Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—"Orientation teeth" at the donor trephination margin and correspondent "notches" at the host margin facilitate graft orientation and avoid "horizontal torsion" induced by asymmetric suture placement. In this study the quality and reproducibility of these structures created by non-mechanical laser corneal trephination were compared using two laser emissions. METHODS—The procedure was performed in 20 enucleated pigs' eyes using open metal masks with eight "orientation teeth/notches" (0.3 × 0.15 mm, base × height), an automated globe rotation device, and either a 193 nm ArF excimer laser or a Q switched 2.94 µm Er:YAG laser. "Teeth/notches" were analysed by planimetry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). RESULTS—Mean size was 0.30 (0.027) × 0.16 (0.017) mm for "teeth" and 0.30 (0.035) × 0.15 (0.021) mm for "notches" (excimer), and 0.31 (0.022) × 0.16 (0.015) mm and 0.30 (0.031) × 0.14 (0.021) mm respectively (Er:YAG). Overall, variability of notches was higher than that of teeth. By SEM, comparable cut regularity and sustained ablation profile were observed with both lasers. However, the corneal surface at the cut edge appeared slightly elevated (⩽35 µm) in the Er:YAG group. CONCLUSION—Orientation teeth/notches resembling those obtained with the excimer laser can be created using the Q switched Er:YAG laser, with potential advantages of lower costs, convenient equipment size, and solid state safety.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (137.2 KB).
Figure 1 .
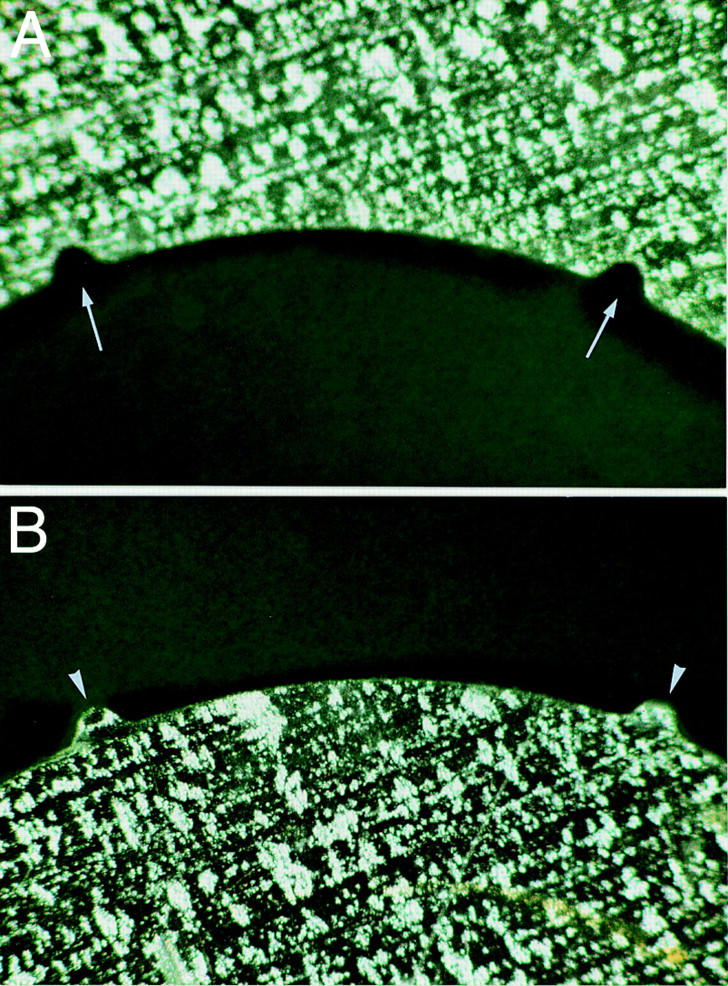
Open metal masks (detail ×30). (A) Recipient mask, showing two "notches" in the internal circumference (arrows). (B) Donor mask, showing two peripheral "orientation teeth" at the external circumference (arrowheads).
Figure 2 .
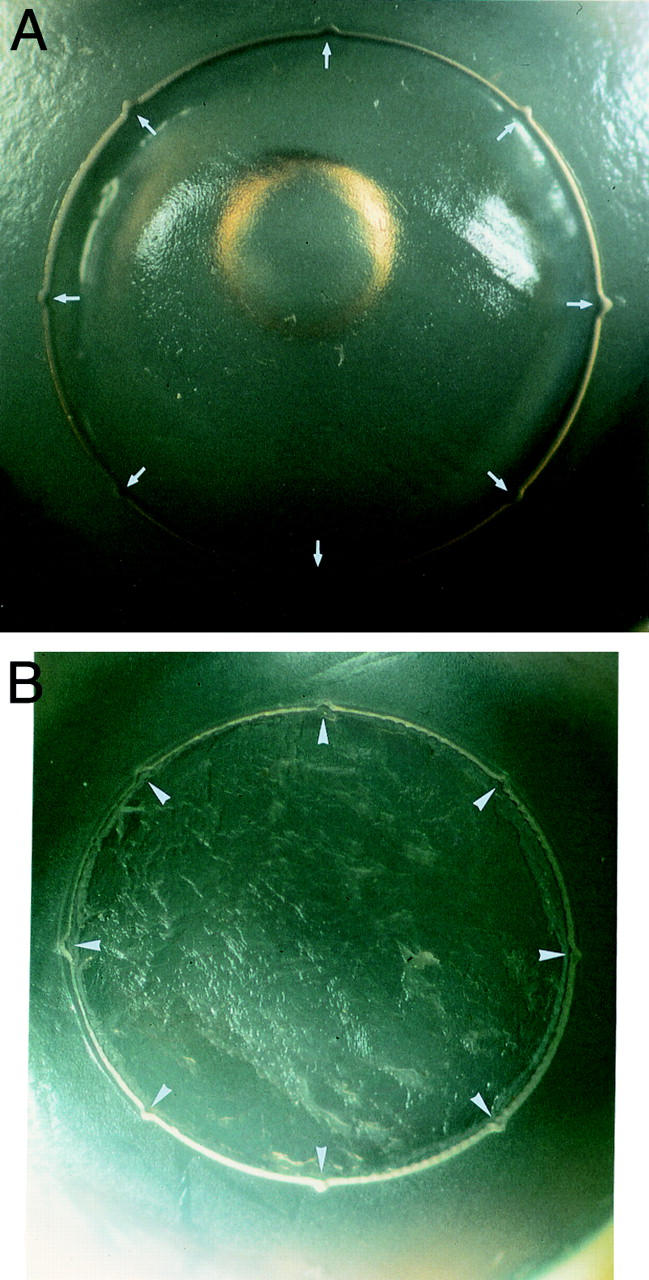
Cut surface in host corneas.(A) Excimer laser cut showing eight full depth "notches" (arrows) in a recipient bed (×9.5). (B) Er:YAG laser cut with eight notches (arrowheads) in a recipient bed (×8).
Figure 3 .
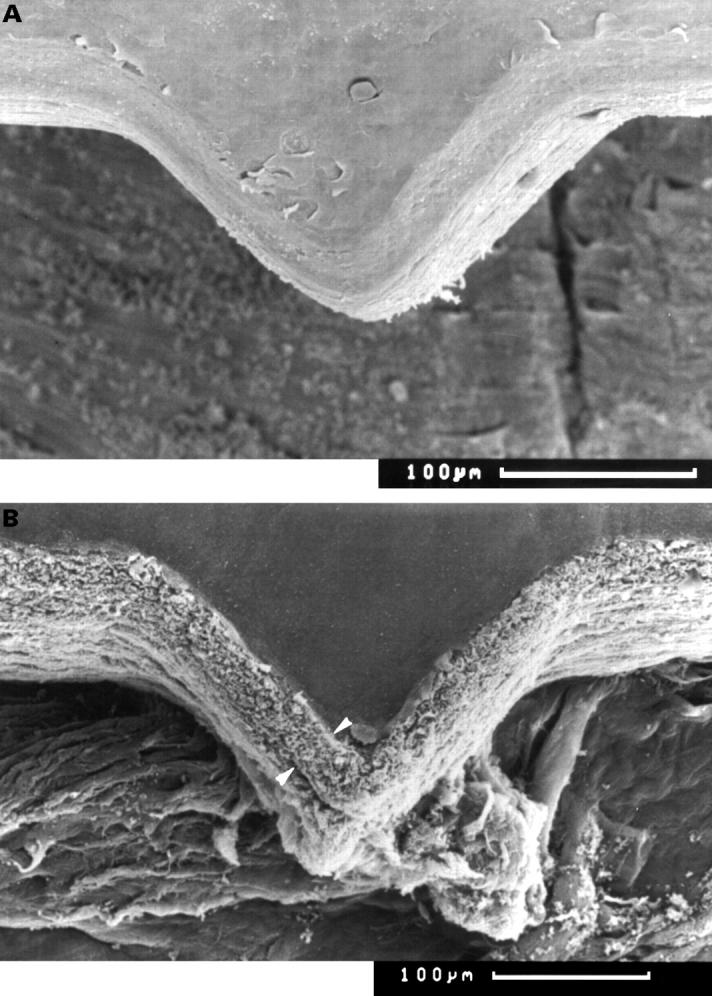
Scanning electron microscopy of "orientation teeth". (A) Excimer laser cut showing the triangular "orientation teeth" (×160). (B) Er:YAG cut of one orientation tooth at the margin of a donor cornea. An elevated surface of up to 35 µm can be observed (between arrowheads) (×150).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assil K. K., Zarnegar S. R., Schanzlin D. J. Visual outcome after penetrating keratoplasty with double continuous or combined interrupted and continuous suture wound closure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992 Jul 15;114(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens A., Küchle M., Seitz B., Langenbucher A., Kus M. M., Amann T., Schlötzer-Schrehardt U., Rummelt C., Naumann G. O. Stromal thermal effects induced by nonmechanical (2.94-mum) erbium:YAG laser corneal trephination. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998 Oct;116(10):1342–1348. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.10.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filatov V., Alexandrakis G., Talamo J. H., Steinert R. F. Comparison of suture-in and suture-out postkeratoplasty astigmatism with single running suture or combined running and interrupted sutures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Nov;122(5):696–700. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbard J. P., Rothman R. C., Kenyon K. R. A new donor cornea marker and punch for penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmic Surg. 1987 Dec;18(12):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang G. K., Koch J. W., Schröder E., Yanoff M., Naumann G. O. Korneale Schnittkonfigurationen mit dem Excimerlaser: eine experimentelle Studie. Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1989;86(5):437–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang G. K., Naumann G. O., Koch J. W. A new elliptical excision for corneal transplantation using an excimer laser. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Jul;108(7):914–915. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070090016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang G. K., Schroeder E., Koch J. W., Yanoff M., Naumann G. O. Excimer laser keratoplasty. Part 1: Basic concepts. Ophthalmic Surg. 1989 Apr;20(4):262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenbucher A., Seitz B., Kus M. M., Naumann G. O. Thermal effects in excimer laser trephination of the cornea. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1996 Aug;234 (Suppl 1):S142–S148. doi: 10.1007/BF02343064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenbucher A., Seitz B., Kus M. M., Vilchis E., Naumann G. O. Graft decentration in penetrating keratoplasty: nonmechanical trephination with the excimer laser (193 nm) versus the motor trephine. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998 Feb;29(2):106–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Trokel S., Rothery S., Krueger R. R. A comparative study of corneal incisions induced by diamond and steel knives and two ultraviolet radiations from an excimer laser. Br J Ophthalmol. 1986 Jul;70(7):482–501. doi: 10.1136/bjo.70.7.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann G. O. Comparison of suture-in and suture-out postkeratoplasty astigmatism with single running suture or combined running and interrupted sutures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997 May;123(5):715–716. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann G. O., Seitz B., Lang G. K., Langenbucher A., Kus M. M. Excimer-Laser-193 nm-Trepanation bei der perforierenden Keratoplastik. Bericht über die ersten 70 Patienten. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1993 Oct;203(4):252–261. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1045677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann G. O. The Bowman Lecture. Eye (Lond) 1995;9(Pt 4):395–421. doi: 10.1038/eye.1995.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson R. J. Corneal curvature changes associated with penetrating keratoplasty: a mathematical model. Ophthalmic Surg. 1980 Dec;11(12):838–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman E. M. An analysis and interpretation of refractive errors after penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 1981 Jan;88(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(81)35086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyman G. A., Badaro R. M., Khoobehi B. Corneal ablation in rabbits using an infrared (2.9-microns) erbium: YAG laser. Ophthalmology. 1989 Aug;96(8):1160–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32755-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pflugfelder S. C., Parel J. M., Denham D., Mandelbaum S. A suction trephine block for marking donor corneal buttons. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Feb;106(2):276–281. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060130290047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz B., Behrens A., Langenbucher A. Corneal topography. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1997 Aug;8(4):8–24. doi: 10.1097/00055735-199708000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz B., Behrens A., Langenbucher A., Kus M. M., Naumann G. O. Experimental 193-nm excimer laser trephination with divergent cut angles in penetrating keratoplasty. Cornea. 1998 Jul;17(4):410–416. doi: 10.1097/00003226-199807000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz B., Langenbucher A., Fischer S., Kus M. M., Vilchis E., Naumann G. O. The regularity of laser keratectomy depth in nonmechanical trephination for penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998 Jan;29(1):33–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz B., Langenbucher A., Kus M. M., Küchle M., Naumann G. O. Nonmechanical corneal trephination with the excimer laser improves outcome after penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 1999 Jun;106(6):1156–1165. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(99)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troutman R. C. Astigmatic considerations in corneal graft. Ophthalmic Surg. 1979 May;10(5):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villacriz E., Rife L., Smith R. E. Oval host wounds and postkeratoplasty astigmatism. Cornea. 1987;6(3):181–184. doi: 10.1097/00003226-198706030-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


