Abstract
AIM—To examine the changes in the short wavelength (S) and mixed long (L) and middle (M) wavelength sensitive cone (L,M-cone) electroretinograms (ERGs) after successful retinal detachment surgery. METHODS—Cone ERGs elicited by different colour flashes were recorded from 19 eyes with unilateral rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treated successfully by conventional buckling surgery. Ganzfeld colour flashes on a bright white background were used to elicit S-cone and L,M-cone ERGs. The ratio (operated eye/fellow eye) of the S-cone b-wave elicited by a 450 nm stimulus and the ratio (operated eye/fellow eye) of the L,M-cone b-wave elicited by a 633 nm stimulus were evaluated preoperatively and 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. RESULTS—Preoperatively, no significant difference was observed between the ratio of the S-cone ERG amplitudes and the ratio of the L,M-cone ERG amplitudes. Postoperatively, the ratio of the L,M-cone ERGs increased significantly over the preoperative value (p=0.001) but the ratio of the S-cone ERG did not improve. There were significant differences between the ratios of the S-cone and the L,M-cone ERGs at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. The postoperative recovery of the S-cone ERG was significantly greater in eyes treated within 4 weeks after the onset of the detachment than in eyes treated later than 4 weeks. CONCLUSIONS—These results indicate that the impairment of the L,M-cone system caused by retinal detachment may be reversible. However, the S-cone system may have more profound permanent damage.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (117.8 KB).
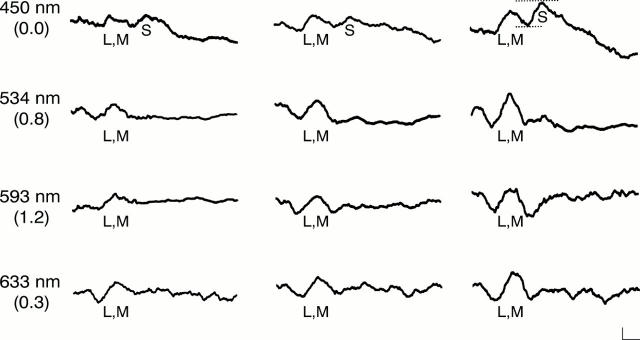
Figure 1 .
Cone ERGs elicited by different colour flash stimuli in the presence of bright white background. The ERGs recorded before surgery (left), 6 months after surgery (middle), and from the normal fellow eye of a 22 year old patient whose macula was involved are shown. The numbers on the left indicate the nominal wavelength of maximum transmission of each filter and the numbers in parentheses indicate the neutral density filter used to adjust flash energy to produce approximately equal L,M-cone b-waves. The broken lines indicate the S-cone b-wave that was measured. S = S-cone b-waves; L,M = mixed L,M-cone b-waves. The calibration marker represents 0.62 µV vertically and 10 ms horizontally.
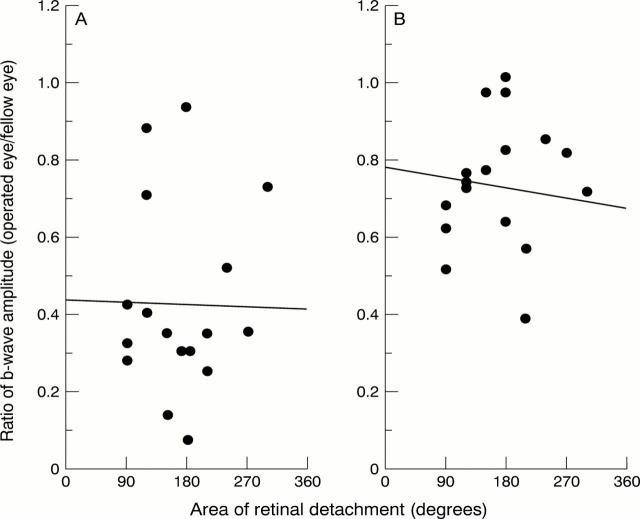
Figure 2 .
(A) Relation between the ratio of the S-cone ERG b-wave amplitude (Sop/Snorm) to 450 nm stimuli recorded at 6 months after surgery and the preoperative area of retinal detachment. The linear regression line for all patients was y=-0.00007x + 0.44 and the coefficient of correlation was r=-0.024, p=0.92. (B) Relation between ratio of the L,M-cone ERG b-wave amplitude to 633 nm stimuli (L,Mop/L,Mnorm) at 6 months postoperatively and the preoperative area of retinal detachment. The linear regression line for all patients was y=-0.0003 + 0.78 and the coefficient of correlation was r=-0.25, p=0.61.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blach R. K., Behrman J. The electrical activity of the eye in retinal detachment. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1967;87:263–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm I. A., McClure E., Foulds W. S. Functional recovery of the retina after retinal detachment. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1975 Apr;95(1):167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds W. S., Reid H., Chisholm I. A. Factors influencing visual recovery after retinal detachment surgery. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1974;12(0):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberg T. R., Eller A. W. Prediction of visual recovery after scleral buckling of macula-off retinal detachments. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992 Dec 15;114(6):715–722. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)74050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouras P., MacKay C. J., Yamamoto S. The human S-cone electroretinogram and its variation among subjects with and without L and M-cone function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Jul;34(8):2437–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundry M. F., Davies E. W. Recovery of visual acuity after retinal detachment surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Mar;77(3):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90735-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamasaki D. I., Machemer R., Norton E. W. Experimental retinal detachment in the owl monkey. VI. The ERG of the detached and reattached retina. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1969;177(3):212–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00571786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama M., Yamamoto S., Nitta K., Hayasaka S. Undetectable S cone electroretinogram b-wave in complete congenital stationary night blindness. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996 Jul;80(7):637–639. doi: 10.1136/bjo.80.7.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreissig I. Prognosis of return of macular function after retinal reattachment. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1977;18:415–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll A. J., Machemer R. Experimental retinal detachment and reattachment in the rhesus monkey. Electron microscopic comparison of rods and cones. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969 Jul;68(1):58–77. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(69)94935-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nork T. M., Millecchia L. L., Strickland B. D., Linberg J. V., Chao G. M. Selective loss of blue cones and rods in human retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995 Aug;113(8):1066–1073. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1995.01100080118039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. C., Ernest J. T., Pokorny J. Effect of hypoxia on FM 100-Hue test performance. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1976;17:248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani P., Robertson D. M., Langworthy A. Prognosis for central vision and anatomic reattachment in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with macula detached. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 Nov;92(5):611–620. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)74651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki H., Miyake Y., Nomura R., Horiguchi M., Suzuki S., Kondo M. Blue-on-yellow perimetry in the complete type of congenital stationary night blindness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999 Oct;40(11):2761–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda M., Adachi-Usami E. Assessment of central visual function after successful retinal detachment surgery by pattern visual evoked cortical potentials. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992 Aug;76(8):482–485. doi: 10.1136/bjo.76.8.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Hayashi M., Takeuchi S. Cone electroretinograms in response to color stimuli after successful retinal detachment surgery. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1998 Jul-Aug;42(4):314–317. doi: 10.1016/s0021-5155(98)00014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Feke G. T., Green G. J., Goger D. G., Matsuhashi M., Jalkh A. E., McMeel J. W. Retinal circulatory changes after scleral buckling procedures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Feb;95(2):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Hirokawa H., Ishiko S., Ogasawara H. Ocular circulatory changes following scleral buckling procedures. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992 Sep;76(9):529–531. doi: 10.1136/bjo.76.9.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]