Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—A recent report has highlighted the decreasing prevalence in recent years of severe intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH) in very low birthweight (VLBW) infants (<1500 g). This study attempted to identify the severity of the grade of IVH in infants with stage 3 retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), and to re-examine the association between threshold ROP and IVH. METHODS—This was a retrospective study carried out over 3 years, between December 1995 and December 1998 of neonates admitted to a single neonatal intensive care unit. 28 infants with stage 3 ROP were identified from the ROP screening database. Cranial ultrasound scans were available on 24 of these infants. The scans were reviewed and the severity of IVH was graded from grade 1 to grade 4. The birth weight, sex, ethnic origin, and gestational age of the babies were recorded. The number of infants progressing to threshold disease and the treatment provided was documented. RESULTS—The 24 infants had a median gestational age of 26 weeks (range 24-28 weeks) and a median birth weight of 762.5 g (range 540-1010 g). 17 infants were treated for threshold disease. 13 infants (54.2%) had IVH, of these eight (61.5%) had grade 1, two (15.4%) had grade 2, one (7.7%) had grade 3, and two (15.4%) had grade 4. 12 of the 13 infants (92.3%) with IVH had treatment with laser or cryotherapy for ROP compared with five of the remaining 11 infants (p = 0.023, Fisher's exact test). These data provide little evidence of any association between IVH and each of ethnic origin (p = 0.856), sex (p = 1), birth weight, or gestational age (p = 0.56 and p = 0.06 respectively) in infants with stage 3 ROP. CONCLUSIONS—These data provide strong evidence (p = 0.023) of an association between the presence of IVH and treatment of threshold ROP. Although the numbers in this study are small the majority of infants with stage 3 ROP had grade 1 IVH, which heralds a more favourable neurological outcome. An association between the severity of ROP and severity of IVH was not demonstrated. With improvements in neonatal care and a reduction in the prevalence of severe IVH, there appears to be a weakening of the previously reported association between severe IVH and severe ROP. However, the presence of even a minor grade of IVH may be a significant risk factor for threshold ROP once stage 3 disease is encountered.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (120.3 KB).
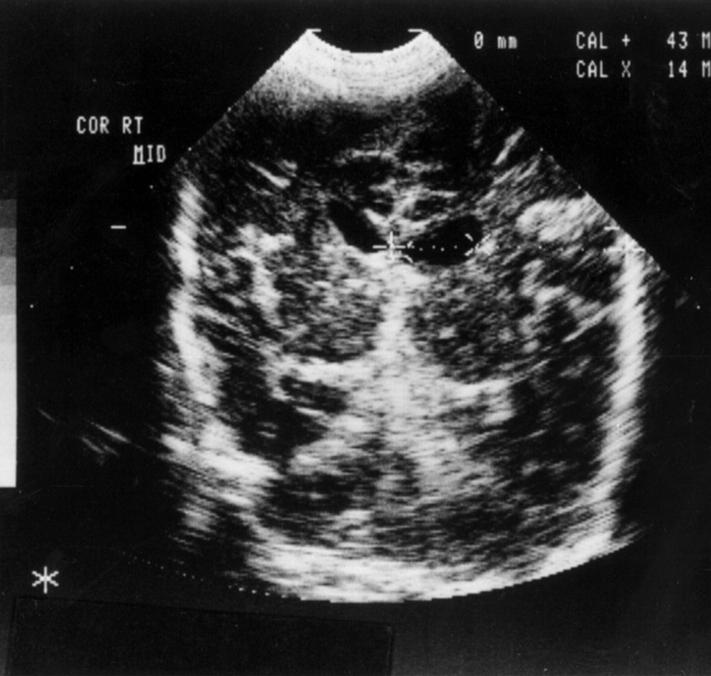
Figure 1 .
Coronal ultrasound scan demonstrating an intermediate grade 1/grade 2 intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH).
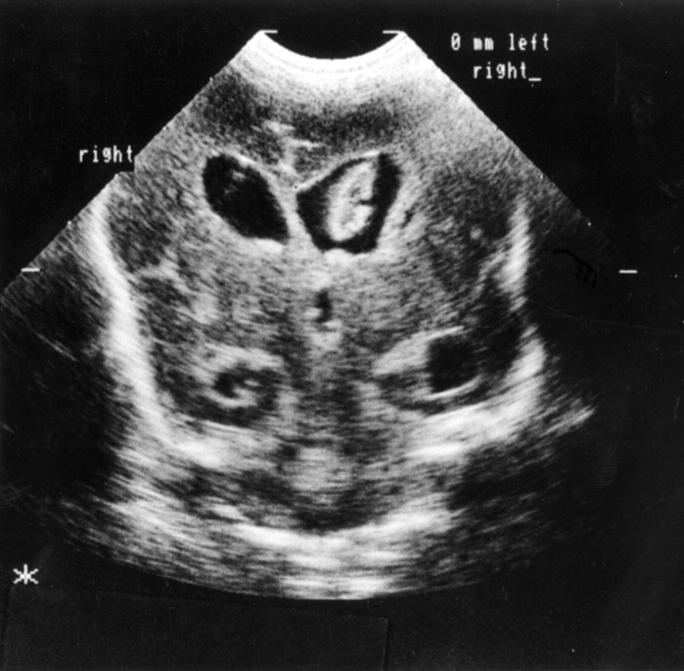
Figure 2 .
Coronal ultrasound scan with grade 3 intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH).
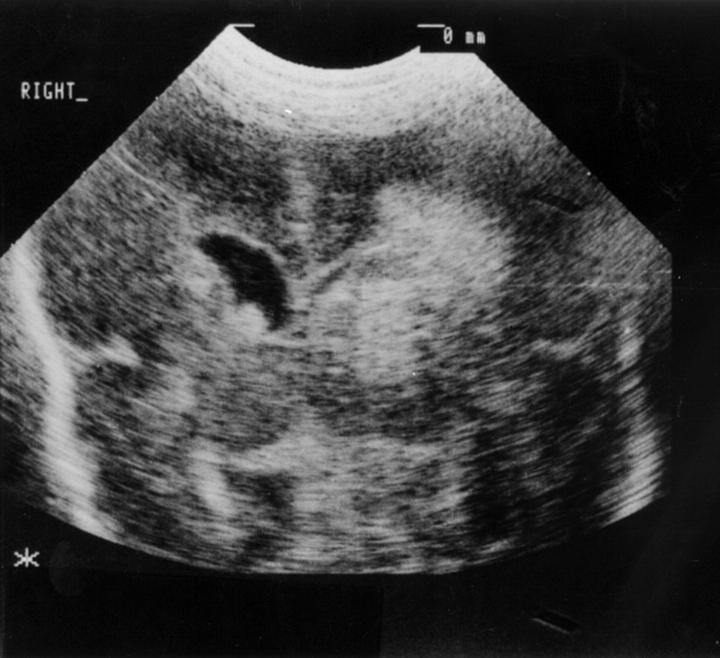
Figure 3 .
Coronal ultrasound scan with grade 4 intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH).
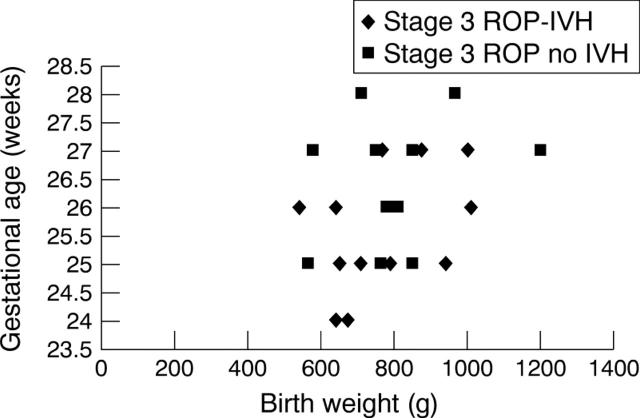
Figure 4 .
Graph comparing the gestational age with birth weight of those stage 3 ROP infants with and without intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH).
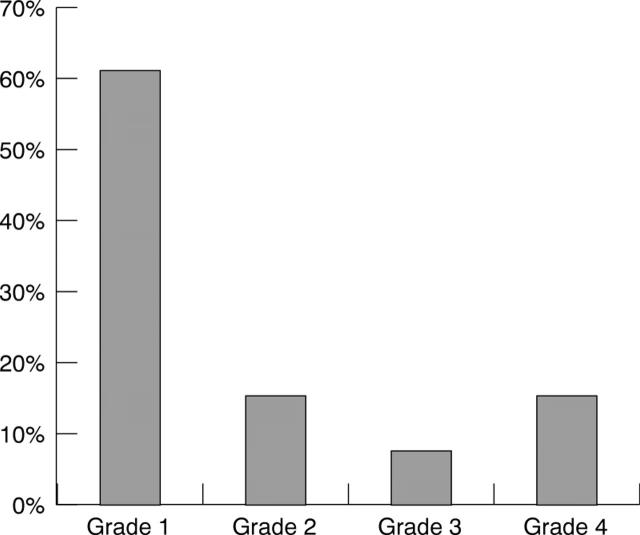
Figure 5 .
Frequency of various grades of intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH) in stage 3 ROP.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooke R. W. Trends in incidence of cranial ultrasound lesions and cerebral palsy in very low birthweight infants 1982-93. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 Mar;80(2):F115–F117. doi: 10.1136/fn.80.2.f115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlow B. A., Clemett R. S., Horwood L. J., Mogridge N. Prospective study of New Zealand infants with birth weight less than 1500 g and screened for retinopathy of prematurity: visual outcome at age 7-8 years. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Nov;81(11):935–940. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.11.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foos R. Y. Retinopathy of prematurity. Pathologic correlation of clinical stages. Retina. 1987;7(4):260–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. D., Mendelsohn A. L., DeFeo M. J., Ucsel R., Hendricks-Munoz K. D. Antenatal dexamethasone and decreased severity of retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998 May;116(5):601–605. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungerford J., Stewart A., Hope P. Ocular sequelae of preterm birth and their relation to ultrasound evidence of cerebral damage. Br J Ophthalmol. 1986 Jun;70(6):463–468. doi: 10.1136/bjo.70.6.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1272–1274. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy K. S., Shannon D. C., DeLong G. R., Todres I. D., Davis K. R. Neurologic sequelae in the survivors of neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Pediatrics. 1979 Aug;64(2):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng Y. K., Fielder A. R., Levene M. I., Trounce J. Q., McLellan N. Are severe acute retinopathy of prematurity and severe periventricular leucomalacia both ischaemic insults? Br J Ophthalmol. 1989 Feb;73(2):111–114. doi: 10.1136/bjo.73.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. A., Flynn J. T., Hardy R. J., Phelps D. L., Phillips C. L., Schaffer D. B., Tung B. Incidence and early course of retinopathy of prematurity. The Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Ophthalmology. 1991 Nov;98(11):1628–1640. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(91)32074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paneth N., Pinto-Martin J., Gardiner J., Wallenstein S., Katsikiotis V., Hegyi T., Hiatt I. M., Susser M. Incidence and timing of germinal matrix/intraventricular hemorrhage in low birth weight infants. Am J Epidemiol. 1993 Jun 1;137(11):1167–1176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J., Christiansen S. P., Ware G., Landers S., Kirby R. S. Ocular morbidity in very low birth-weight infants with intraventricular hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997 Feb;123(2):218–223. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procianoy R. S., Garcia-Prats J. A., Hittner H. M., Adams J. M., Rudolph A. J. An association between retinopathy of prematurity and intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Jul;70(4):473–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaver D. C., Bada H. S., Korones S. B., Anderson G. D., Wong S. P., Arheart K. L. Early and late intraventricular hemorrhage: the role of obstetric factors. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Nov;80(5):831–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D. K., Wright L. L., Lemons J. A., Oh W., Korones S. B., Papile L. A., Bauer C. R., Stoll B. J., Tyson J. E., Shankaran S. Very low birth weight outcomes of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network, January 1993 through December 1994. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998 Dec;179(6 Pt 1):1632–1639. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(98)70037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymonowicz W., Yu V. Y., Bajuk B., Astbury J. Neurodevelopmental outcome of periventricular haemorrhage and leukomalacia in infants 1250 g or less at birth. Early Hum Dev. 1986 Jul;14(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(86)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]