Abstract
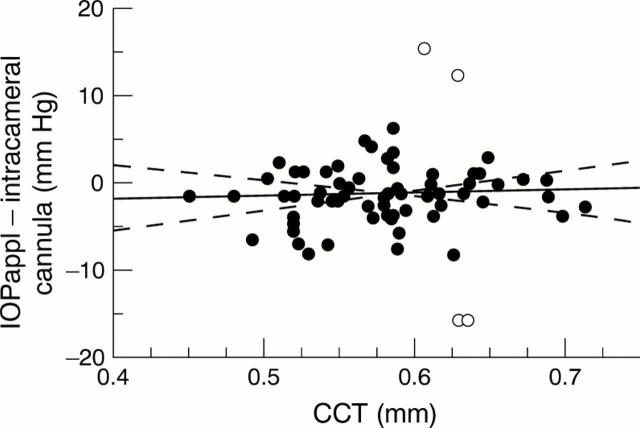
BACKGROUND—Several authors reported incorrect high intraocular pressure (IOP) values in eyes with a thick cornea using applanation tonometry. This hypothesis was checked by comparing applanation tonometry with direct intracameral manometry. METHODS—73 patients, scheduled for intraocular surgery, were enrolled. Immediately before surgery, the following were registered: (i) central corneal thickness (CCT), (ii) applanatory IOP (Perkins/Tonopen), and (iii) intracameral IOP. RESULTS—The difference between applanatory and intraocular measurements was completely independent of CCT (y=−3.43+3.8x; where y is the difference between applanatory and intracamerally measured IOP (mm Hg) and x is CCT (mm); r2=0.002; p=0.72). CONCLUSIONS—There is no systematic error of applanation tonometry with increasing CCT. Therefore it is inadequate to recalculate IOP based on regression formula of applanatory IOP versus CCT.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (114.5 KB).
Figure 1 .
Cannula placed in the anterior chamber.
Figure 2 .
Difference between IOPappl and intracameral cannula correlated with CCT. Readings differing by more than 10 mm Hg are marked as circles. y = −3.43+3.8*CCT, r2=0.002; p=0.72, n=73.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argus W. A. Ocular hypertension and central corneal thickness. Ophthalmology. 1995 Dec;102(12):1810–1812. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(95)30790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copt R. P., Thomas R., Mermoud A. Corneal thickness in ocular hypertension, primary open-angle glaucoma, and normal tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999 Jan;117(1):14–16. doi: 10.1001/archopht.117.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers N., Bramsen T., Sperling S. Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1975 Mar;53(1):34–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1975.tb01135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMANN H., SCHMIDT T. Uber Applanationstonometrie. Ophthalmologica. 1957 Oct;134(4):221–242. doi: 10.1159/000303213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMANN H., SCHMIDT T. [Further contribution to applanation tonometry]. Ophthalmologica. 1961 Jun;141:441–456. doi: 10.1159/000304099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. K., Ehlers N. Elevated tonometer readings caused by a thick cornea. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1971;49(5):775–778. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1971.tb08677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon L. W., Choudhri S. A., Cox T., Damji K. F., Shields M. B., Allingham R. R. Central corneal thickness in normal, glaucomatous, and ocular hypertensive eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997 Sep;115(9):1137–1141. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100160307007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M., Kass M. A., Moses R. A., Grodzki W. J. Increased corneal thickness simulating elevated intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Apr;96(4):664–665. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910050360012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx W., Madjlessi F., Reinhard T., Althaus C., Sundmacher R. Mehr als vier Jahre Erfahrung mit der elektronischen intraokularen Nadel-Druckmessung bei irregulären Hornhäuten. Ophthalmologe. 1999 Aug;96(8):498–502. doi: 10.1007/s003470050444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stodtmeister R. Applanation tonometry and correction according to corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1998 Jun;76(3):319–324. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0420.1998.760313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitacre M. M., Stein R. A., Hassanein K. The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 May 15;115(5):592–596. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71455-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]