Abstract
AIMS—To evaluate the relation of the optic nerve head topographic measurements and age with the thickness of the retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) in normal Caucasoid subjects by means of scanning laser polarimetry and tomography. METHODS—Topographic optic disc measurements and RNFL thickness values of 38 normal Caucasoid subjects of both sexes aged 20 to 78 were measured using a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope and a confocal scanning laser polarimeter. One eye was randomly selected for statistical analysis. The effects of optic disc size, age, and optic disc head topographic measurements of total and regional RNFL thickness were evaluated. RESULTS—Age showed a significant correlation with the integral of the total RNFL thickness (R=−0.341, p<0.05). The optic disc size showed a significant correlation with the integral of the total, superior, and inferior quadrant RNFL thickness (R=0.425, p<0.01), (R=0.361, p<0.05), (R=0.468, p<0.05). Neuroretinal rim area (NRA) had a correlation with the superior and inferior quadrant RNFL thickness values (R=0.339, p<0.05) (R=0.393, p<0.05). There was no significant correlation between the other optic disc topographic measurements and RNFL thickness values (p>0.05). CONCLUSION—The thickness of total as well as superior and inferior quadrant peripapillary RNFL as measured by scanning laser polarimetry increased significantly with an increase in optic disc size. The cross sectional area occupied by superior and inferior polar RNFL increased significantly with an increase in NRA. The total cross sectional area occupied by RNFL decreased significantly with an increase in age. The effects of optic disc size, age, and NRA should be considered when the peripapillary RNFL thickness is evaluated.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (126.0 KB).
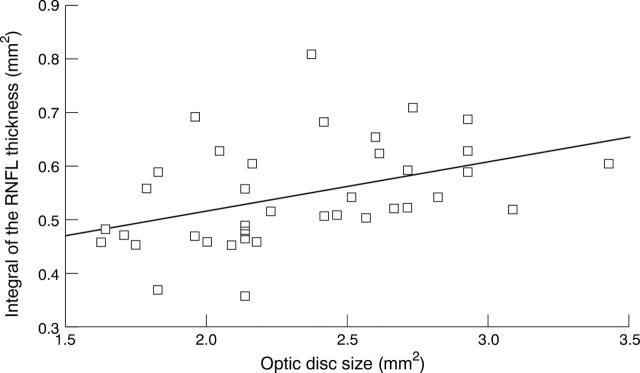
Figure 1 .
Correlation between the optic disc size and the integral of the total RNFL thickness in 38 normal eyes (Y = 0.093x+0.330, p<0.01, R=0.425, R2 = 0.181).
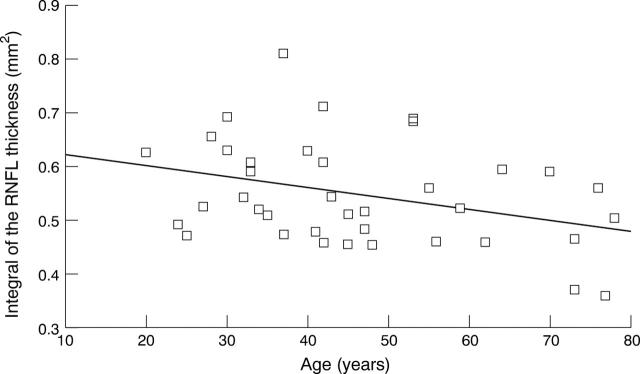
Figure 2 .
Correlation between age and the integral of the total RNFL thickness of the RNFL in 38 normal eyes (Y = −0.002x+0.641, p<0.05, R= −0.341, R2=0.117).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton A., Zangwill L., Emdadi A., Weinreb R. N. Nerve fiber layer measurements with scanning laser polarimetry in ocular hypertension. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Mar;115(3):331–334. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150333004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazsi A. G., Rootman J., Drance S. M., Schulzer M., Douglas G. R. The effect of age on the nerve fiber population of the human optic nerve. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Jun;97(6):760–766. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beausencourt E., Elsner A. E., Hartnett M. E., Trempe C. L. Quantitative analysis of macular holes with scanning laser tomography. Ophthalmology. 1997 Dec;104(12):2018–2029. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton R. J., Drance S. M., Schulzer M., Douglas G. R., Mawson D. K. The area of the neuroretinal rim of the optic nerve in normal eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Apr 15;103(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)74271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli J., Miller J. M. Optic disc rim area is related to disc size in normal subjects. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Dec;105(12):1683–1685. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060120081030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan B. C., LeBlanc R. P., McCormick T. A., Rogers J. B. Test-retest variability of topographic measurements with confocal scanning laser tomography in patients with glaucoma and control subjects. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994 Jul 15;118(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choplin N. T., Lundy D. C., Dreher A. W. Differentiating patients with glaucoma from glaucoma suspects and normal subjects by nerve fiber layer assessment with scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology. 1998 Nov;105(11):2068–2076. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(98)91127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichtl A., Jonas J. B., Mardin C. Y. Comparison between tomographic scanning evaluation and photographic measurement of the neuroretinal rim. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 May;121(5):494–501. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher A. W., Tso P. C., Weinreb R. N. Reproducibility of topographic measurements of the normal and glaucomatous optic nerve head with the laser tomographic scanner. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 Feb 15;111(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funaki S., Shirakashi M., Abe H. Relation between size of optic disc and thickness of retinal nerve fibre layer in normal subjects. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998 Nov;82(11):1242–1245. doi: 10.1136/bjo.82.11.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh S. T., Ishikawa H., Greenfield D. S., Liebmann J. M., Chew S. J., Ritch R. Peripapillary nerve fiber layer thickness measurement reproducibility using scanning laser polarimetry. J Glaucoma. 1998 Feb;7(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Naumann G. O. Optic disc, cup and neuroretinal rim size, configuration and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jul;29(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Müller-Bergh J. A., Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. M., Naumann G. O. Histomorphometry of the human optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Apr;31(4):736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Schmidt A. M., Müller-Bergh J. A., Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. M., Naumann G. O. Human optic nerve fiber count and optic disc size. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 May;33(6):2012–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kee C., Koo H., Ji Y., Kim S. Effect of optic disc size or age on evaluation of optic disc variables. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Dec;81(12):1046–1049. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.12.1046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F. E., Burk R. O., Völcker H. E., Zinser G., Harbarth U. Reproducibility of topographic measurements of the optic nerve head with laser tomographic scanning. Ophthalmology. 1989 Sep;96(9):1320–1324. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32719-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelberg F. S., Drance S. M., Schulzer M., Yidegiligne H. M., Weis M. M. The normal human optic nerve. Axon count and axon diameter distribution. Ophthalmology. 1989 Sep;96(9):1325–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32718-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelberg F. S., Yidegiligne H. M., White V. A., Schulzer M. Relation between optic nerve axon number and axon diameter to scleral canal area. Ophthalmology. 1991 Jan;98(1):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(91)32341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minckler D. S., McLean I. W., Tso M. O. Distribution of axonal and glial elements in the rhesus optic nerve head studied by electron microscopy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Aug;82(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen A. G., Van Den Berg T. J., Langerhorst C. T., Greve E. L. Retinal nerve fiber layer assessment by scanning laser polarimetry and standardized photography. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 May;121(5):484–493. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden T. E. Nerve fiber layer of the primate retina: thickness and glial content. Vision Res. 1983;23(6):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poinoosawmy D., Fontana L., Wu J. X., Fitzke F. W., Hitchings R. A. Variation of nerve fibre layer thickness measurements with age and ethnicity by scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 May;81(5):350–354. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.5.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Brown A. E., Morrison J. D., Drance S. M. The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Jan;108(1):51–57. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070030057028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Coleman A. L., Dorman-Pease M. E. Larger optic nerve heads have more nerve fibers in normal monkey eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Oct;109(10):1441–1443. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080100121056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radius R. L. Thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer in primate eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980 Sep;98(9):1625–1629. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020040477018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repka M. X., Quigley H. A. The effect of age on normal human optic nerve fiber number and diameter. Ophthalmology. 1989 Jan;96(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32928-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjon-Fo-Sang M. J., de Vries J., Lemij H. G. Measurement by nerve fiber analyzer of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal subjects and patients with ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Aug;122(2):220–227. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma R., Quigley H. A., Pease M. E. Changes in optic disk characteristics and number of nerve fibers in experimental glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992 Nov 15;114(5):554–559. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)74482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma R., Skaf M., Barron E. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal human eyes. Ophthalmology. 1996 Dec;103(12):2114–2119. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(96)30381-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma R., Tielsch J. M., Quigley H. A., Hilton S. C., Katz J., Spaeth G. L., Sommer A. Race-, age-, gender-, and refractive error-related differences in the normal optic disc. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994 Aug;112(8):1068–1076. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1994.01090200074026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Dreher A. W., Coleman A., Quigley H., Shaw B., Reiter K. Histopathologic validation of Fourier-ellipsometry measurements of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Apr;108(4):557–560. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070060105058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Shakiba S., Sample P. A., Shahrokni S., van Horn S., Garden V. S., Asawaphureekorn S., Zangwill L. Association between quantitative nerve fiber layer measurement and visual field loss in glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995 Dec;120(6):732–738. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72726-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Shakiba S., Zangwill L. Scanning laser polarimetry to measure the nerve fiber layer of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995 May;119(5):627–636. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Zangwill L., Berry C. C., Bathija R., Sample P. A. Detection of glaucoma with scanning laser polarimetry. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998 Dec;116(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.12.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yücel Y. H., Gupta N., Kalichman M. W., Mizisin A. P., Hare W., de Souza Lima M., Zangwill L., Weinreb R. N. Relationship of optic disc topography to optic nerve fiber number in glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998 Apr;116(4):493–497. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zangwill L., Berry C. A., Garden V. S., Weinreb R. N. Reproducibility of retardation measurements with the nerve fiber analyzer II. J Glaucoma. 1997 Dec;6(6):384–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]