1136/bjo.80.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pe'er J., Shweiki D., Itin A., Hemo I., Gnessin H., Keshet E. Hypoxia-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by retinal cells is a common factor in neovascularizing ocular diseases. Lab Invest. 1995 Jun;72(6):638–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. P., Peters K. G., De Vries C., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. Fetal liver kinase 1 is a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor and is selectively expressed in vascular endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7533–7537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins S. G., Mixon R. N., Wilson D. J., Hart C. E., Robertson J. E., Westra I., Planck S. R., Rosenbaum J. T. Platelet-derived growth factor ligands and receptors immunolocalized in proliferative retinal diseases. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 Sep;35(10):3649–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Van de Water L., Brown L. F., Nagy J. A., Yeo K. T., Yeo T. K., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):303–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00665960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme H., Aiello L. P., Takagi H., Ferrara N., King G. L. Comparative analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors on retinal and aortic vascular endothelial cells. Diabetes. 1995 Jan;44(1):98–103. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolentino M. J., Miller J. W., Gragoudas E. S., Jakobiec F. A., Flynn E., Chatzistefanou K., Ferrara N., Adamis A. P. Intravitreous injections of vascular endothelial growth factor produce retinal ischemia and microangiopathy in an adult primate. Ophthalmology. 1996 Nov;103(11):1820–1828. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(96)30420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuder R. M., Flook B. E., Voelkel N. F. Increased gene expression for VEGF and the VEGF receptors KDR/Flk and Flt in lungs exposed to acute or to chronic hypoxia. Modulation of gene expression by nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1798–1807. doi: 10.1172/JCI117858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries C., Escobedo J. A., Ueno H., Houck K., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1312256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]