Abstract
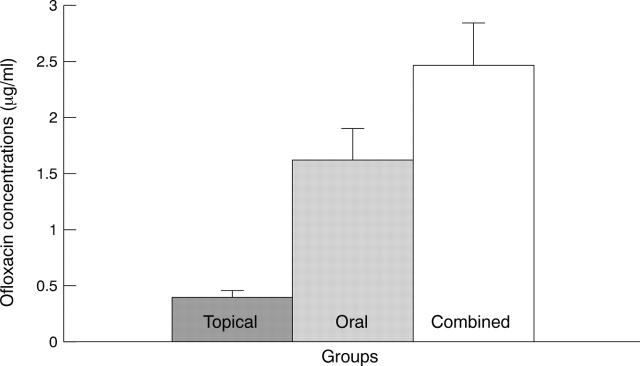
AIMS—To assess the subretinal fluid (SRF) levels of ofloxacin following topical, oral or combined administration. METHODS—31 patients undergoing conventional retinal reattachment surgery were randomly assigned to three groups. Nine patients received topical ofloxacin, 11 patients received oral ofloxacin, and the other 11 patients received combined administration. Collected SRF samples were analysed for drug level by using high performance liquid chromatography. RESULTS—SRF drug levels after oral and combined administration were significantly higher than that after topical administration (p=0.0002 and p=0.0002, respectively) while there was no significant difference between oral and combined administration (p=0.0844). CONCLUSIONS—Ocular bioavailability of ofloxacin in SRF after oral and combined administration is equivalent. The addition of oral ofloxacin to topical therapy increased drug SRF penetration sixfold.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (74.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
Comparison of subretinal fluid levels of ofloxacin obtained after different modes of administration.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkan A. G., Mutlu I., Ozyazgan S., Gok A., Yigit U., Ozuner Z., Senses V., Pekel H. Penetration of topically applied ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin into the aqueous humor of the uninflamed human eye. J Chemother. 1997 Aug;9(4):257–262. doi: 10.1179/joc.1997.9.4.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akkan A. G., Mutlu I., Ozyazgan S., Gök A., Yigit U., Ozüner Z., Senses V., Pekel H. Comparative tear concentrations of topically applied ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and norfloxacin in human eyes. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997 May;35(5):214–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro D. V., Davis J., Kim S., Bia F., Bogard J. F., Briggs J. W., Liggett P. E. Experimental Bacillus cereus post-traumatic endophthalmitis and treatment with ciprofloxacin. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996 Aug;80(8):755–758. doi: 10.1136/bjo.80.8.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basci N. E., Hanioglu-Kargi S., Soysal H., Bozkurt A., Kayaalp S. O. Determination of ofloxacin in human aqueous humour by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1997 Feb;15(5):663–666. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(96)01889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens-Baumann W. Absorption of topically administered ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and gentamicin in the inflamed rabbit eye. Ophthalmologica. 1996;210(2):119–122. doi: 10.1159/000310687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cekic O., Batman C., Yasar U., Basci N. E., Bozkurt A., Kayaalp S. O. Penetration of ofloxacin in human aqueous and vitreous humors following oral and topical administration. Retina. 1998;18(6):521–525. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199806000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cekiç O., Batman C., Totan Y., Yasar U., Basci N. E., Bozkurt A., Kayaalp S. O. Penetration of ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in aqueous humor after topical administration. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999 Jun;30(6):465–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J., Faria de Abreu J. R., Campos A. J. Early breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Nov;59(11):649–656. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.11.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David D. B., Kirkby G. R., Noble B. A. Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994 Jul;78(7):577–580. doi: 10.1136/bjo.78.7.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. P., White L., Leeming J. P., Bing Hoh H., Easty D. L. Topical 0.3% ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin in treatment of bacterial keratitis: a new method for comparative evaluation of ocular drug penetration. Br J Ophthalmol. 1995 Jun;79(6):606–609. doi: 10.1136/bjo.79.6.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenfeld E. D., Perry H. D., Snyder R. W., Moadel R., Elsky M., Jones H. Intracorneal, aqueous humor, and vitreous humor penetration of topical and oral ofloxacin. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Feb;115(2):173–176. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150175004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew R. H., Gallis H. A. Ofloxacin: its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and potential for clinical application. Pharmacotherapy. 1988;8(1):35–46. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1988.tb04063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durmaz B., Marol S., Durmaz R., Oram O., Hepsen I. F., Günal S. Aqueous humor penetration of topically applied ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and tobramycin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1997 Apr;47(4):413–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti G., Panozzo G. Effect of inflammation on intraocular penetration of intravenous ofloxacin in albino rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Feb;39(2):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.39.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwon A. Topical ofloxacin compared with gentamicin in the treatment of external ocular infection. Ofloxacin Study Group. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992 Dec;76(12):714–718. doi: 10.1136/bjo.76.12.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanioglu-Kargi S., Basci N., Soysal H., Bozkurt A., Gürsel E., Kayaalp O. The penetration of ofloxacin into human aqueous humor given by various routes. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1998 Jan-Mar;8(1):33–36. doi: 10.1177/112067219800800108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk M. R., Ammann H., Marcil G., Vinet B., Lamer L., Sebag M. The penetration of oral ciprofloxacin into the aqueous humor, vitreous, and subretinal fluid of humans. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 May 15;115(5):623–628. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman J., Zolezio H., Tang-Liu D. Comparison of ofloxacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin concentrations in tears and in vitro MICs for 90% of test organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1602–1604. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. A., Faulds D. Ofloxacin. A reappraisal of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1991 Nov;42(5):825–876. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199142050-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]