Abstract
AIM—To determine whether pharmacological mydriasis leads to a significant difference in interobserver agreement of optic disc measurement compared with examination without mydriasis. METHOD—A cross sectional study was performed with a pair of observers examining the optic disc of two randomised groups of patients, one group before diagnostic mydriasis, and the other afterwards. Horizontal and vertical disc diameters and cup/disc ratios were measured with a 78 dioptre lens. The study was repeated with another observer pair and two further groups of patients. RESULTS—In study A 86 subjects were examined in total (52 without and 34 with mydriasis). In study B 87 subjects were examined (45 without and 42 with mydriasis). The 95% limits of agreement of the cup/disc ratio measurement differences were significantly larger without mydriasis (p<0.001 for all studies (F test)). For both studies examination after mydriasis gave significantly greater agreement for vertical and horizontal cup/disc ratios. The cases with good agreement (0.1 difference or better) for vertical cup/disc ratios were 37/52 (72%) and 34 /45 (76%) without mydriasis and 33/34 (97%) and 40/42 (95%) respectively with mydriasis. Similar differences were recorded for horizontal cup/disc ratios. Disc diameter measurement results showed similar differences in study A but were not affected by mydriasis in study B. CONCLUSIONS—Examination of the optic disc without pharmacological mydriasis gives significantly poorer interobserver agreement. In this study, the mean 95% limits of agreement values for all cup/disc ratio values were 0.27 for examination without mydriasis and 0.13 for examination with mydriasis. A measure outside these limits would suggest a real difference. This study indicates that mydriasis is important for reproducible clinical examination in glaucoma.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (143.5 KB).
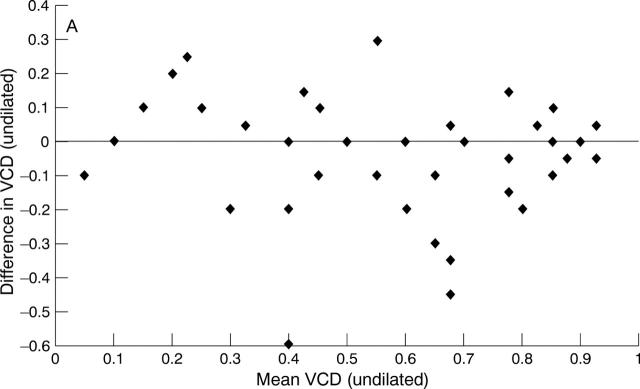
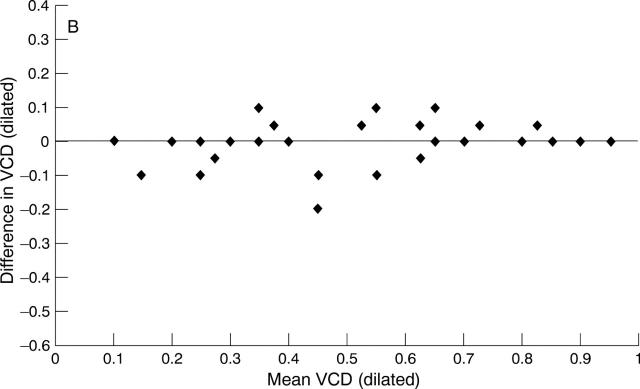
Figure 1 .
(A) Bland-Altman plot of interobserver agreement for VCD without mydriasis (study A data). (B) Bland-Altman plot of interobserver agreement for VCD with mydriasis (study A data).
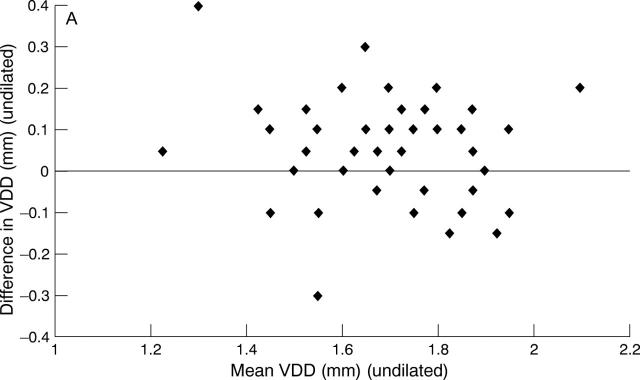
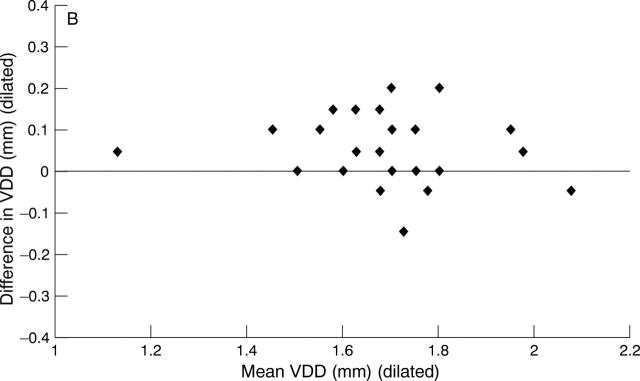
Figure 2 .
(A) Bland-Altman plot of interobserver agreement for VDD without mydriasis (study A data). (B) Bland-Altman plot of interobserver agreement for VDD with mydriasis (study A data).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armaly M. F., Sayegh R. E. The cup-disc ratio. The findings of tonometry and tonography in the normal eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Aug;82(2):191–196. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020193008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelder T. J., Fireman B., Friedman G. D., Matas B. R., Wong I. G., Barricks M. E., Burke S., Beasley L. The value of routine dilated pupil screening examination. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Sep;115(9):1179–1184. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100160349014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garway-Heath D. F., Ruben S. T., Viswanathan A., Hitchings R. A. Vertical cup/disc ratio in relation to optic disc size: its value in the assessment of the glaucoma suspect. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998 Oct;82(10):1118–1124. doi: 10.1136/bjo.82.10.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett R. S., Batterbury M., Cuypers M., Cooper R. L. Inter-observer agreement in clinical optic disc measurement using a modified 60 D lens. Eye (Lond) 1997;11(Pt 5):692–697. doi: 10.1038/eye.1997.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim C. S., O'Brien C., Bolton N. M. A simple clinical method to measure the optic disc size in glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 1996 Aug;5(4):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard R. THE ALTERATION IN SIZE OF THE NORMAL OPTIC DISC CUP. Br J Ophthalmol. 1948 Jun;32(6):355–361. doi: 10.1136/bjo.32.6.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack A. L., Brodie S. E. Diagnostic yield of the routine dilated fundus examination. Ophthalmology. 1998 Feb;105(2):382–386. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(98)93718-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. Estimation of optic disc size using indirect biomicroscopy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994 May;78(5):363–364. doi: 10.1136/bjo.78.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer A. F., Vernon S. A. Optic disc height measurement with the Zeiss 4-mirror contact lens and 78 dioptre lens compared. Eye (Lond) 1996;10(Pt 3):371–376. doi: 10.1038/eye.1996.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer A. F., Vernon S. A. Repeatability and reproducibility of optic disc measurement with the Zeiss 4-mirror contact lens. Ophthalmology. 1996 Jan;103(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(96)30745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tielsch J. M., Katz J., Quigley H. A., Miller N. R., Sommer A. Intraobserver and interobserver agreement in measurement of optic disc characteristics. Ophthalmology. 1988 Mar;95(3):350–356. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(88)33177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita G., Honbe K., Kitazawa Y. Reproducibility of measurements by laser scanning tomography in eyes before and after pilocarpine treatment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994 Jul;232(7):406–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00186581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma R., Steinmann W. C., Scott I. U. Expert agreement in evaluating the optic disc for glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1992 Feb;99(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(92)31990-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollstein G., Garway-Heath D. F., Hitchings R. A. Identification of early glaucoma cases with the scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Ophthalmology. 1998 Aug;105(8):1557–1563. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(98)98047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]