Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (116.3 KB).
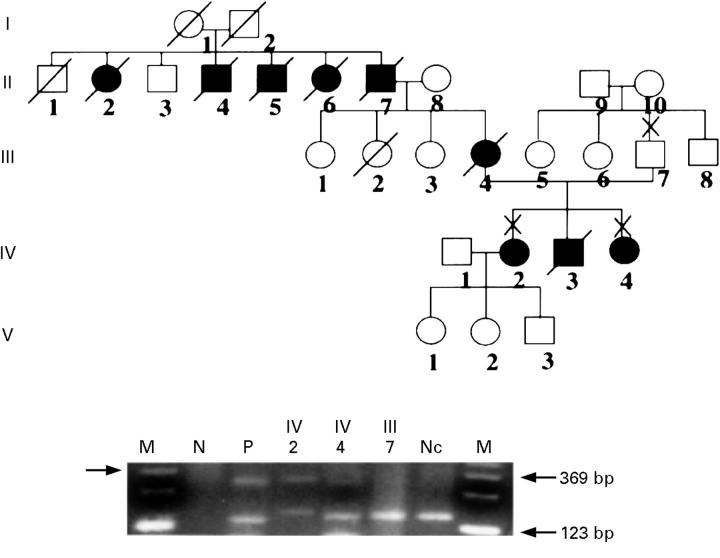
Figure 1 .
Pedigree of the family with spinocerebellar degeneration and trinucleotide examination of DRPLA gene showing generations (roman numerals) of affected (solid symbols) and unaffected (open symbols) members. Squares indicate male members; circles, female; X, examined; and slash, deceased. The results of PCR showed that the affected patients (IV-2 and IV-4) had expanded allele of DRPLA gene, when they were compared with an unaffected family member (III-7) or normal healthy control (Nc). Primers used for amplification of the gene were described elsewhere.4 N is a negative control without DNA and P is a positive control as we previously reported.4 M is a marker of 123 base pair. The arrow in the left margin indicates the larger bands due to expanded allele of the DRPLA gene.
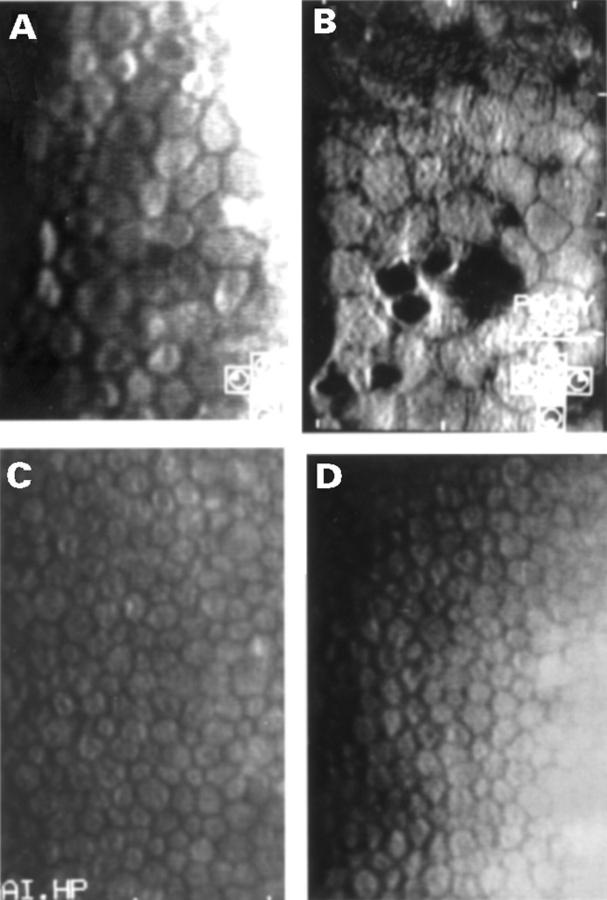
Figure 2 .
Specular microscopy reveals that patients with the mutated allele of DRPLA gene show severely decreased cell density in the corneal endothelium. Endothelial photographs of (A) patient IV-4 in Figure 1; (B) patient IV-2 in Figure 1; (C) family member III-7 in Figure 1 (2724 cells/mm2); and (D) a patient with Machado-Joseph disease who has a trinucleotide expansion allele with a normal repeat allele of the Machado-Joseph disease gene (2814 cells/mm2). Actual cell densities are reported in the text.