Abstract
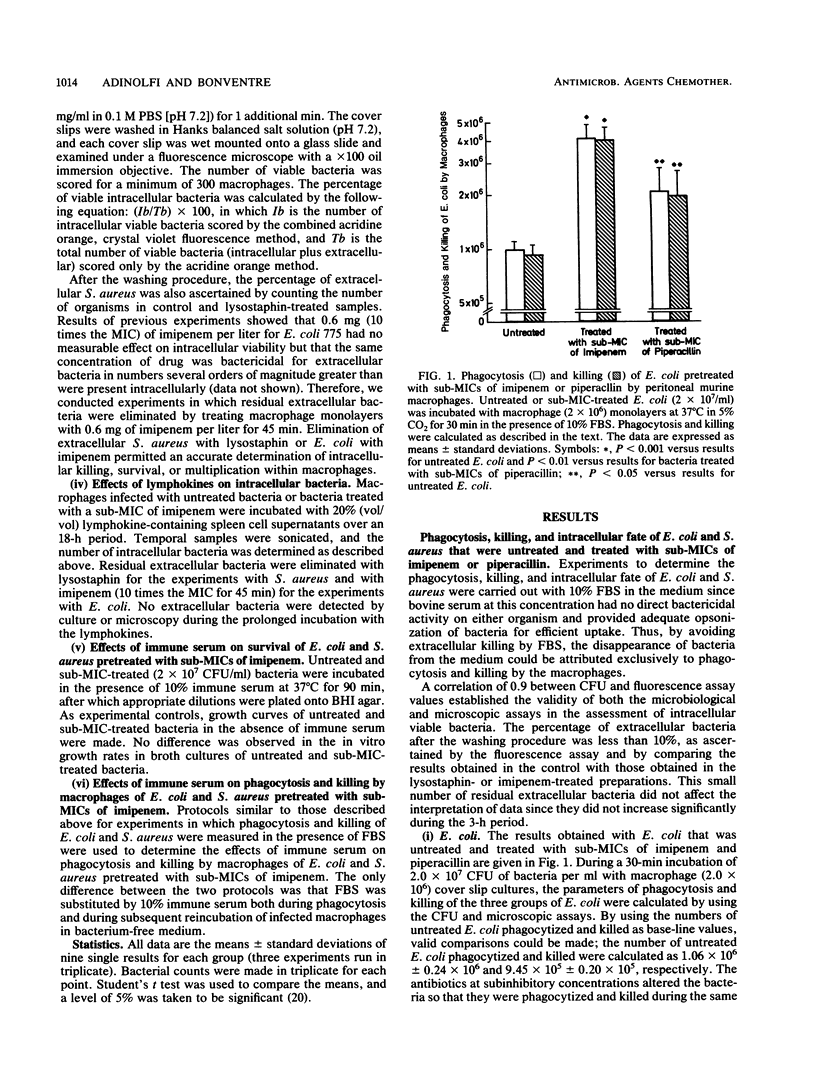
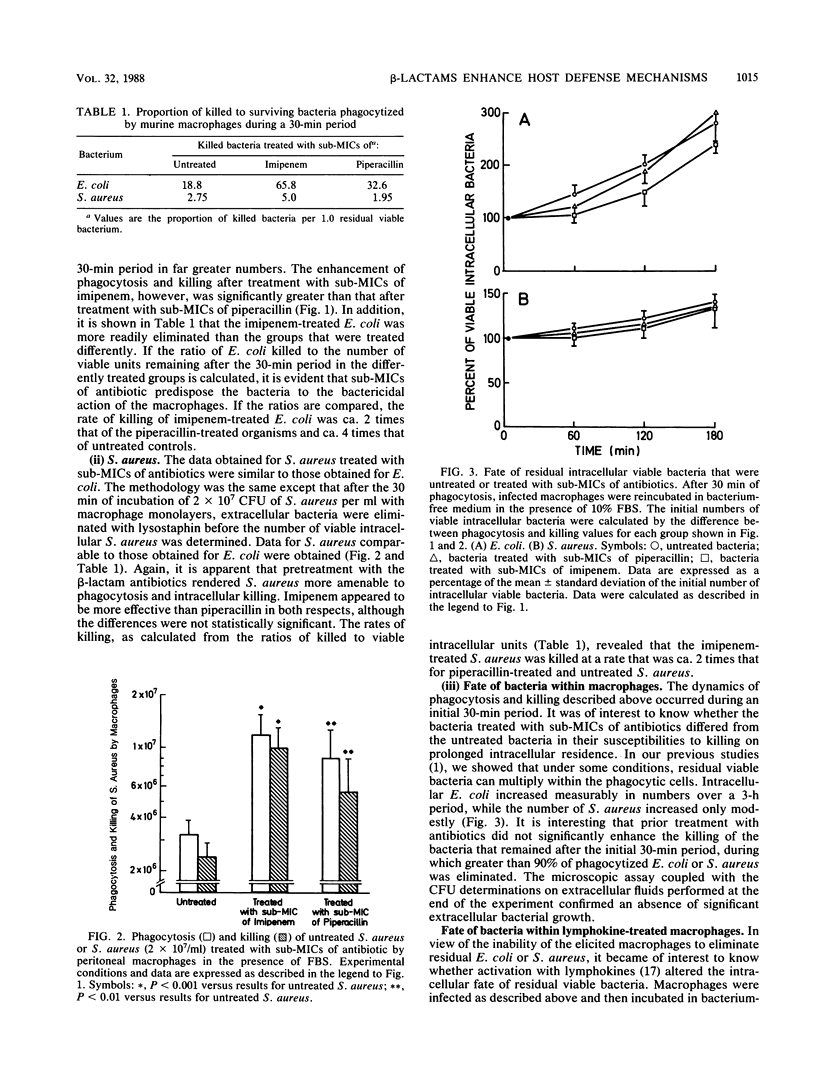
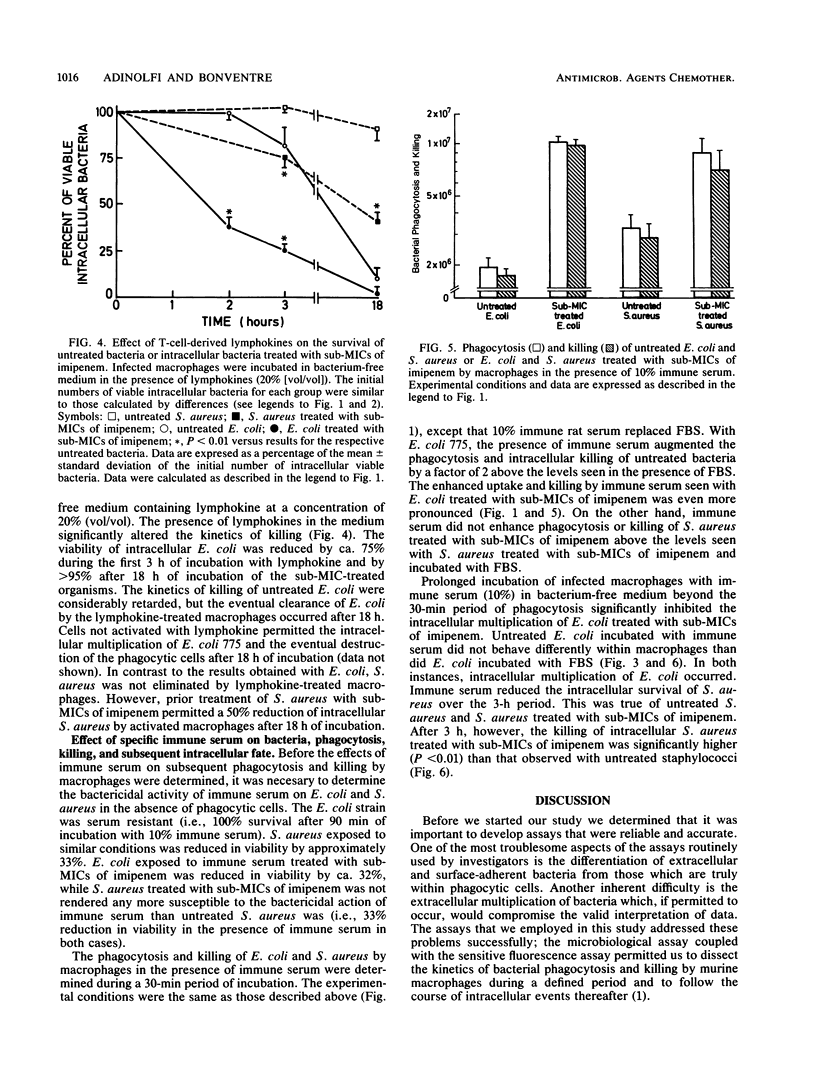
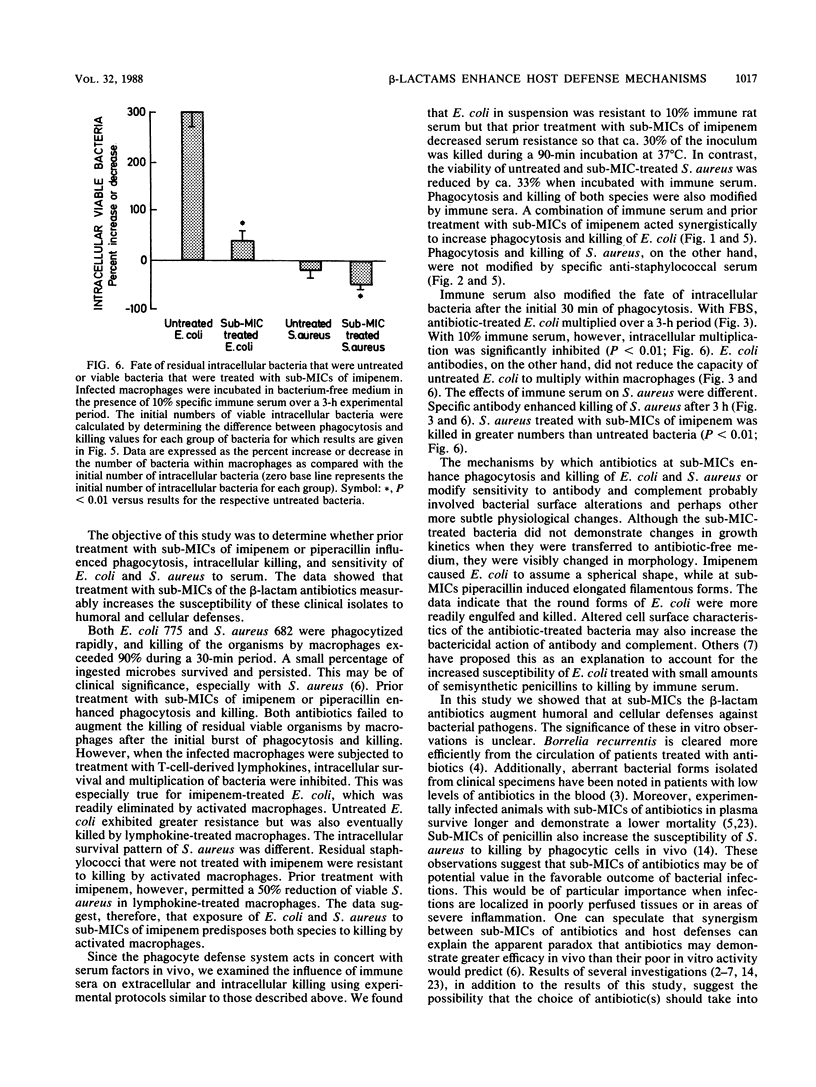
The influence of pretreatment of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus with sub-MICs of the new beta-lactam antibiotic imipenem on phagocytosis and killing by murine peritoneal macrophages and the susceptibility of these organisms to serum bactericidal activity were studied. The effects of imipenem, a round form inducer in gram-negative rods, and piperacillin, a filamentous form inducer, were compared. Bacteria grown in the presence of sub-MICs of imipenem or piperacillin were incubated for 30 min with macrophage monolayers in the absence of antibiotic. Phagocytosis, killing, and survival within macrophages were evaluated by microbiological and fluorescence microscope assays. Bacteria grown in the presence of a sub-MIC of imipenem were phagocytized and killed in numbers significantly higher than untreated or piperacillin-treated bacteria were. Intracellular bacteria pretreated with a sub-MIC of imipenem were also readily killed by lymphokine-activated macrophages. Prior treatment with a sub-MIC of imipenem resulted in an increased susceptibility of E. coli but not S. aureus to the bactericidal activity of immune serum. Imipenem treatment and immune serum acted synergistically to enhance phagocytosis and killing. The data indicate that exposure of E. coli and S. aureus to a sub-MIC of imipenem enhances the susceptibility of these potential pathogens to cellular and humoral host defense mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi L. E., Dilillo M., Tripodi M. F., Utili R., Bonventre P. F., Ruggiero G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and killing of E. coli by murine macrophages in presence of different serum preparations. Microbiologica. 1988 Jan;11(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreana A., Perna P., Utili R., Dilillo M., Ruggiero G. Increased phagocytosis and killing of Escherichia coli treated with subinhibitory concentrations of cefamandole and gentamicin in isolated rat livers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):182–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson B. A., Amaral L. Sublethal concentrations of antibiotics, effects on bacteria and the immune system. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1982;9(2):101–138. doi: 10.3109/10408418209104487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Aikawa M., Habte-Michael A., Wallace C. Phagocytosis of Borrelia recurrentis by blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes is enhanced by antibiotic treatment. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1009–1013. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1009-1013.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comber K. R., Boon R. J., Sutherland R. Comparative effects of amoxycillin and ampicillin on the morphology of Escherichia coli in vivo and correlation with activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):736–744. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott G. R., Peterson P. K., Verbrugh H. A., Freiberg M. R., Hoidal J. R., Quie P. G. Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of penicillin, cephalothin, and clindamycin on Staphylococcus aureus growth in human phagocytic cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):781–784. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H., Warren G. H. Antibody-mediated bacteriolysis: enhanced killing of cyclacillin-treated bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Nov;153(2):301–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Birnbaum J. Thienamycin: development of imipenen-cilastatin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):1–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesado T., Hashizume T., Asahi Y. Antibacterial activities of a new stabilized thienamycin, N-formimidoyl thienamycin, in comparison with other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):912–917. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Gerckens L., Sundelof J. G., Kahan F. M. Antibacterial activity of imipenem: the first thienamycin antibiotic. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7 (Suppl 3):S389–S410. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_3.s389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam C., Georgopoulos A., Laber G., Schütze E. Therapeutic relevance of penicillin-induced hypersensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus to killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):149–154. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Visceral leishmaniasis in congenic mice of susceptible and resistant phenotypes: immunosuppression by adherent spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.160-168.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N. Subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Mar;3(2):111–113. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Rommel F. A rapid micro method for the simultaneous determination of phagocytic-microbiocidal activity of human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Yang Y. J., Livermore D. M. Mechanisms by which imipenem may overcome resistance in gram-negative bacilli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18 (Suppl E):9–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_e.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak O., Kradolfer F. Effects of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in experimental infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):862–879. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.5.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek P. J., Buys L. F., Mattie H., van Furth R. Effect of penicillin G on Staphylococcus aureus phagocytosed by human monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):586–592. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



