Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—Chemokines are a family of low molecular weight cytokines that attract and activate leucocytes. The CC chemokines act on eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes, suggesting that they play an important part in allergic diseases. The aims of this study were to investigate the expression of the CC chemokines, RANTES, eotaxin, monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP) 1, MCP-2, and MCP-3 in the conjunctiva of patients with vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and to determine the cellular source of these chemokines. METHODS—Conjunctival biopsy specimens from nine subjects with active VKC, and six control subjects were studied by immunohistochemical techniques using a panel of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies directed against RANTES, eotaxin, MCP-1, MCP-2, and MCP-3. The phenotype of inflammatory cells expressing chemokines was examined by sequential double immunohistochemistry. RESULTS—In the normal conjunctiva, superficial epithelial cells showed a constitutive, weak cytoplasmic expression of eotaxin. Few inflammatory cells in the perivascular areas expressed RANTES, MCP-1, MCP-2, and MCP-3. In VKC specimens, the epithelium showed intense cytoplasmic eotaxin staining in all cells, and cytoplasmic RANTES staining mainly in the superficial layers. Furthermore, RANTES and eotaxin were expressed on the vascular endothelium mainly in the upper substantia propria. Compared with normal controls, VKC specimens showed significantly more inflammatory cells expressing RANTES, eotaxin, MCP-1, and MCP-3 (p<0.001, 0.0028, 0.0092, and <0.001, respectively). In VKC specimens, the numbers of inflammatory cells expressing RANTES were significantly higher than the numbers of inflammatory cells expressing eotaxin, MCP-1, and MCP-2 (all p values <0.001). Colocalisation studies revealed that the majority of inflammatory cells expressing chemokines were CD68 positive monocytes/macrophages. CONCLUSIONS—These results demonstrate an increase in the expression of RANTES, eotaxin, MCP-1, and MCP-3 in the conjunctiva of patients with VKC compared with control subjects. These data suggest a potential role for these chemokines in the pathogenesis of VKC. Antagonists of chemokine receptors may provide new therapeutic modalities in VKC.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (228.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
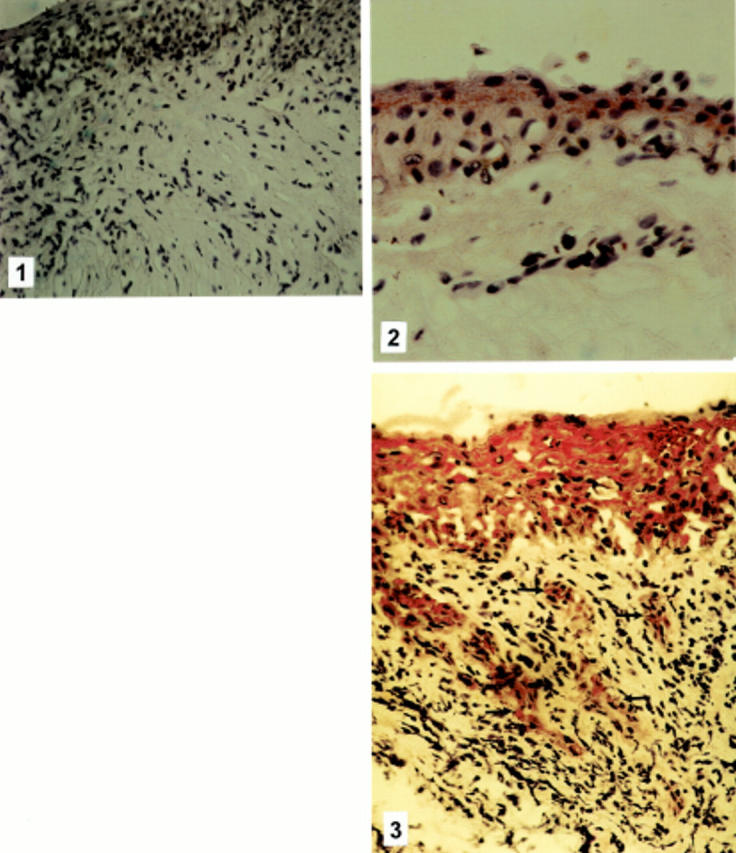
(1) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis control slide, treated identically, using an irrelevant monoclonal antibody showing no staining (×300).(2) Immunohistochemical staining for eotaxin of conjunctiva from a normal control subject showing weak cytoplasmic expression in the superficial epithelial layers (×500). (3) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Immunohistochemical staining for eotaxin showing intense cytoplasmic staining in all epithelial cells and staining on the vascular endothelium (arrows) (×500).
Figure 2 .
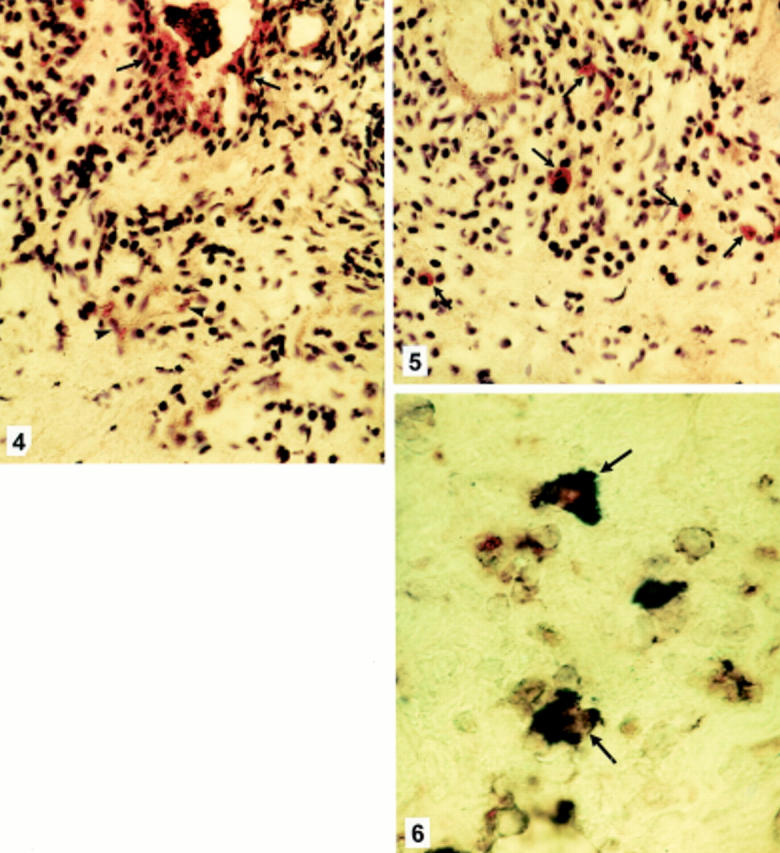
(4) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Immunohistochemical staining for RANTES showing cytoplasmic staining in epithelial cells (arrows) and staining on the vascular endothelium (arrowheads) (×500). (5) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Immunohistochemical staining for MCP-1 showing cytoplasmic staining in inflammatory cells (arrows) (×500). (6) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Double immunohistochemical staining for RANTES (blue), and CD68 (red) showing RANTES positive cells coexpressing CD68 marker (arrows) (×1200).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu el-Asrar A. M., Geboes K., al-Kharashi S., Tabbara K. F., Missotten L., Desmet V. Adhesion molecules in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Dec;81(12):1099–1106. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.12.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abu el-Asrar A. M., Van den Oord J. J., Geboes K., Missotten L., Emarah M. H., Desmet V. Immunopathological study of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1989;227(4):374–379. doi: 10.1007/BF02169416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam R. Chemokines in allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Mar;99(3):273–277. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam R., Stafford S., Forsythe P., Harrison R., Faubion D., Lett-Brown M. A., Grant J. A. RANTES is a chemotactic and activating factor for human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3442–3448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam R., York J., Boyars M., Stafford S., Grant J. A., Lee J., Forsythe P., Sim T., Ida N. Increased MCP-1, RANTES, and MIP-1alpha in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of allergic asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Apr;153(4 Pt 1):1398–1404. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.4.8616572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allansmith M. R., Ross R. N. Ocular allergy. Clin Allergy. 1988 Jan;18(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1988.tb02837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon A. S., McGill J. I., Anderson D. F., Baddeley S., Lightman S. L., Holgate S. T. Adhesion molecules and relationship to leukocyte levels in allergic eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998 Feb;39(2):322–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon K. B., Premack B. A., Gardner P., Schall T. J. Activation of dual T cell signaling pathways by the chemokine RANTES. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1727–1730. doi: 10.1126/science.7569902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. A., Dalke S., Leiferman K. M., Bickel C. A., Hamilton R., Rosen H., Bochner B. S., Schleimer R. P. Cutaneous injection of RANTES causes eosinophil recruitment: comparison of nonallergic and allergic human subjects. J Immunol. 1997 Sep 15;159(6):2962–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. A., Stellato C., Beall L. D., Schall T. J., Leopold D., Bickel C. A., Baroody F., Bochner B. S., Schleimer R. P. Detection of the chemokine RANTES and endothelial adhesion molecules in nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Oct;98(4):766–780. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Krieger M., Brunner T., Dahinden C. A. Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 is a potent activator of human basophils. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1271–1275. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. S., Klunk D. A., Sterbinsky S. A., Coffman R. L., Schleimer R. P. IL-13 selectively induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):799–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. J. Vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988 Winter;28(4):303–308. doi: 10.1097/00004397-198802840-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciprandi G., Buscaglia S., Pesce G., Villaggio B., Bagnasco M., Canonica G. W. Allergic subjects express intercellular adhesion molecule--1 (ICAM-1 or CD54) on epithelial cells of conjunctiva after allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Mar;91(3):783–792. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin H. B., Allansmith M. R. Basophils in vernal conjunctivitis in humans: an electron microscopic study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Sep;16(9):858–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Geiser T., Brunner T., von Tscharner V., Caput D., Ferrara P., Minty A., Baggiolini M. Monocyte chemotactic protein 3 is a most effective basophil- and eosinophil-activating chemokine. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):751–756. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty B. L., Siciliano S. J., DeMartino J. A., Malkowitz L., Sirotina A., Springer M. S. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human eosinophil eotaxin receptor. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2349–2354. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisawa M., Liu M. C., Yamada T., Kato M., Lichtenstein L. M., Bochner B. S., Schleimer R. P. Eosinophil transendothelial migration induced by cytokines. II. Potentiation of eosinophil transendothelial migration by eosinophil-active cytokines. J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4590–4596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisawa M., Yamada T., Bickel C., Klunk D., Schleimer R. P. Eosinophil transendothelial migration induced by cytokines. III. Effect of the chemokine RANTES. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 1;153(5):2153–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsner J., Höchstetter R., Kimmig D., Kapp A. Human eotaxin represents a potent activator of the respiratory burst of human eosinophils. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Aug;26(8):1919–1925. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsner J., Petering H., Höchstetter R., Kimmig D., Wells T. N., Kapp A., Proudfoot A. E. The CC chemokine antagonist Met-RANTES inhibits eosinophil effector functions through the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR3. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Nov;27(11):2892–2898. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa K., Saito H., Tsubota K., Shimmura S., Tachimoto H., Akasawa A., Oguchi Y. RANTES production in a conjunctival epithelial cell line. Cornea. 1997 Sep;16(5):564–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths-Johnson D. A., Collins P. D., Rossi A. G., Jose P. J., Williams T. J. The chemokine, eotaxin, activates guinea-pig eosinophils in vitro and causes their accumulation into the lung in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 30;197(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath H., Qin S., Rao P., Wu L., LaRosa G., Kassam N., Ponath P. D., Mackay C. R. Chemokine receptor usage by human eosinophils. The importance of CCR3 demonstrated using an antagonistic monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1997 Jan 15;99(2):178–184. doi: 10.1172/JCI119145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Bodey K. S., Janezic A., Frew A. J., Kaplan A. P., Teran L. M. Release of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MCP-1 into asthmatic airways following endobronchial allergen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Nov;156(5):1377–1383. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.5.9610064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert M., Ying S., Corrigan C., Menz G., Barkans J., Pfister R., Meng Q., Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Durham S. R. Bronchial mucosal expression of the genes encoding chemokines RANTES and MCP-3 in symptomatic atopic and nonatopic asthmatics: relationship to the eosinophil-active cytokines interleukin (IL)-5, granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor, and IL-3. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997 Jan;16(1):1–8. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.16.1.8998072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jose P. J., Griffiths-Johnson D. A., Collins P. D., Walsh D. T., Moqbel R., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Williams T. J. Eotaxin: a potent eosinophil chemoattractant cytokine detected in a guinea pig model of allergic airways inflammation. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):881–887. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyoshi Y., Dörschner A., Mallet A. I., Christophers E., Schröder J. M. Cytokine RANTES released by thrombin-stimulated platelets is a potent attractant for human eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):587–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Barata L., Meng Q., Durham S. R., Ying S. Eosinophils and eosinophil-associated cytokines in allergic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997 May-Jul;113(1-3):196–199. doi: 10.1159/000237545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata H., Yoshida A., Ishioka C., Fujimoto M., Lindley I., Furusho K. RANTES and macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha selectively enhance immunoglobulin (IgE) and IgG4 production by human B cells. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2397–2402. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuna P., Alam R., Ruta U., Gorski P. RANTES induces nasal mucosal inflammation rich in eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Mar;157(3 Pt 1):873–879. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.3.9610052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuna P., Reddigari S. R., Schall T. J., Rucinski D., Viksman M. Y., Kaplan A. P. RANTES, a monocyte and T lymphocyte chemotactic cytokine releases histamine from human basophils. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):636–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly C. M., Nakamura H., Kesselman H., Nagler-Anderson C., Asano K., Garcia-Zepeda E. A., Rothenberg M. E., Drazen J. M., Luster A. D. Expression of eotaxin by human lung epithelial cells: induction by cytokines and inhibition by glucocorticoids. J Clin Invest. 1997 Apr 1;99(7):1767–1773. doi: 10.1172/JCI119341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Biswas P., Del Prete G., Parronchi P., Macchia D., Simonelli C., Emmi L., De Carli M., Tiri A., Ricci M. Accumulation of Th-2-like helper T cells in the conjunctiva of patients with vernal conjunctivitis. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews A. N., Friend D. S., Zimmermann N., Sarafi M. N., Luster A. D., Pearlman E., Wert S. E., Rothenberg M. E. Eotaxin is required for the baseline level of tissue eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 May 26;95(11):6273–6278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshall E. M., Cameron L., Lavigne F., Leung D. Y., Hamilos D., Garcia-Zepada E. A., Rothenberg M., Luster A. D., Hamid Q. Eotaxin mRNA and protein expression in chronic sinusitis and allergen-induced nasal responses in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997 Dec;17(6):683–690. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.17.6.2865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montan P. G., Biberfeld P. J., Scheynius A. IgE, IgE receptors, and other immunocytochemical markers in atopic and nonatopic patients with vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Ophthalmology. 1995 May;102(5):725–732. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(95)30962-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller A., Henz B. M., Grützkau A., Lippert U., Aragane Y., Schwarz T., Krüger-Krasagakes S. Comparative cytokine gene expression: regulation and release by human mast cells. Immunology. 1998 Feb;93(2):289–295. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1998.00425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponath P. D., Qin S., Post T. W., Wang J., Wu L., Gerard N. P., Newman W., Gerard C., Mackay C. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human eotaxin receptor expressed selectively on eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2437–2448. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajakulasingam K., Hamid Q., O'Brien F., Shotman E., Jose P. J., Williams T. J., Jacobson M., Barkans J., Durham S. R. RANTES in human allergen-induced rhinitis: cellular source and relation to tissue eosinophilia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Feb;155(2):696–703. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.155.2.9032215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J. Chemokines. Blood. 1997 Aug 1;90(3):909–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabroe I., Conroy D. M., Gerard N. P., Li Y., Collins P. D., Post T. W., Jose P. J., Williams T. J., Gerard C. J., Ponath P. D. Cloning and characterization of the guinea pig eosinophil eotaxin receptor, C-C chemokine receptor-3: blockade using a monoclonal antibody in vivo. J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6139–6147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallusto F., Mackay C. R., Lanzavecchia A. Selective expression of the eotaxin receptor CCR3 by human T helper 2 cells. Science. 1997 Sep 26;277(5334):2005–2007. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5334.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J. Biology of the RANTES/SIS cytokine family. Cytokine. 1991 May;3(3):165–183. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisson S. D., Dinarello C. A. Production of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor by human mononuclear cells stimulated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1368–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Abboud M., Potter G. K., Yung Y. P., Moore M. A. Presence of tumour necrosis factor or a related factor in human basophil/mast cells. Immunology. 1989 Mar;66(3):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellato C., Beck L. A., Gorgone G. A., Proud D., Schall T. J., Ono S. J., Lichtenstein L. M., Schleimer R. P. Expression of the chemokine RANTES by a human bronchial epithelial cell line. Modulation by cytokines and glucocorticoids. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):410–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyf S., Proost P., Schols D., De Clercq E., Opdenakker G., Lenaerts J. P., Detheux M., Parmentier M., De Meester I., Scharpé S. CD26/dipeptidyl-peptidase IV down-regulates the eosinophil chemotactic potency, but not the anti-HIV activity of human eotaxin by affecting its interaction with CC chemokine receptor 3. J Immunol. 1999 Apr 15;162(8):4903–4909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taha R. A., Minshall E. M., Miotto D., Shimbara A., Luster A., Hogg J. C., Hamid Q. A. Eotaxin and monocyte chemotactic protein-4 mRNA expression in small airways of asthmatic and nonasthmatic individuals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Mar;103(3 Pt 1):476–483. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada N., Maesako K., Hamano N., Ikeda T., Sai M., Yamashita T., Fukuda S., Konno A. RANTES production in nasal epithelial cells and endothelial cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Dec;98(6 Pt 2):S230–S237. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill M. H., Wellicome S. M., Mahiouz D. L., Lanchbury J. S., Kyan-Aung U., Haskard D. O. Tumor necrosis factor combines with IL-4 or IFN-gamma to selectively enhance endothelial cell adhesiveness for T cells. The contribution of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1-dependent and -independent binding mechanisms. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):592–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trocme S. D., Kephart G. M., Allansmith M. R., Bourne W. M., Gleich G. J. Conjunctival deposition of eosinophil granule major basic protein in vernal keratoconjunctivitis and contact lens-associated giant papillary conjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Jul 15;108(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trocmé S. D., Hallberg C. K., Gill K. S., Gleich G. J., Tyring S. K., Brysk M. M. Effects of eosinophil granule proteins on human corneal epithelial cell viability and morphology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997 Mar;38(3):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trocmé S. D., Kephart G. M., Bourne W. M., Buckley R. J., Gleich G. J. Eosinophil granule major basic protein deposition in corneal ulcers associated with vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 May 15;115(5):640–643. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71463-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uguccioni M., Mackay C. R., Ochensberger B., Loetscher P., Rhis S., LaRosa G. J., Rao P., Ponath P. D., Baggiolini M., Dahinden C. A. High expression of the chemokine receptor CCR3 in human blood basophils. Role in activation by eotaxin, MCP-4, and other chemokines. J Clin Invest. 1997 Sep 1;100(5):1137–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI119624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Proost P., Lenaerts J. P., Opdenakker G. Structural and functional identification of two human, tumor-derived monocyte chemotactic proteins (MCP-2 and MCP-3) belonging to the chemokine family. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):59–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh G. M., Mermod J. J., Hartnell A., Kay A. B., Wardlaw A. J. Human eosinophil, but not neutrophil, adherence to IL-1-stimulated human umbilical vascular endothelial cells is alpha 4 beta 1 (very late antigen-4) dependent. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3419–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Devalia J. L., Xia C., Sapsford R. J., Davies R. J. Expression of RANTES by human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo and the effect of corticosteroids. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;14(1):27–35. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.14.1.8534483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Uguccioni M., Ochensberger B., Baggiolini M., Clark-Lewis I., Dahinden C. A. Monocyte chemotactic protein MCP-2 activates human basophil and eosinophil leukocytes similar to MCP-3. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):4166–4172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells T. N., Proudfoot A. E. Chemokine receptors and their antagonists in allergic lung disease. Inflamm Res. 1999 Jul;48(7):353–362. doi: 10.1007/s000110050472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S., Robinson D. S., Meng Q., Rottman J., Kennedy R., Ringler D. J., Mackay C. R., Daugherty B. L., Springer M. S., Durham S. R. Enhanced expression of eotaxin and CCR3 mRNA and protein in atopic asthma. Association with airway hyperresponsiveness and predominant co-localization of eotaxin mRNA to bronchial epithelial and endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Dec;27(12):3507–3516. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S., Taborda-Barata L., Meng Q., Humbert M., Kay A. B. The kinetics of allergen-induced transcription of messenger RNA for monocyte chemotactic protein-3 and RANTES in the skin of human atopic subjects: relationship to eosinophil, T cell, and macrophage recruitment. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2153–2159. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Asrar A. M., Tabbara K. F., Geboes K., Missotten L., Desmet V. An immunohistochemical study of topical cyclosporine in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Feb;121(2):156–161. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


