Abstract
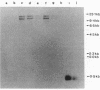
A gene bank from a clinical isolate of Clostridium difficile expressing high chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity was constructed by cloning Sau3A-cleaved clostridial DNA fragments into the plasmid vector pUC13. Among 1,020 clones tested, 11 were resistant to chloramphenicol; 1 of these, with an insert size of 1.9 kilobases (pPPM9), was studied further. The clone pPPM9 was mapped using a variety of restriction enzymes, and a 0.27-kilobase EcoRV-TaqI restriction fragment was shown to be within the chloramphenicol resistance (Cmr) gene by using transposon (Tn1000) mutagenesis. The 0.27-kilobase fragment and the 1.9-kilobase insert were radiolabeled and used as DNA probes in hybridization studies. Southern blot analysis with the gene probes against chromosomal DNA from Cmr strains of C. difficile obtained from five distinct geographical locations revealed that at least two copies of the same chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene were present for each strain. Hybridization of the gene probes against Cmr strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella edwardsii, Escherichia coli, and to four other clostridial species revealed no homology even under conditions of low stringency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham L. J., Rood J. I. Identification of Tn4451 and Tn4452, chloramphenicol resistance transposons from Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1579–1584. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1579-1584.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Mongkolsuk S., Kaufman J. D., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol-induced translation of cat-86 mRNA requires two cis-acting regulatory regions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. G., Shaw W. V. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides with universal templates for rapid DNA sequencing: results with staphylococcal replicon pC221. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):561–568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byeon W. H., Weisblum B. Post-transcriptional regulation of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.543-550.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Mongkolsuk S., Kim U. J., Lovett P. S., Henkin T. M., Chambliss G. H. Induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 through the action of the ribosomal antibiotic amicetin: involvement of a Bacillus subtilis ribosomal component in cat induction. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.665-672.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. R., Williams D. M., Lovett P. S. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus pumilus gene specifying chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard S. R., O'Farrell S., Holland D., Crook S., Barnett M. J., Tabaqchali S. The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile with use of a typing scheme: nosocomial acquisition and cross-infection among immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):159–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hächler H., Berger-Bächi B., Kayser F. H. Genetic characterization of a Clostridium difficile erythromycin-clindamycin resistance determinant that is transferable to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hächler H., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Homology of a transferable tetracycline resistance determinant of Clostridium difficile with Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecalis transposon Tn916. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1033–1038. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B. Pseudomembranous colitis: Presence of clostridial toxin. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1312–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Hu S. T., Swiatek P. J., Moseley S. L., Allen S. D., So M. Isolation of a novel transposon which carries the Escherichia coli enterotoxin STII gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.615-620.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby J. M., Wilkins T. D. Production of antitoxins to two toxins of Clostridium difficile and immunological comparison of the toxins by cross-neutralization studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):374–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.374-376.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Serikawa T., Mikawa M., Nakashio S., Yamakawa K., Nishida S. Agglutination, toxigenicity and sorbitol fermentation of Clostridium difficile. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(9):863–870. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce P. F., Jr, Wilson R., Silva J., Jr, Garagusi V. F., Rifkin G. D., Fekety R., Nunez-Montiel O., Dowell V. R., Jr, Hughes J. M. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis: an epidemiologic investigation of a cluster of cases. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I., Holmes W. M., Hylemon P. B. Modified plasmid isolation method for Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium absonum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):197–199. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.197-199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: enzymology and molecular biology. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth R., Taylor M., Jones D. M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Oct;33(10):1002–1005. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.10.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Markowitz S. M., Macrina F. L. Transferable tetracycline resistance in Clostridium difficile. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):997–1003. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Hiratsuka K., Ray H., Manavathu E. K. Characterization and expression of a cloned tetracycline resistance determinant from Campylobacter jejuni plasmid pUA466. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2984–2989. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2984-2989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B. W., Clayton C. L., Mullany P. P., Tabaqchali S. Molecular cloning and expression of Clostridium difficile toxin A in Escherichia coli K12. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B. W., Tabaqchali S. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2402–2404. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2402-2404.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B., Heard S. R., Tabaqchali S. Association between production of toxins A and B and types of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Dec;40(12):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.12.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüst J., Sullivan N. M., Hardegger U., Wilkins T. D. Investigation of an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis by various typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]