Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—The requirement for an effective, minimally toxic immunosuppressive agent remains a major obstacle to performing high risk corneal transplantation. Although therapy with cyclosporin A (CSA) allows superior graft survival, its use is limited because of a wide range of side effects. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) has been shown to be a safe and effective immunosuppressive agent following renal transplantation. This prospective, randomised clinical trial was carried out to investigate the efficacy and safety of MMF in preventing corneal allograft rejection. METHODS—Recipients of corneal transplants who were at high risk for graft failure were randomly assigned to either CSA or MMF immunosuppressive therapy. CSA was given in doses to achieve whole blood trough levels of 120-150 ng/ml. MMF was given in a daily dose of 2 g. Both therapy groups additionally received oral corticosteroids (fluocortolone 1 mg/kg) which were tapered and discontinued within the first 3 postoperative weeks. Patients were monitored closely for evidence of corneal graft rejection and adverse side effects. Drug efficacy was measured, primarily, by the number of patients who experienced at least one episode of clinical graft rejection. Safety analysis focused on reported adverse side effects and laboratory measurements. RESULTS—41 patients were enrolled in the study. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups. 20 patients received CSA and 21 patients received MMF. Two patients in each group showed evidence of acute graft rejection which could be treated effectively by corticosteroids. All corneal grafts remained clear throughout the follow up. CONCLUSIONS—In this study it was shown that MMF is just as effective as CSA in preventing acute rejection following high risk corneal transplantation. Mycophenolate mofetil represents a promising alternative therapeutic option in patients who are at high risk for corneal graft failure.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (85.7 KB).
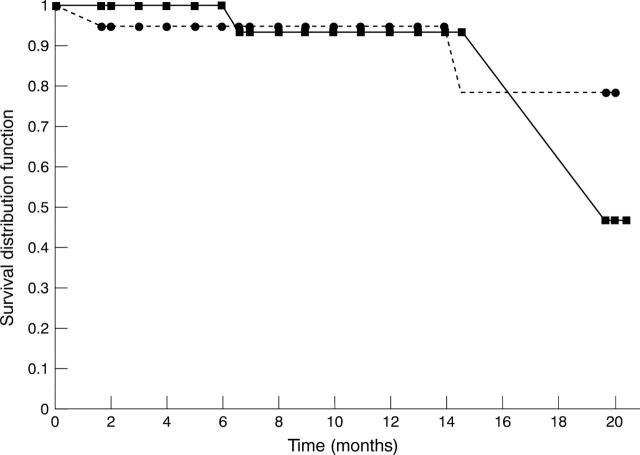
Figure 1 .
Kaplan-Meier survival plot. (•) CSA; (▪) MMF.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Hovi T., Watts R. W., Webster A. D. The role of de novo purine synthesis in lymphocyte transformation. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(48):207–224. doi: 10.1002/9780470720301.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deierhoi M. H., Sollinger H. W., Diethelm A. G., Belzer F. O., Kauffman R. S. One-year follow-up results of a phase I trial of mycophenolate mofetil (RS61443) in cadaveric renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1993 Feb;25(1 Pt 1):693–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. C. Systemic cyclosporine in high-risk keratoplasty. Short- versus long-term therapy. Ophthalmology. 1994 Jan;101(1):128–133. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(13)31253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Hoyt E. G., Murphy M. P., Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Mycophenolic acid morpholinoethylester (RS-61443) is a new immunosuppressant that prevents and halts heart allograft rejection by selective inhibition of T- and B-cell purine synthesis. Transplant Proc. 1990 Aug;22(4):1659–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederkorn J. Y., Mellon J. Anterior chamber-associated immune deviation promotes corneal allograft survival. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996 Dec;37(13):2700–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Reinhard T., Sundmacher R., Braunstein C., Godehardt E. Effect of mycophenolate mofetil, cyclosporin A, and both in combination in a murine corneal graft rejection model. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998 Jun;82(6):700–703. doi: 10.1136/bjo.82.6.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W. Peripheral tolerance induction: lessons from immune privileged sites and tissues. Transplant Proc. 1996 Aug;28(4):2066–2070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundmacher R., Reinhard T., Heering P. Six years' experience with systemic cyclosporin A prophylaxis in high-risk perforating keratoplasty patients. A retrospective study. Ger J Ophthalmol. 1992;1(6):432–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]