Abstract
AIMS—To report the appearances of iridocorneal endothelial (ICE) syndrome from real time, white light confocal microscopy. METHODS—Three consecutive patients, each with ICE syndrome, were examined prospectively. Corneal specular and confocal microscopic examinations were performed in all three patients. In the first patient, a penetrating keratoplasty was performed and the cornea was examined by light and scanning electron microscopy. No surgery was performed in the remaining two patients. RESULTS—In the first patient corneal oedema prevented endothelial specular microscopy. Confocal microscopy performed before penetrating keratoplasty successfully revealed abnormal epithelial-like endothelial cells. Histological examinations of the cornea following penetrating keratoplasty revealed the presence of multilayered endothelial cells with epithelial features (microvilli). In the remaining two patients, specular microscopy showed the presence of ICE cells with typical dark/light reversal. Confocal microscopy demonstrated groups of endothelial cells with epitheloid appearances. In all three patients, the contralateral endothelial appearance was normal by specular and confocal microscopy, except for moderate endothelial polymegathism in one patient. Epithelial-like endothelial cells were characterised by prominent nuclei on confocal microscopy. CONCLUSIONS—The application of confocal microscopy indicates that the ICE syndrome is characterised by epitheloid changes in the endothelium. Confocal microscopy may be used to diagnose the ICE syndrome by demonstrating epithelial-like endothelial cells with hyperreflective nuclei. This technique is especially of value in cases of corneal oedema, since specular microscopy may fail to image the endothelium in such cases.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (178.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
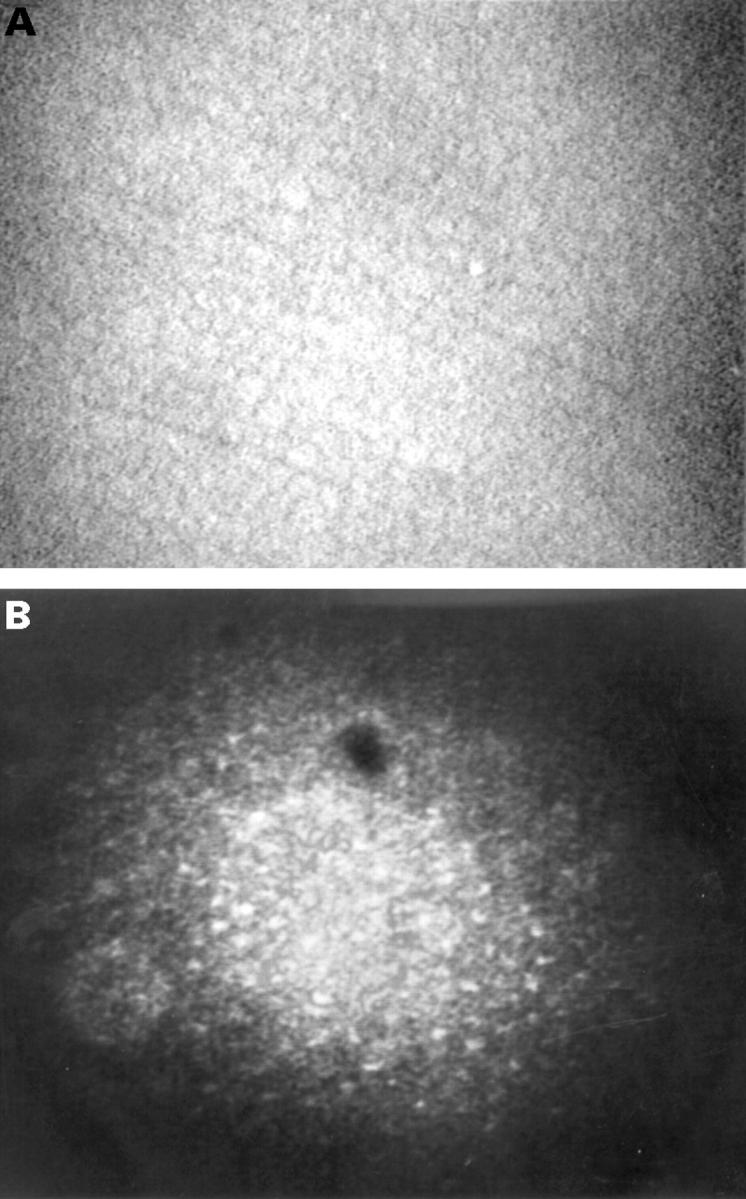
(A) Confocal microscopic appearance of normal endothelial cells from a normal subject. (B) Confocal microscopy (original magnification ×210 ). Abnormal endothelial cells with well identifiable nuclei resembling the confocal microscopic appearance of corneal epithelial cells were found. The cells were relatively regular in shape and size. The dark oval image at the upper part of the picture is an artefact.
Figure 2 .
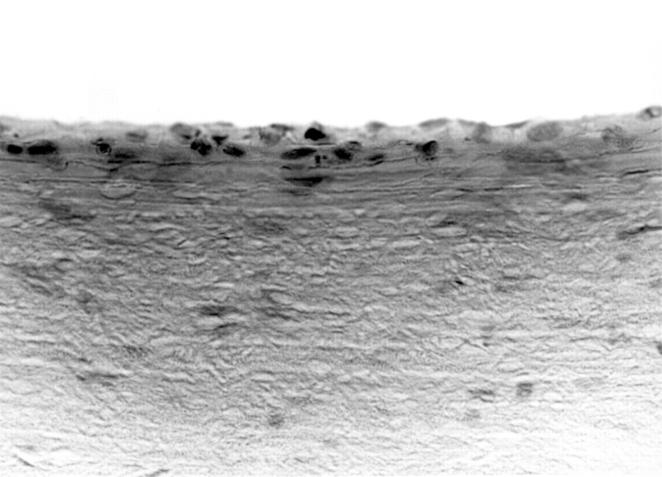
Light microscopy. Histological examination of the endothelium demonstrated multilayered epithelial-like cells.
Figure 3 .
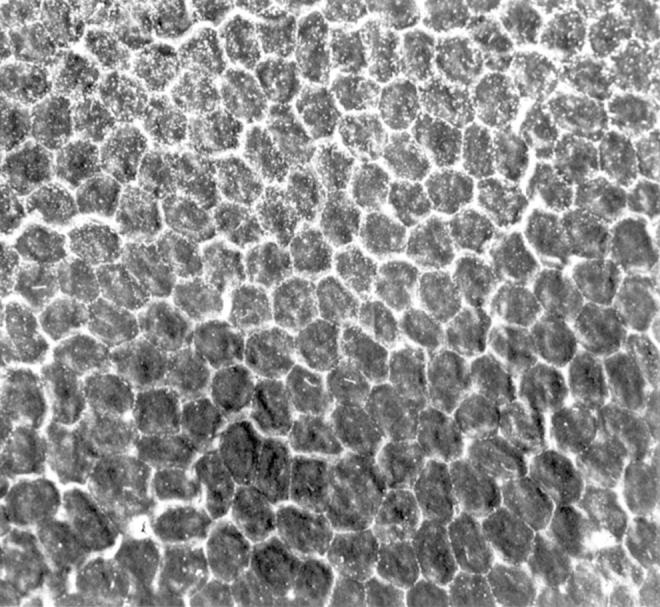
Scanning electron microscopy. Microvilli were found in abnormally high numbers on the surface of many endothelial cells (upper half of the photograph).
Figure 4 .
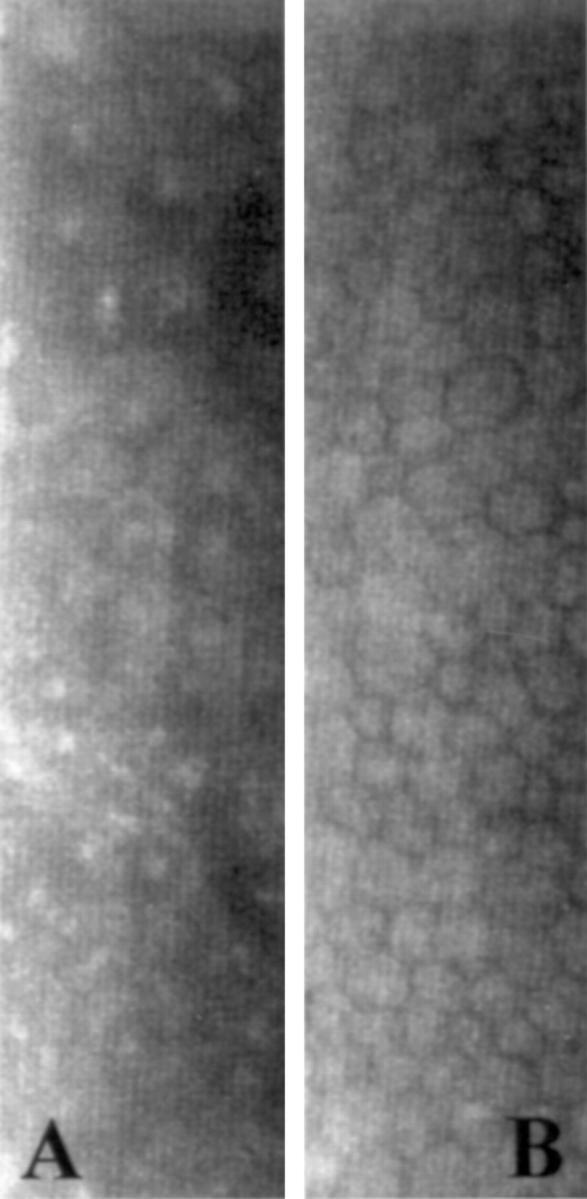
Specular microscopy. (A) Rounded dark cells with light borders and occasional light bodies within cell boundaries could be identified in the endothelium of the abnormal cornea. (B) In the fellow eye, the endothelium exhibited polymegathism, but no characteristics of ICE syndrome.
Figure 5 .
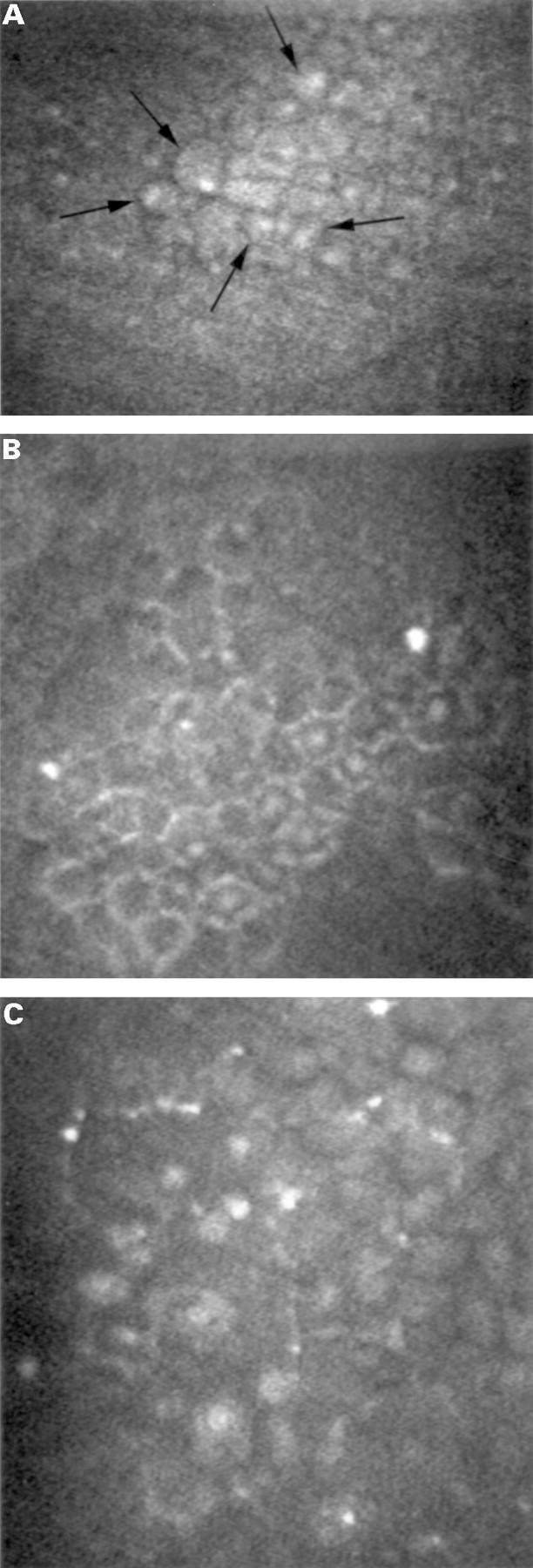
Confocal microscopy (original magnification ×210). (A) Epithelial-like endothelial cells with well recognisable nuclei, of which some are indicated by arrows, were detected. Note the regularity of the cells. (B) Less hyperreflective cell bodies with central hyperreflective nuclei resembling the confocal microscopic appearance of epithelial wing cells were seen. The cells were relatively regular in size and shape. (C) Areas of highly abnormal cells characterised by marked epithelial-like appearance and loss of regularity in size and shape were found. Hyperreflective structures were found within and adjacent to these abnormal areas. Relatively normal appearing endothelial cells were also detected (upper right corner of the photograph).
Figure 6 .
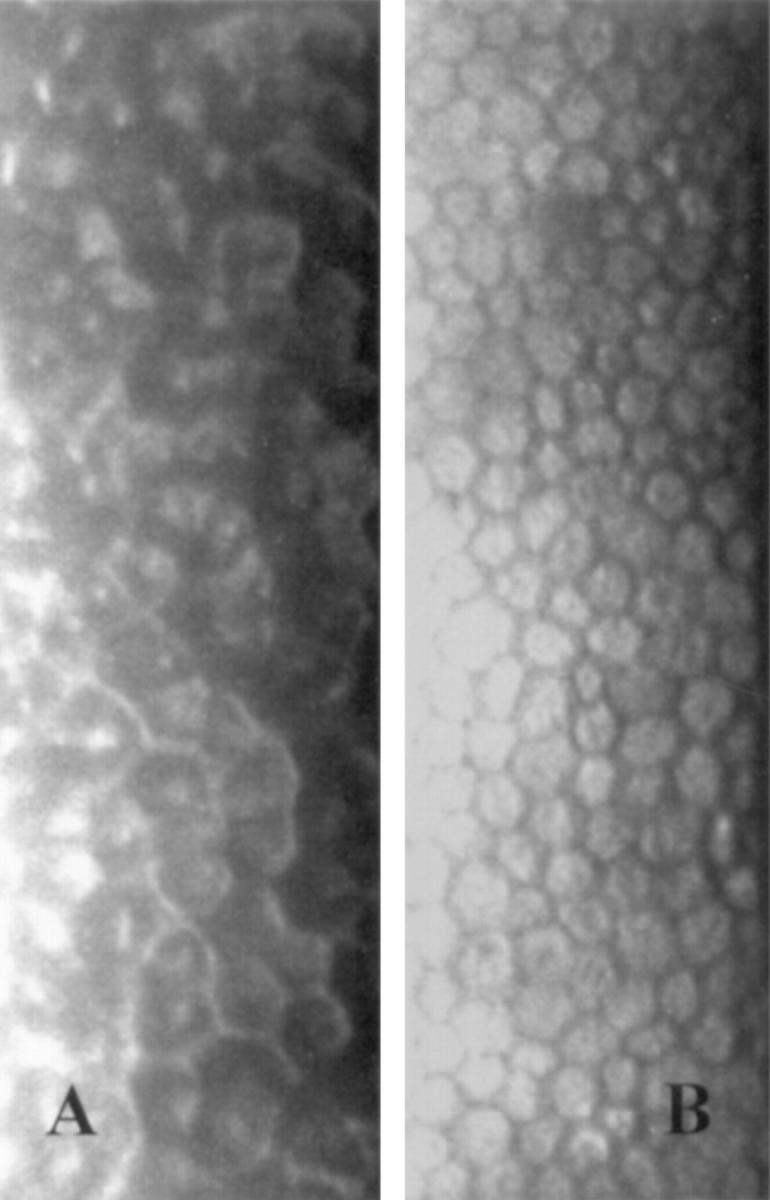
Specular microscopy. Endothelial cells are seen with dark/light reversal and occasional central bright reflex in the clinically abnormal eye (A), not in the normal eye (B).
Figure 7 .
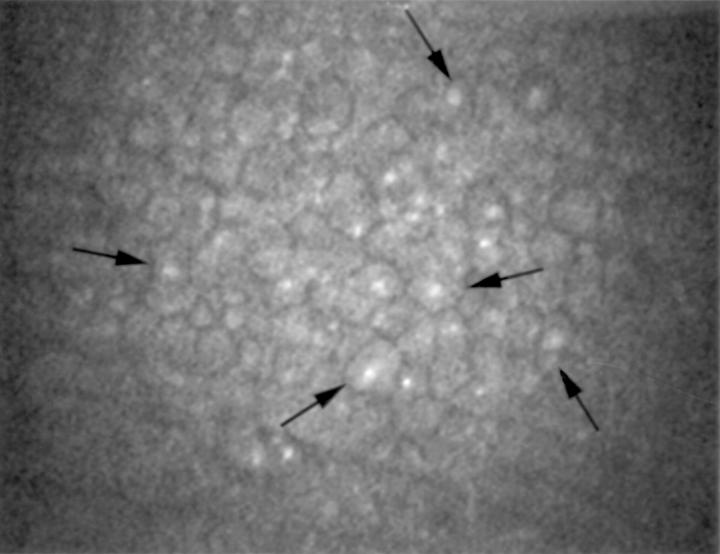
Confocal microscopy (original magnification ×210). The arrows indicate some epithelial-like endothelial cells with nuclear hyperreflectivity.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beuerman R. W. Confocal microscopy: into the clinic. Cornea. 1995 Jan;14(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boruchoff S. A., Kuwabara T. Electron microscopy of posterior polymorphous degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971 Nov;72(5):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(71)91683-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. G., Shields M. B., Smith T. R. The corneal endothelium and the spectrum of essential iris atrophy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978 Sep;86(3):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(78)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh H. D., McCulley J. P. In vivo confocal microscopy and Acanthamoeba keratitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Feb;121(2):207–208. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh H. D., Petroll W. M., Alizadeh H., He Y. G., McCulley J. P., Jester J. V. Clinical and diagnostic use of in vivo confocal microscopy in patients with corneal disease. Ophthalmology. 1993 Oct;100(10):1444–1454. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew S. J., Beuerman R. W., Assouline M., Kaufman H. E., Barron B. A., Hill J. M. Early diagnosis of infectious keratitis with in vivo real time confocal microscopy. CLAO J. 1992 Jul;18(3):197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou A. G., Cadez R., Böhnke M. Diagnosis of Dieffenbachia induced corneal injury by confocal microscopy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Feb;81(2):168–169. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.2.168a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florakis G. J., Moazami G., Schubert H., Koester C. J., Auran J. D. Scanning slit confocal microscopy of fungal keratitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Nov;115(11):1461–1463. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100160631019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst L. W., Bancroft J., Yamauchi K., Green W. R. Immunohistochemical pathology of the corneal endothelium in iridocorneal endothelial syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 Apr;36(5):820–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst L. W., Quigley H. A., Stark W. J., Shields M. B. Specular microscopy of iridocorneal endothelia syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Jan;89(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. N., Damms T., Burchette J. L., Jr, Green W. R. Endothelial metaplasia in the iridocorneal endothelial syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997 Aug;38(9):1896–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. H., Bourne W. M., Campbell R. J. The ultrastructure of Descemet's membrane. I. Changes with age in normal corneas. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982 Dec;100(12):1942–1947. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1982.01030040922011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. C., Beuerman R. W., Kaufman H. E. Diagnosis of advanced Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy with the confocal microscope. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 Nov 15;116(5):652–653. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. C., Chew S. J., Capps S. C., Beuerman R. W. Confocal microscopy of corneal penetration by tarantula hairs. Scanning. 1994 Sep-Oct;16(5):312–315. doi: 10.1002/sca.4950160511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laganowski H. C., Sherrard E. S., Muir M. G., Buckley R. J. Distinguishing features of the iridocorneal endothelial syndrome and posterior polymorphous dystrophy: value of endothelial specular microscopy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991 Apr;75(4):212–216. doi: 10.1136/bjo.75.4.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. R., Marshall G. E., Kirkness C. M. Corneal endothelial cell abnormalities in an early stage of the iridocorneal endothelial syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994 Aug;78(8):624–631. doi: 10.1136/bjo.78.8.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. G., McCartney A. C., Baghai M. H., Barrett M. C., Moss J. Pathology of the iridocorneal-endothelial syndrome. The ICE-cell. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 Dec;36(13):2592–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. G., Moss J., Sawada H., Dopping-Hepenstal P. J., McCartney A. C. The composition of wide-spaced collagen in normal and diseased Descemet's membrane. Curr Eye Res. 1996 Jan;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.3109/02713689609017610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Glass T. C., Baratz K. H., Nelson L. R., Hodge D. O., Bourne W. M. The contralateral corneal endothelium in the iridocorneal endothelial syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Jan;115(1):40–44. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150042006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister D. R., Cameron J. D., Krachmer J. H., Holland E. J. Confocal microscopy findings of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Feb;121(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70576-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. P., Hettinger M. E. Endothelial and epithelial-like cell formations in a case of posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Oct;103(10):1520–1524. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050100096028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues M. M., Sun T. T., Krachmer J., Newsome D. Epithelialization of the corneal endothelium in posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 Jul;19(7):832–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G. K., Pfister D., Probst L. E., Ferrieri P., Holland E. Diagnosis of microsporidial keratitis by confocal microscopy and the chromatrope stain. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Jan;121(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutphin J. E., Kantor A. L., Mathers W. D., Mehaffey M. G. Evaluation of infectious crystalline keratitis with confocal microscopy in a case series. Cornea. 1997 Jan;16(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomii S., Kinoshita S. Observations of human corneal epithelium by tandem scanning confocal microscope. Scanning. 1994 Sep-Oct;16(5):305–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester K., Mathers W. D., Sutphin J. E. Diagnosis of Aspergillus keratitis in vivo with confocal microscopy. Cornea. 1997 Jan;16(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]